Supply chain finance optimizes cash flow by allowing suppliers to receive early payments through third-party funding, improving liquidity along the supply chain. Letters of credit guarantee payment to exporters by a trusted financial institution upon meeting specific terms, mitigating transactional risks in international trade. Explore deeper insights into how these financial instruments enhance trade efficiency and risk management.
Why it is important
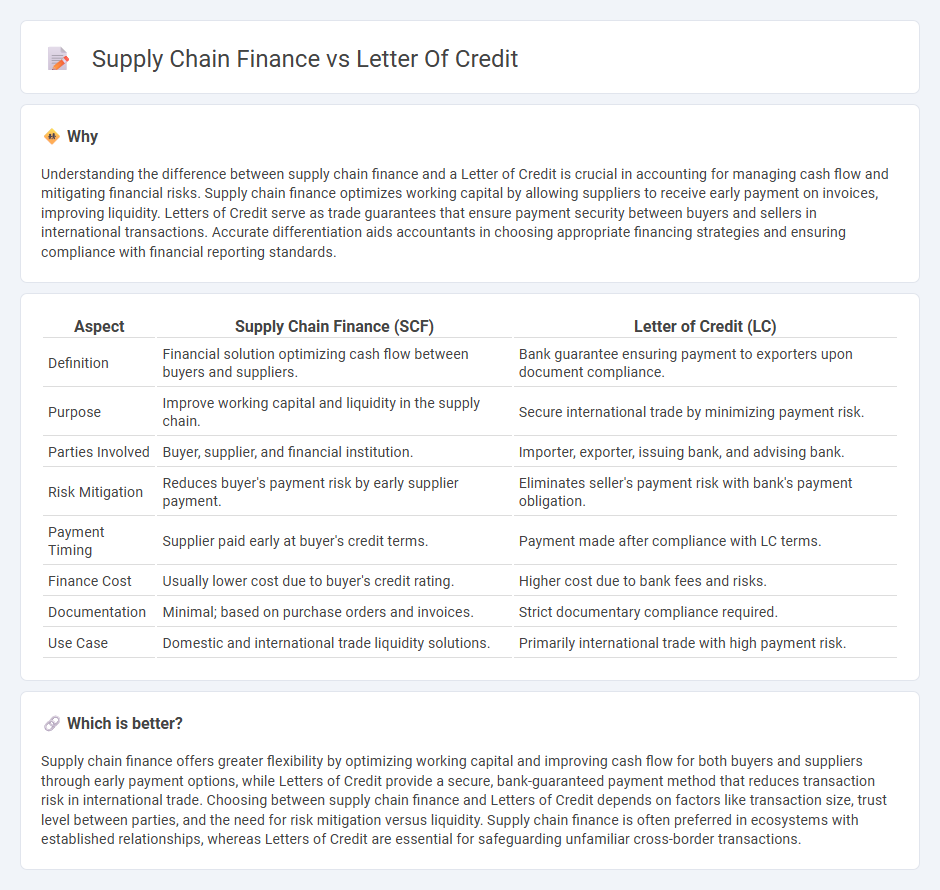
Understanding the difference between supply chain finance and a Letter of Credit is crucial in accounting for managing cash flow and mitigating financial risks. Supply chain finance optimizes working capital by allowing suppliers to receive early payment on invoices, improving liquidity. Letters of Credit serve as trade guarantees that ensure payment security between buyers and sellers in international transactions. Accurate differentiation aids accountants in choosing appropriate financing strategies and ensuring compliance with financial reporting standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Supply Chain Finance (SCF) | Letter of Credit (LC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial solution optimizing cash flow between buyers and suppliers. | Bank guarantee ensuring payment to exporters upon document compliance. |
| Purpose | Improve working capital and liquidity in the supply chain. | Secure international trade by minimizing payment risk. |
| Parties Involved | Buyer, supplier, and financial institution. | Importer, exporter, issuing bank, and advising bank. |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduces buyer's payment risk by early supplier payment. | Eliminates seller's payment risk with bank's payment obligation. |
| Payment Timing | Supplier paid early at buyer's credit terms. | Payment made after compliance with LC terms. |
| Finance Cost | Usually lower cost due to buyer's credit rating. | Higher cost due to bank fees and risks. |
| Documentation | Minimal; based on purchase orders and invoices. | Strict documentary compliance required. |
| Use Case | Domestic and international trade liquidity solutions. | Primarily international trade with high payment risk. |
Which is better?
Supply chain finance offers greater flexibility by optimizing working capital and improving cash flow for both buyers and suppliers through early payment options, while Letters of Credit provide a secure, bank-guaranteed payment method that reduces transaction risk in international trade. Choosing between supply chain finance and Letters of Credit depends on factors like transaction size, trust level between parties, and the need for risk mitigation versus liquidity. Supply chain finance is often preferred in ecosystems with established relationships, whereas Letters of Credit are essential for safeguarding unfamiliar cross-border transactions.
Connection
Supply chain finance optimizes cash flow between buyers and suppliers by leveraging financial instruments like Letters of Credit to guarantee payment security and reduce transaction risk. Letters of Credit serve as a reliable payment mechanism ensuring sellers receive funds promptly upon meeting delivery terms, which facilitates smoother credit terms and strengthens supplier relationships within supply chains. Integrating Letters of Credit into supply chain finance enhances liquidity management and supports international trade by minimizing payment delays and fostering trust among parties.
Key Terms
Creditworthiness
Letters of credit provide a guaranteed payment mechanism relying heavily on the buyer's creditworthiness and the issuing bank's credibility, mitigating seller risk in international trade. Supply chain finance, by contrast, optimizes working capital by enabling suppliers to receive early payment based on the buyer's stronger credit profile without needing a letter of credit. Explore the advantages and creditworthiness criteria in both financial tools to enhance your trade financing strategy.
Receivables
Letters of credit (LC) provide guaranteed payment to exporters by banks, reducing receivables risk in international trade. Supply chain finance (SCF) optimizes working capital by allowing suppliers to receive early payment on receivables through third-party financing solutions. Explore the key differences and benefits of LC and SCF to improve receivables management.
Risk mitigation
Letters of credit provide a secure payment guarantee by a bank, mitigating risks of non-payment in international trade transactions through documented compliance. Supply chain finance enhances cash flow and reduces supplier default risk by enabling early payment based on approved invoices, improving overall financial stability within the supply chain. Explore how these financing tools strategically mitigate risk to optimize your trade operations.
Source and External Links
letter of credit | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - A letter of credit is a financial instrument issued by a bank authorizing the bearer to demand payment, often used to guarantee payment under specific conditions in commercial transactions.
What is a letter of credit? | BDC.ca - It is a financial contract between a bank, its customer (importer), and the beneficiary (exporter) that guarantees payment once conditions are met, commonly used to reduce risk in international trade.
Letter of credit - Wikipedia - A letter of credit is a payment mechanism in international trade, providing an economic guarantee from a bank to the exporter, ensuring payment upon presentation of stipulated documents.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com