Dark data auditing focuses on uncovering and analyzing unused or hidden data within an organization's systems to ensure compliance and reduce risks. Cybersecurity audits evaluate the effectiveness of security controls and protocols in protecting sensitive financial information from cyber threats. Explore the differences and importance of both audits to enhance your organization's financial security strategy.
Why it is important
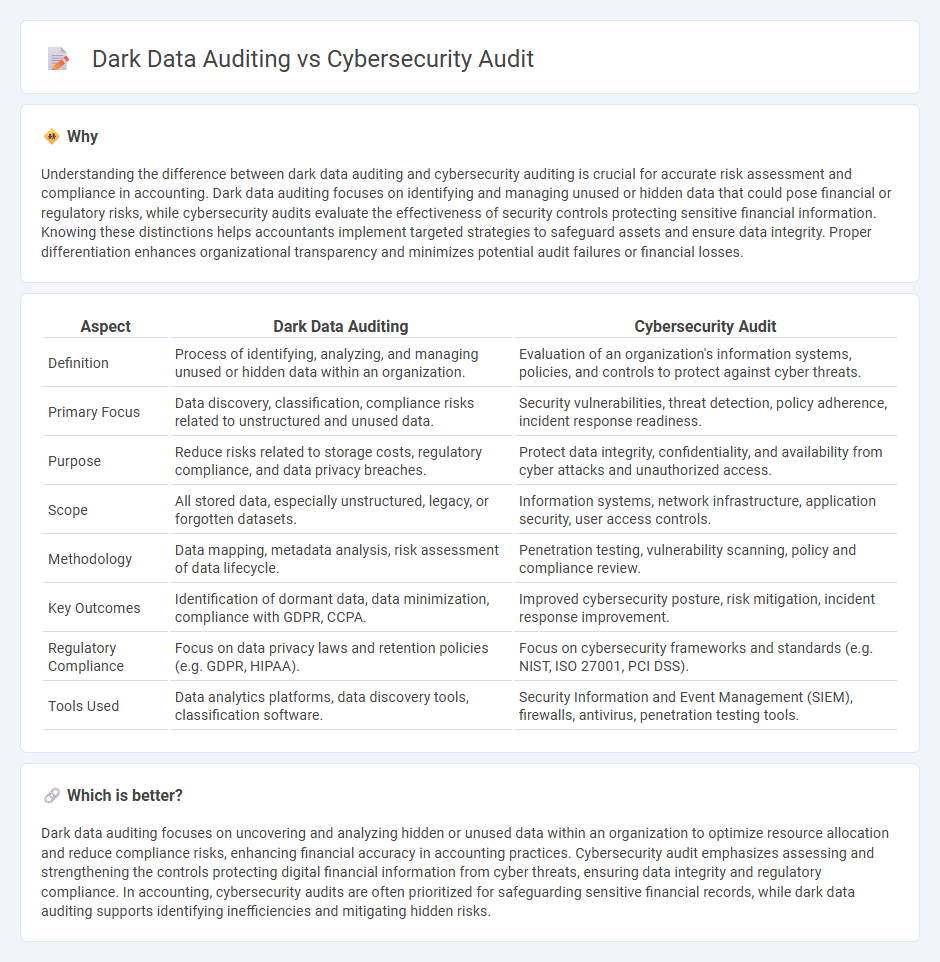
Understanding the difference between dark data auditing and cybersecurity auditing is crucial for accurate risk assessment and compliance in accounting. Dark data auditing focuses on identifying and managing unused or hidden data that could pose financial or regulatory risks, while cybersecurity audits evaluate the effectiveness of security controls protecting sensitive financial information. Knowing these distinctions helps accountants implement targeted strategies to safeguard assets and ensure data integrity. Proper differentiation enhances organizational transparency and minimizes potential audit failures or financial losses.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Data Auditing | Cybersecurity Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process of identifying, analyzing, and managing unused or hidden data within an organization. | Evaluation of an organization's information systems, policies, and controls to protect against cyber threats. |
| Primary Focus | Data discovery, classification, compliance risks related to unstructured and unused data. | Security vulnerabilities, threat detection, policy adherence, incident response readiness. |
| Purpose | Reduce risks related to storage costs, regulatory compliance, and data privacy breaches. | Protect data integrity, confidentiality, and availability from cyber attacks and unauthorized access. |
| Scope | All stored data, especially unstructured, legacy, or forgotten datasets. | Information systems, network infrastructure, application security, user access controls. |
| Methodology | Data mapping, metadata analysis, risk assessment of data lifecycle. | Penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, policy and compliance review. |
| Key Outcomes | Identification of dormant data, data minimization, compliance with GDPR, CCPA. | Improved cybersecurity posture, risk mitigation, incident response improvement. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Focus on data privacy laws and retention policies (e.g. GDPR, HIPAA). | Focus on cybersecurity frameworks and standards (e.g. NIST, ISO 27001, PCI DSS). |
| Tools Used | Data analytics platforms, data discovery tools, classification software. | Security Information and Event Management (SIEM), firewalls, antivirus, penetration testing tools. |
Which is better?
Dark data auditing focuses on uncovering and analyzing hidden or unused data within an organization to optimize resource allocation and reduce compliance risks, enhancing financial accuracy in accounting practices. Cybersecurity audit emphasizes assessing and strengthening the controls protecting digital financial information from cyber threats, ensuring data integrity and regulatory compliance. In accounting, cybersecurity audits are often prioritized for safeguarding sensitive financial records, while dark data auditing supports identifying inefficiencies and mitigating hidden risks.
Connection
Dark data auditing and cybersecurity audit intersect through their shared focus on identifying and mitigating risks associated with unstructured, unmanaged data that may harbor security vulnerabilities. Effective dark data auditing uncovers hidden, unused data repositories, enabling cybersecurity audits to assess potential attack vectors and compliance gaps more accurately. Integrating these audits enhances organizational defenses by ensuring comprehensive data governance and reducing exposure to data breaches or regulatory penalties.
Key Terms
**Cybersecurity audit:**
Cybersecurity audit involves a thorough evaluation of an organization's information systems, policies, and controls to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security standards like ISO 27001 and NIST frameworks. This process includes penetration testing, risk assessment, and reviewing access controls to safeguard against cyber threats such as data breaches, malware, and insider attacks. Discover how integrating cybersecurity audits can strengthen your defense mechanisms and protect critical digital assets.
Access Controls
Cybersecurity audits rigorously evaluate access controls to ensure only authorized users can interact with sensitive systems, minimizing the risk of breaches and unauthorized data exposure. Dark data auditing targets hidden or unknown data repositories, emphasizing the identification and securing of access points often overlooked, which can harbor unmonitored and vulnerable information. Explore deeper insights to understand how these auditing practices protect organizational assets and enhance data security frameworks.
Network Security
Cybersecurity audits systematically evaluate an organization's network security measures to identify vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance with industry standards like ISO 27001 or NIST. Dark data auditing targets unstructured and unmanaged data within networks, uncovering hidden security risks that traditional audits often overlook, such as unauthorized data access or storage. Explore how combining these audits enhances network security strategies and protects against evolving cyber threats.
Source and External Links
Six Benefits of a Cybersecurity Audit - This article outlines the benefits and steps involved in conducting a cybersecurity audit to enhance an organization's security posture.
Cybersecurity Audit: The Ultimate Guide for 2025 - This guide provides a comprehensive overview of best practices and procedures for performing a cybersecurity audit effectively.
How to Perform a Cybersecurity Audit: A 3-Step Guide - This guide explains the steps to conduct a cybersecurity audit for managing and improving an organization's security measures.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com