Forensic data analytics specializes in detecting and preventing fraud by analyzing financial data patterns and anomalies, while operational auditing focuses on evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes and internal controls. Both disciplines utilize data-driven techniques, but forensic analytics primarily supports legal investigations and compliance, whereas operational audits aim to improve organizational performance. Explore the distinct methodologies and applications of forensic data analytics versus operational auditing to enhance your accounting proficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between forensic data analytics and operational auditing is crucial for accurately identifying fraud versus assessing business efficiency. Forensic data analytics focuses on detecting, investigating, and preventing fraud through detailed analysis of financial data patterns. Operational auditing evaluates the effectiveness, efficiency, and compliance of business processes to improve performance. Misinterpreting these can lead to incorrect conclusions, impacting decision-making and risk management.
Comparison Table
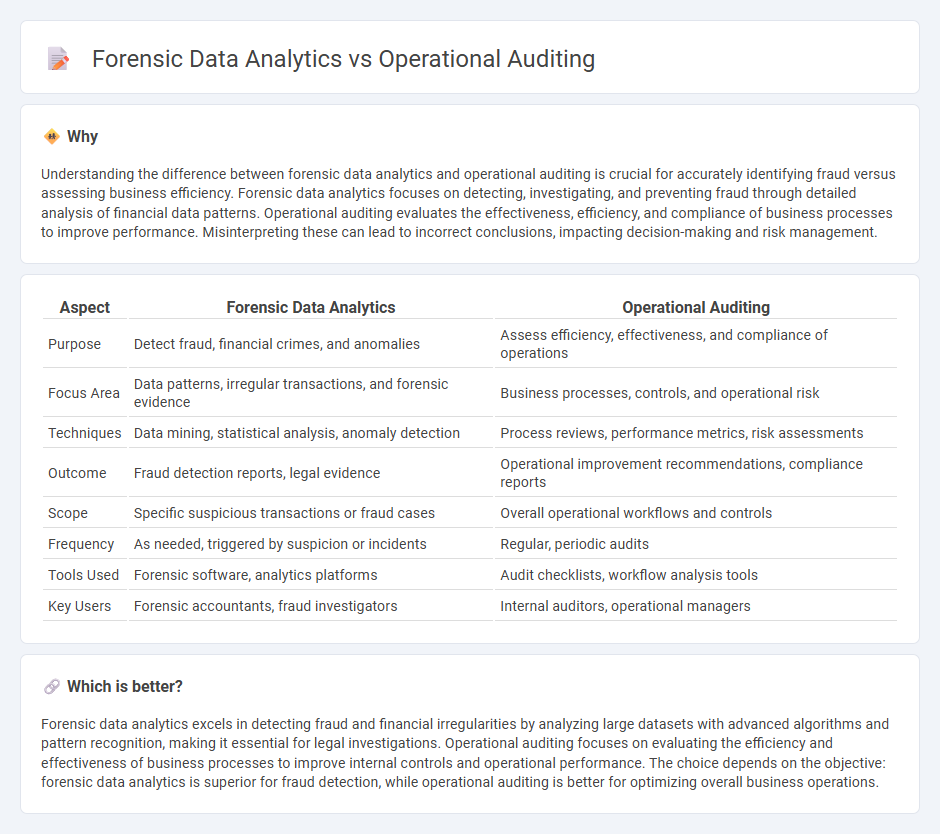
| Aspect | Forensic Data Analytics | Operational Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, financial crimes, and anomalies | Assess efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance of operations |
| Focus Area | Data patterns, irregular transactions, and forensic evidence | Business processes, controls, and operational risk |
| Techniques | Data mining, statistical analysis, anomaly detection | Process reviews, performance metrics, risk assessments |
| Outcome | Fraud detection reports, legal evidence | Operational improvement recommendations, compliance reports |
| Scope | Specific suspicious transactions or fraud cases | Overall operational workflows and controls |
| Frequency | As needed, triggered by suspicion or incidents | Regular, periodic audits |
| Tools Used | Forensic software, analytics platforms | Audit checklists, workflow analysis tools |
| Key Users | Forensic accountants, fraud investigators | Internal auditors, operational managers |
Which is better?
Forensic data analytics excels in detecting fraud and financial irregularities by analyzing large datasets with advanced algorithms and pattern recognition, making it essential for legal investigations. Operational auditing focuses on evaluating the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes to improve internal controls and operational performance. The choice depends on the objective: forensic data analytics is superior for fraud detection, while operational auditing is better for optimizing overall business operations.
Connection
Forensic data analytics enhances operational auditing by identifying anomalies and patterns that indicate fraud or inefficiencies within business processes. Leveraging advanced data analysis techniques, auditors can detect risks and control weaknesses more accurately, leading to improved financial integrity and compliance. The integration of forensic analytics into operational auditing strengthens investigative capabilities and supports proactive risk management.
Key Terms
Internal Controls
Operational auditing evaluates the effectiveness of internal controls by examining processes and procedures to ensure compliance and operational efficiency. Forensic data analytics targets detecting and investigating fraud within internal controls through data-driven techniques such as anomaly detection and pattern recognition. Explore how integrating these approaches can strengthen your organization's risk management and fraud prevention strategies.
Fraud Detection
Operational auditing evaluates internal controls, compliance, and efficiency to identify weaknesses that could lead to fraud, using systematic testing and process reviews. Forensic data analytics employs advanced techniques like data mining, machine learning, and anomaly detection to uncover patterns, irregular transactions, or evidence of fraudulent activities. Explore the distinct methodologies and applications of these approaches to enhance your organization's fraud detection capabilities.
Data Mining
Operational auditing leverages data mining techniques to systematically analyze business processes and identify inefficiencies or compliance issues through pattern recognition and anomaly detection. Forensic data analytics emphasizes advanced data mining methods to detect fraud, financial misconduct, and suspicious activities by scrutinizing transaction data for irregularities. Explore the distinct methodologies and applications of data mining in these fields to enhance audit accuracy and fraud prevention.
Source and External Links
Operational Audit: Overview and Guide - AuditBoard - An operational audit is a tool that evaluates a company's internal processes, policies, and controls to optimize efficiency, manage resources effectively, and ensure compliance with laws and regulations by identifying areas for improvement.
A practical guide to operational audits - ITGRC Advisory - Operational audits provide a systematic evaluation of an organization's internal processes through clear objectives, examination of internal controls, data collection and analysis, an audit program, and follow-up to ensure improvements are implemented effectively.
What Is an Operational Audit? - GoCardless - Operational audits assess both daily and broader company operations via steps including pre-audit meetings, risk identification, control testing, documentation, and follow-ups to improve organizational efficiency and control systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com