Zero trust accounting focuses on stringent verification and continuous monitoring of financial transactions, minimizing the risk of fraud and errors by assuming no transaction is inherently trustworthy. Cash accounting records revenues and expenses only when cash changes hands, offering simplicity but potentially lacking real-time accuracy and fraud detection. Explore the key differences and benefits to determine which method suits your financial management needs best.
Why it is important
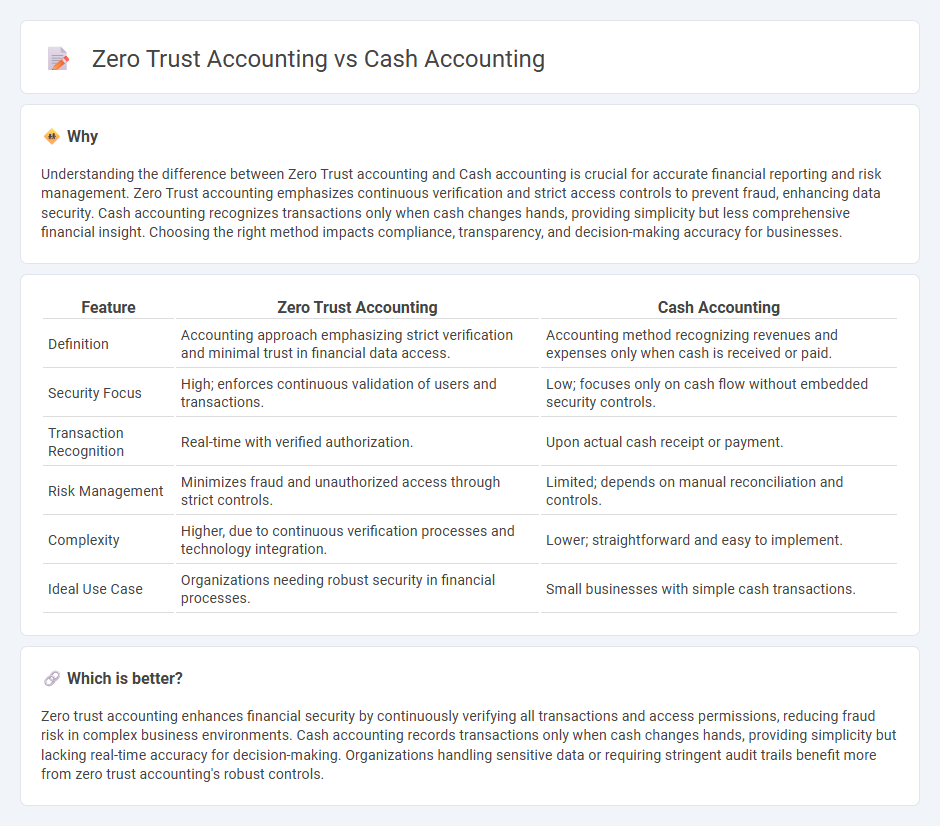
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust accounting and Cash accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and risk management. Zero Trust accounting emphasizes continuous verification and strict access controls to prevent fraud, enhancing data security. Cash accounting recognizes transactions only when cash changes hands, providing simplicity but less comprehensive financial insight. Choosing the right method impacts compliance, transparency, and decision-making accuracy for businesses.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Trust Accounting | Cash Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting approach emphasizing strict verification and minimal trust in financial data access. | Accounting method recognizing revenues and expenses only when cash is received or paid. |
| Security Focus | High; enforces continuous validation of users and transactions. | Low; focuses only on cash flow without embedded security controls. |
| Transaction Recognition | Real-time with verified authorization. | Upon actual cash receipt or payment. |
| Risk Management | Minimizes fraud and unauthorized access through strict controls. | Limited; depends on manual reconciliation and controls. |
| Complexity | Higher, due to continuous verification processes and technology integration. | Lower; straightforward and easy to implement. |
| Ideal Use Case | Organizations needing robust security in financial processes. | Small businesses with simple cash transactions. |
Which is better?
Zero trust accounting enhances financial security by continuously verifying all transactions and access permissions, reducing fraud risk in complex business environments. Cash accounting records transactions only when cash changes hands, providing simplicity but lacking real-time accuracy for decision-making. Organizations handling sensitive data or requiring stringent audit trails benefit more from zero trust accounting's robust controls.
Connection
Zero trust accounting and cash accounting are connected through their shared focus on minimizing financial risks and enhancing transaction transparency. Zero trust accounting enforces strict verification protocols for every transaction, while cash accounting records revenue and expenses only when cash is exchanged, promoting real-time accuracy. Together, they ensure reliable financial reporting and secure cash flow management in organizations.
Key Terms
Revenue Recognition
Cash accounting recognizes revenue only when cash is received, offering simplicity but less accuracy in reflecting financial performance. Zero trust accounting applies stringent verification processes to revenue recognition, ensuring data integrity and reducing risks of fraud. Explore the detailed differences to understand which method aligns best with your financial strategy.
Access Control
Cash accounting tracks financial transactions based on actual cash flow, emphasizing transparent and straightforward record-keeping without access control complexities. Zero trust accounting implements stringent access control measures, assuming no user or device is inherently trustworthy, thereby enforcing continuous verification for financial data access. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how access control strategies impact financial accountability and security.
Transaction Authorization
Cash accounting records transactions only when cash changes hands, emphasizing real-time cash flow but lacking granular control over transaction approvals. Zero trust accounting requires continuous verification and strict transaction authorization protocols, ensuring every financial action is authenticated regardless of network location or device. Explore the detailed mechanisms behind transaction authorization in zero trust accounting to enhance financial security.
Source and External Links
Cash-based accounting: A guide to the cash basis - This article explains how cash-based accounting works, including its pros and cons, and how it affects tax reporting.
Cash Basis Accounting: Definition, Example, Pros and Cons - This resource provides a detailed overview of cash basis accounting, including its definition, advantages, disadvantages, and tax implications.
Cash method of accounting - This webpage describes the cash method of accounting, contrasting it with the accrual method and highlighting how it records revenues and expenses when cash is received or paid.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com