Sustainability reporting focuses on a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, providing stakeholders with insights into long-term value creation beyond traditional financial metrics. Financial reporting centers on quantifiable economic performance, presenting historical data such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements to comply with regulatory standards like GAAP or IFRS. Explore how integrating both reporting types can enhance transparency and decision-making in modern business practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainability reporting and financial reporting is crucial because sustainability reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, while financial reporting emphasizes financial performance and compliance with accounting standards. Accurate interpretation of sustainability reports helps stakeholders assess long-term risks and opportunities beyond traditional financial metrics. Companies use sustainability reporting to demonstrate corporate responsibility and attract ESG-focused investors. Clear differentiation ensures compliance with regulations like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) guidelines.
Comparison Table
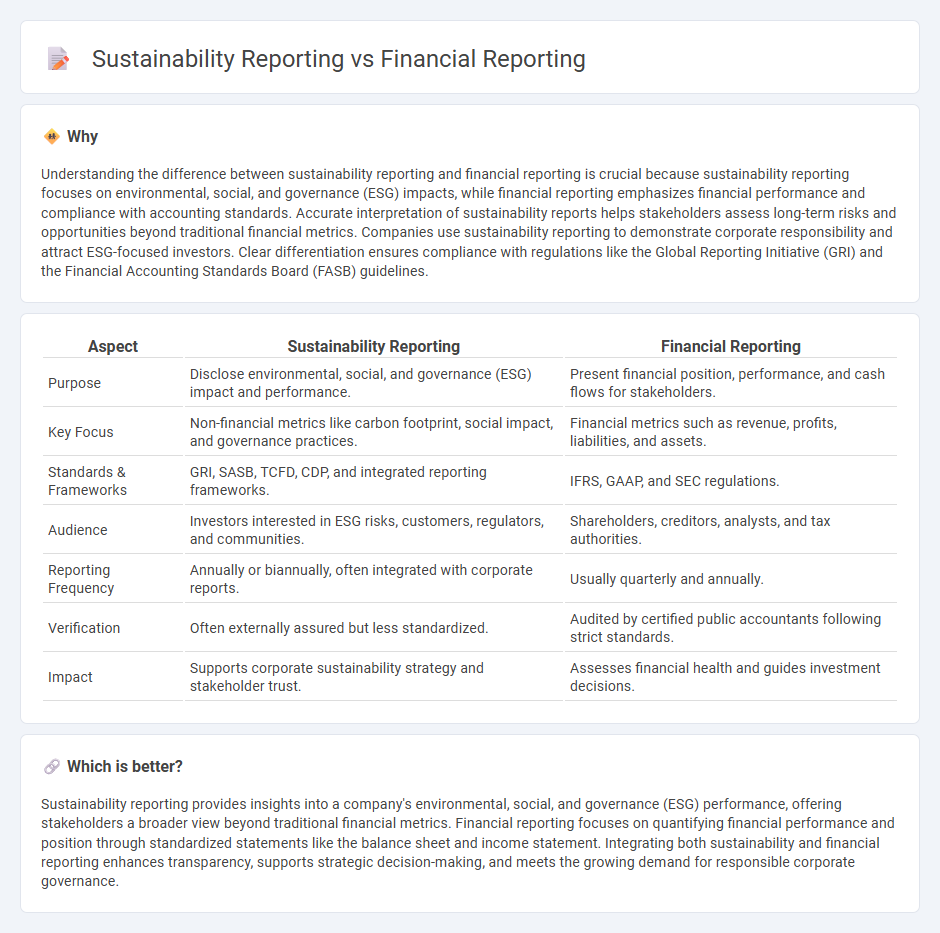
| Aspect | Sustainability Reporting | Financial Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Disclose environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impact and performance. | Present financial position, performance, and cash flows for stakeholders. |
| Key Focus | Non-financial metrics like carbon footprint, social impact, and governance practices. | Financial metrics such as revenue, profits, liabilities, and assets. |
| Standards & Frameworks | GRI, SASB, TCFD, CDP, and integrated reporting frameworks. | IFRS, GAAP, and SEC regulations. |
| Audience | Investors interested in ESG risks, customers, regulators, and communities. | Shareholders, creditors, analysts, and tax authorities. |
| Reporting Frequency | Annually or biannually, often integrated with corporate reports. | Usually quarterly and annually. |
| Verification | Often externally assured but less standardized. | Audited by certified public accountants following strict standards. |
| Impact | Supports corporate sustainability strategy and stakeholder trust. | Assesses financial health and guides investment decisions. |
Which is better?
Sustainability reporting provides insights into a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, offering stakeholders a broader view beyond traditional financial metrics. Financial reporting focuses on quantifying financial performance and position through standardized statements like the balance sheet and income statement. Integrating both sustainability and financial reporting enhances transparency, supports strategic decision-making, and meets the growing demand for responsible corporate governance.
Connection
Sustainability reporting and financial reporting are interconnected through the integration of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics into traditional financial disclosures, enhancing transparency and accountability for stakeholders. Accurate sustainability data influences financial performance assessments and risk management, aligning corporate strategies with long-term value creation. Regulatory frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) facilitate standardized reporting that bridges non-financial and financial information.
Key Terms
Financial Reporting:
Financial reporting centers on the accurate presentation of a company's financial performance and position through standardized statements such as the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It complies with regulatory frameworks like GAAP or IFRS to ensure transparency, accountability, and comparability for investors, creditors, and stakeholders. Explore more to understand how financial reporting impacts corporate decision-making and investor relations.
Income Statement
Financial reporting emphasizes the Income Statement to present an organization's revenues, expenses, and net profit, reflecting overall financial performance during a specific period. Sustainability reporting integrates non-financial metrics related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, offering insights into the company's long-term impact and ethical practices beyond traditional financial outcomes. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how these reporting frameworks complement each other in corporate transparency.
Balance Sheet
Financial reporting emphasizes the Balance Sheet by detailing assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity to provide a snapshot of an organization's financial position at a specific point in time. Sustainability reporting complements this by incorporating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, such as resource usage and carbon footprint, which influence long-term value and risk but are often absent from traditional financial statements. Explore more to understand how integrating sustainability factors can enhance balance sheet analysis and decision-making.
Source and External Links
What Is Financial Reporting & Why Is It Important? - Financial reporting involves communicating financial information through documents like balance sheets and income statements, serving both external and internal stakeholders.
What Is Financial Reporting? Definition, Importance, and Types - Financial reporting provides essential financial information to stakeholders, including investors, and is crucial for a company's growth and compliance with regulations like GAAP.
What Is Financial Reporting? Definition, Types and Importance - Financial reporting is the process of documenting and communicating financial activities over specific periods, helping stakeholders evaluate financial performance and make informed decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com