Real-time audit leverages advanced software and continuous data monitoring to detect discrepancies instantly, enhancing accuracy and reducing errors compared to traditional manual audits. Manual audits rely on periodic reviews and physical document examination, often leading to time-consuming processes and delayed issue identification. Explore the differences between real-time and manual audits to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
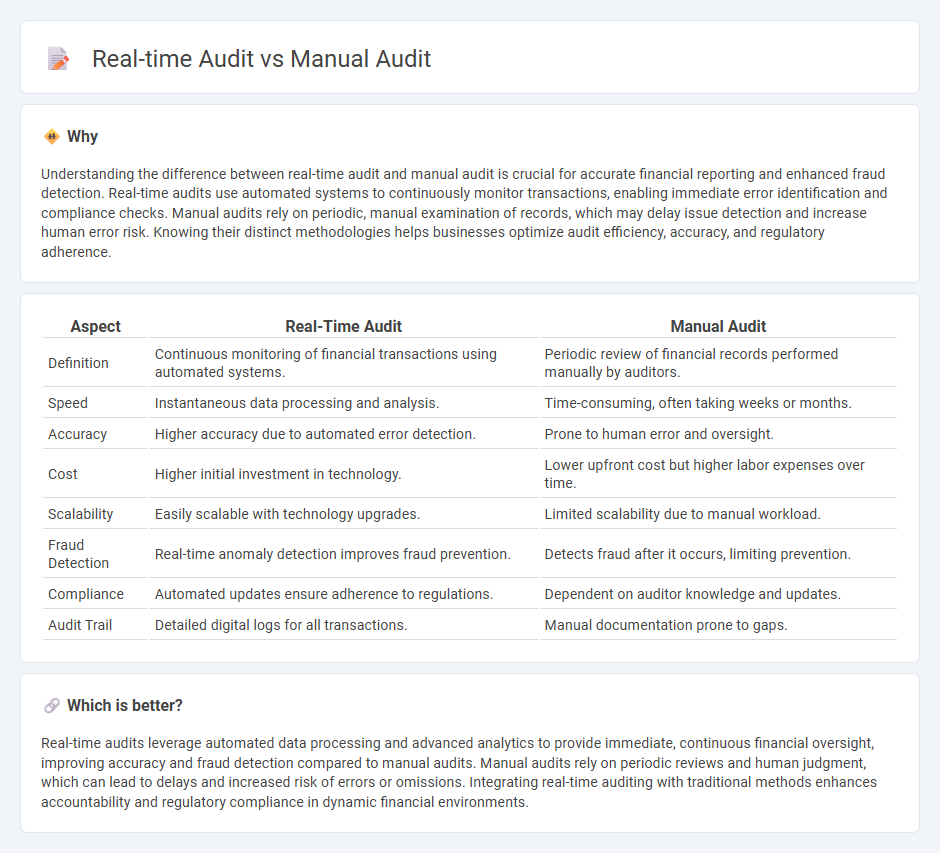
Understanding the difference between real-time audit and manual audit is crucial for accurate financial reporting and enhanced fraud detection. Real-time audits use automated systems to continuously monitor transactions, enabling immediate error identification and compliance checks. Manual audits rely on periodic, manual examination of records, which may delay issue detection and increase human error risk. Knowing their distinct methodologies helps businesses optimize audit efficiency, accuracy, and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Real-Time Audit | Manual Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous monitoring of financial transactions using automated systems. | Periodic review of financial records performed manually by auditors. |
| Speed | Instantaneous data processing and analysis. | Time-consuming, often taking weeks or months. |
| Accuracy | Higher accuracy due to automated error detection. | Prone to human error and oversight. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment in technology. | Lower upfront cost but higher labor expenses over time. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable with technology upgrades. | Limited scalability due to manual workload. |
| Fraud Detection | Real-time anomaly detection improves fraud prevention. | Detects fraud after it occurs, limiting prevention. |
| Compliance | Automated updates ensure adherence to regulations. | Dependent on auditor knowledge and updates. |
| Audit Trail | Detailed digital logs for all transactions. | Manual documentation prone to gaps. |
Which is better?
Real-time audits leverage automated data processing and advanced analytics to provide immediate, continuous financial oversight, improving accuracy and fraud detection compared to manual audits. Manual audits rely on periodic reviews and human judgment, which can lead to delays and increased risk of errors or omissions. Integrating real-time auditing with traditional methods enhances accountability and regulatory compliance in dynamic financial environments.
Connection
Real-time audit integrates automated data analysis and continuous monitoring to identify discrepancies instantly, enhancing the accuracy of financial records. Manual audit complements this process by providing detailed scrutiny and professional judgment on flagged anomalies or complex transactions that require human expertise. Together, they create a comprehensive auditing approach that combines technology-driven insights with traditional verification methods to ensure regulatory compliance and financial integrity.
Key Terms
Documentation
Manual audits rely heavily on physical documentation, requiring auditors to review paper records and handwritten notes, which can lead to delays and errors. Real-time audits utilize digital documentation and automated data capture, enabling instant access, verification, and continuous compliance tracking. Explore how integrating advanced documentation methods can optimize audit accuracy and efficiency.
Timeliness
Manual audits often suffer from delays due to the reliance on periodic reviews and human processing, which can lead to outdated findings and slower response times. Real-time audits leverage automated systems and continuous monitoring, enabling immediate detection of anomalies and quicker corrective actions to enhance operational efficiency. Explore how real-time audit technology transforms compliance and risk management for timely decision-making.
Error Detection
Manual audits involve human review of financial records, enabling detection of nuanced errors through detailed examination, but can be time-consuming and prone to oversight. Real-time audits use automated systems to continuously monitor transactions, enabling immediate error detection and faster corrective actions while improving accuracy. Explore more to understand which audit method best suits your organization's error detection needs.
Source and External Links
GENERAL AUDIT MANUAL - This manual contains detailed policies, procedures, and guidelines on conducting audits, including documentation, communication with taxpayers, and audit reporting processes used by the New Mexico Taxation and Revenue Department.
Audit Manual from University of Illinois - This manual emphasizes internal audit processes focusing on quality assurance, communication, ongoing monitoring, and self-assessment to improve audit effectiveness.
Audit Manual - Chapter 1 Introduction - CDTFA - A guide outlining tax audit procedures, auditor standards, legal references, and confidentiality rules relevant for state audits conducted by the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com