Smart contracts accounting leverages blockchain technology to automate financial transactions and ensure immutability, enhancing transparency and reducing errors compared to traditional auditing procedures that rely on manual verification and sampling techniques. This innovation streamlines reconciliation processes and minimizes human intervention, offering real-time data accuracy and audit trails. Explore the evolving landscape of smart contracts accounting and its impact on auditing efficiency to stay informed.
Why it is important
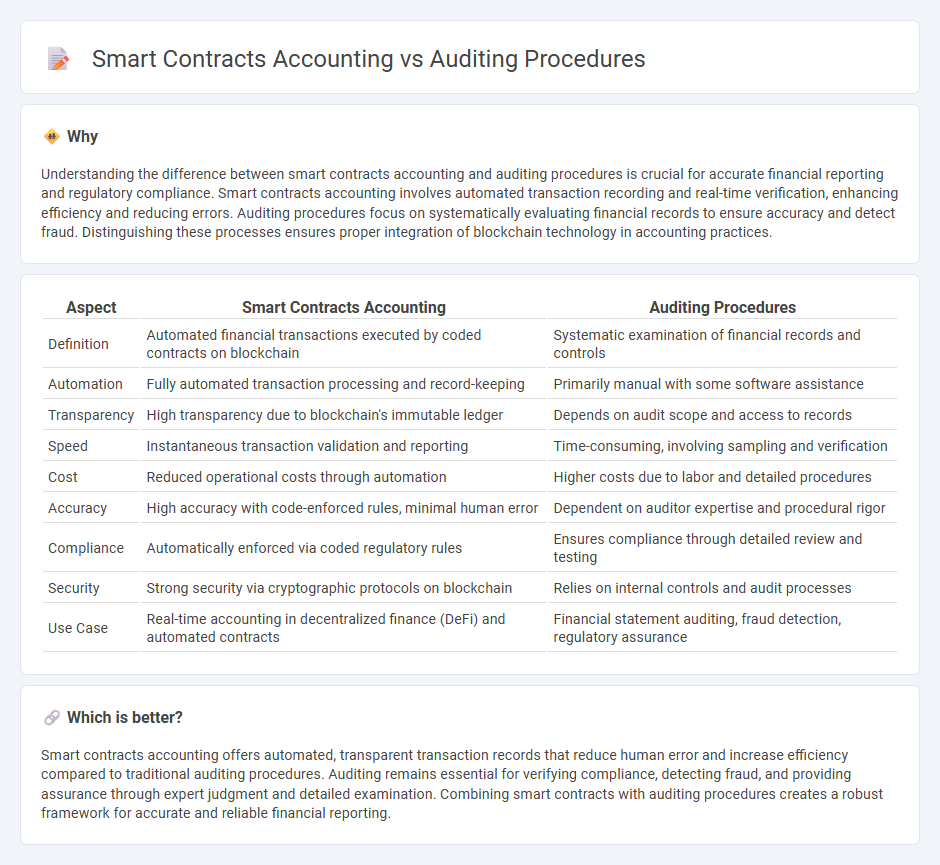
Understanding the difference between smart contracts accounting and auditing procedures is crucial for accurate financial reporting and regulatory compliance. Smart contracts accounting involves automated transaction recording and real-time verification, enhancing efficiency and reducing errors. Auditing procedures focus on systematically evaluating financial records to ensure accuracy and detect fraud. Distinguishing these processes ensures proper integration of blockchain technology in accounting practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Contracts Accounting | Auditing Procedures |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated financial transactions executed by coded contracts on blockchain | Systematic examination of financial records and controls |
| Automation | Fully automated transaction processing and record-keeping | Primarily manual with some software assistance |
| Transparency | High transparency due to blockchain's immutable ledger | Depends on audit scope and access to records |
| Speed | Instantaneous transaction validation and reporting | Time-consuming, involving sampling and verification |
| Cost | Reduced operational costs through automation | Higher costs due to labor and detailed procedures |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with code-enforced rules, minimal human error | Dependent on auditor expertise and procedural rigor |
| Compliance | Automatically enforced via coded regulatory rules | Ensures compliance through detailed review and testing |
| Security | Strong security via cryptographic protocols on blockchain | Relies on internal controls and audit processes |
| Use Case | Real-time accounting in decentralized finance (DeFi) and automated contracts | Financial statement auditing, fraud detection, regulatory assurance |
Which is better?
Smart contracts accounting offers automated, transparent transaction records that reduce human error and increase efficiency compared to traditional auditing procedures. Auditing remains essential for verifying compliance, detecting fraud, and providing assurance through expert judgment and detailed examination. Combining smart contracts with auditing procedures creates a robust framework for accurate and reliable financial reporting.
Connection
Smart contracts revolutionize accounting and auditing procedures by automating transaction verification and ensuring real-time accuracy of financial records through blockchain technology. These self-executing contracts provide immutable audit trails, enhancing transparency and reducing the risk of fraud during financial audits. Integrating smart contracts into accounting systems streamlines compliance, improves data integrity, and accelerates the auditing process.
Key Terms
Evidence gathering
Auditing procedures focus on systematic evidence gathering through documentation review, transaction verification, and control testing to ensure accuracy and compliance in financial statements. Smart contracts accounting automates evidence collection by recording every transaction immutably on the blockchain, providing real-time, transparent, and tamper-proof audit trails. Explore how integrating smart contracts transforms traditional auditing processes for enhanced evidence reliability and efficiency.
Automated verification
Automated verification in auditing procedures leverages software to systematically examine financial records, ensuring accuracy and compliance through algorithmic checks. In contrast, smart contracts accounting employs blockchain technology to autonomously enforce and record financial agreements, minimizing human intervention and enhancing transparency. Explore how these innovations revolutionize financial oversight by offering faster and more reliable verification methods.
Immutable ledger
Auditing procedures rely on traditional verification methods to ensure accuracy and compliance, often involving manual checks and reconciliations, whereas smart contracts automate accounting processes using code executed on a blockchain, creating an immutable ledger that records every transaction transparently and tamper-proof. The immutable ledger enhances trust and auditability by providing a decentralized, unalterable history of financial activities, reducing risks of fraud and errors inherent in conventional accounting systems. Explore the transformative impact of immutable ledgers on auditing and accounting by diving deeper into smart contract technologies.
Source and External Links
Audit Procedures to Obtain Evidence | SafetyCulture - Audit procedures include inspection of documents, physical assets, recalculation, and reperformance, used by auditors to gather reliable evidence and validate transactions.
Audit Procedures and Internal Controls: How They Work Together - Key audit procedures include inspection of documents and assets, and observation of processes to assess the effectiveness of internal controls.
Understanding Audit Procedures: Methods & Test of Controls - Five main audit testing methods are inquiry, observation, examination/inspection of evidence, reperformance, and computer-assisted audit techniques.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com