Greenwashing detection evaluates the authenticity of companies' environmental claims by identifying misleading or exaggerated sustainability statements. Environmental reporting verification ensures the accuracy and reliability of disclosed environmental data through independent auditing and validation processes. Explore more to understand how these measures enhance corporate transparency and accountability.
Why it is important
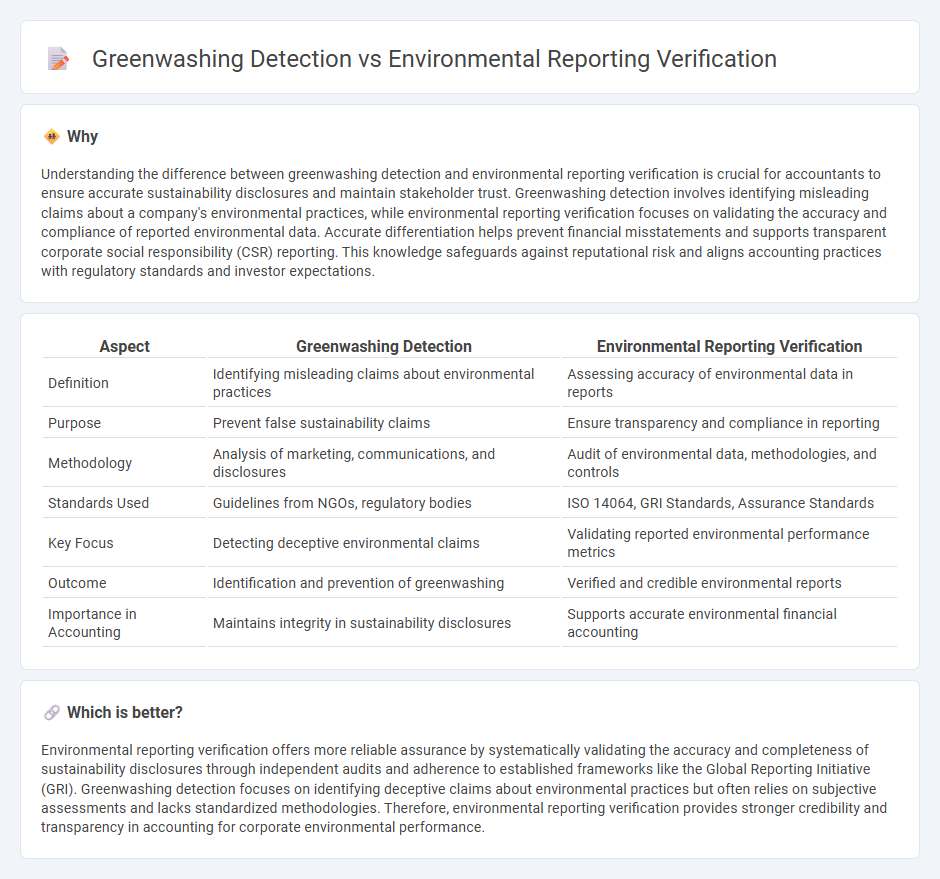
Understanding the difference between greenwashing detection and environmental reporting verification is crucial for accountants to ensure accurate sustainability disclosures and maintain stakeholder trust. Greenwashing detection involves identifying misleading claims about a company's environmental practices, while environmental reporting verification focuses on validating the accuracy and compliance of reported environmental data. Accurate differentiation helps prevent financial misstatements and supports transparent corporate social responsibility (CSR) reporting. This knowledge safeguards against reputational risk and aligns accounting practices with regulatory standards and investor expectations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenwashing Detection | Environmental Reporting Verification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifying misleading claims about environmental practices | Assessing accuracy of environmental data in reports |
| Purpose | Prevent false sustainability claims | Ensure transparency and compliance in reporting |
| Methodology | Analysis of marketing, communications, and disclosures | Audit of environmental data, methodologies, and controls |
| Standards Used | Guidelines from NGOs, regulatory bodies | ISO 14064, GRI Standards, Assurance Standards |
| Key Focus | Detecting deceptive environmental claims | Validating reported environmental performance metrics |
| Outcome | Identification and prevention of greenwashing | Verified and credible environmental reports |
| Importance in Accounting | Maintains integrity in sustainability disclosures | Supports accurate environmental financial accounting |
Which is better?
Environmental reporting verification offers more reliable assurance by systematically validating the accuracy and completeness of sustainability disclosures through independent audits and adherence to established frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI). Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying deceptive claims about environmental practices but often relies on subjective assessments and lacks standardized methodologies. Therefore, environmental reporting verification provides stronger credibility and transparency in accounting for corporate environmental performance.
Connection
Greenwashing detection and environmental reporting verification are interconnected through the accounting principles of transparency and accuracy in financial and non-financial disclosures. Environmental reporting verification ensures the reliability of sustainability claims by auditing carbon footprints, resource usage, and waste management data, which helps identify misleading or exaggerated green claims typical of greenwashing. Both processes support corporate accountability by providing stakeholders with validated information on environmental performance, reducing the risk of reputational damage and regulatory penalties.
Key Terms
Assurance engagement
Assurance engagement in environmental reporting verification ensures the accuracy, reliability, and transparency of sustainability data disclosed by organizations, which is critical for stakeholders assessing genuine environmental performance. Unlike greenwashing detection that primarily identifies misleading or deceptive claims, assurance provides a systematic evaluation through established standards like ISAE 3000 or AA1000, enhancing credibility and investor confidence. Explore how assurance engagements can strengthen environmental reporting integrity and combat greenwashing effectively.
Materiality assessment
Environmental reporting verification ensures the accuracy and completeness of disclosed data by evaluating the materiality of sustainability metrics aligned with global standards such as GRI and SASB. Greenwashing detection involves scrutinizing claims for misleading information, often identifying gaps in materiality assessment where non-substantive or irrelevant data is presented as significant. Explore how advanced materiality assessment methodologies can enhance transparency and trust in sustainability communications.
Misrepresentation risk
Environmental reporting verification ensures the accuracy and reliability of sustainability disclosures by cross-checking data against established standards such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). Greenwashing detection focuses specifically on identifying deceptive claims that exaggerate or falsely portray environmental efforts, addressing the misrepresentation risk inherent in corporate communications. Explore effective strategies for mitigating misrepresentation risks to enhance corporate transparency and stakeholder trust.
Source and External Links
What is sustainability report verification? - Verifying a sustainability report involves an external audit to ensure accuracy and compliance with recognized standards like GRI or CSRD.
Environmental and Sustainability Report Verification - Intertek provides third-party verification to make environmental and sustainability reports credible by adhering to international standards.
Mandatory GHG Reporting - Verification - California requires entities to have their GHG emissions data reports verified annually by CARB-accredited bodies to ensure compliance with reporting regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com