Sustainability assurance examines the accuracy and reliability of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures to ensure transparent reporting on a company's sustainable practices. Corporate governance audit evaluates the effectiveness of internal controls, board oversight, and compliance with regulatory frameworks to safeguard shareholder interests and organizational integrity. Explore further to understand how these distinct audit types enhance accountability and stakeholder trust in corporate reporting.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainability assurance and corporate governance audit is crucial for accurate risk assessment and compliance. Sustainability assurance focuses on validating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, ensuring transparency and stakeholder trust in sustainability initiatives. Corporate governance audits evaluate the effectiveness of board structures, internal controls, and compliance with regulatory frameworks to safeguard shareholder interests. Differentiating these audits helps professionals implement targeted strategies for ethical reporting and organizational accountability.
Comparison Table
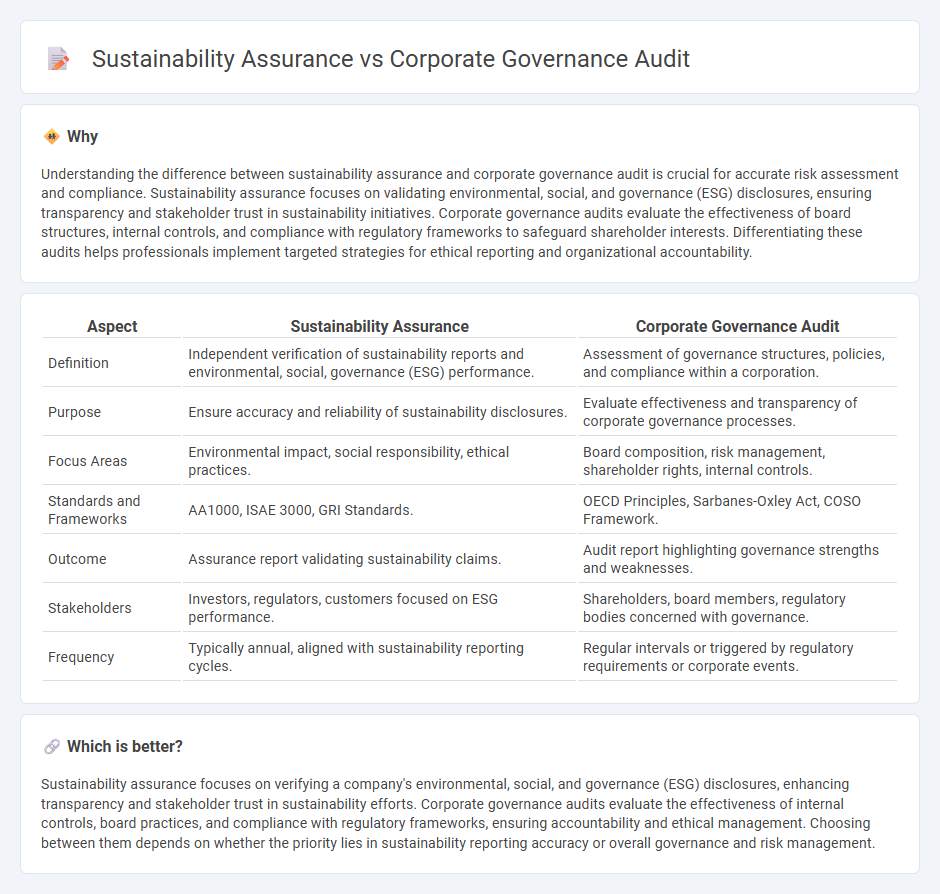
| Aspect | Sustainability Assurance | Corporate Governance Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Independent verification of sustainability reports and environmental, social, governance (ESG) performance. | Assessment of governance structures, policies, and compliance within a corporation. |
| Purpose | Ensure accuracy and reliability of sustainability disclosures. | Evaluate effectiveness and transparency of corporate governance processes. |
| Focus Areas | Environmental impact, social responsibility, ethical practices. | Board composition, risk management, shareholder rights, internal controls. |
| Standards and Frameworks | AA1000, ISAE 3000, GRI Standards. | OECD Principles, Sarbanes-Oxley Act, COSO Framework. |
| Outcome | Assurance report validating sustainability claims. | Audit report highlighting governance strengths and weaknesses. |
| Stakeholders | Investors, regulators, customers focused on ESG performance. | Shareholders, board members, regulatory bodies concerned with governance. |
| Frequency | Typically annual, aligned with sustainability reporting cycles. | Regular intervals or triggered by regulatory requirements or corporate events. |
Which is better?
Sustainability assurance focuses on verifying a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, enhancing transparency and stakeholder trust in sustainability efforts. Corporate governance audits evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls, board practices, and compliance with regulatory frameworks, ensuring accountability and ethical management. Choosing between them depends on whether the priority lies in sustainability reporting accuracy or overall governance and risk management.
Connection
Sustainability assurance and corporate governance audit are interconnected through their shared objective of enhancing transparency and accountability in organizational practices. Sustainability assurance evaluates the accuracy and reliability of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, while corporate governance audits assess the effectiveness of internal controls and board oversight mechanisms. Integrating these processes strengthens stakeholder confidence by ensuring that sustainability initiatives align with governance standards and regulatory compliance.
Key Terms
Internal Controls
Corporate governance audits rigorously evaluate internal controls related to financial reporting, risk management, and compliance to ensure accountability and transparency within an organization. Sustainability assurance focuses on verifying non-financial data such as environmental impact and social responsibility metrics, emphasizing controls over sustainability reporting processes. Explore detailed distinctions and best practices to enhance your organization's assurance framework.
Materiality
Corporate governance audits focus on evaluating the effectiveness of an organization's governance structures, risk management, and compliance with regulations, emphasizing material risks that could impact financial performance and stakeholder trust. Sustainability assurance centers on verifying the accuracy and reliability of non-financial disclosures, particularly environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, with materiality assessed based on stakeholders' interests and long-term impacts. Discover more about how materiality shapes these assurances and their implications for corporate accountability.
Stakeholder Engagement
Corporate governance audits emphasize evaluating the effectiveness of stakeholder engagement processes to ensure accountability, transparency, and alignment with regulatory requirements. Sustainability assurance prioritizes verifying the accuracy and credibility of reported environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data, highlighting genuine stakeholder involvement in sustainable business practices. Explore more insights on how these approaches enhance stakeholder trust and organizational performance.
Source and External Links
The role of internal audit in ensuring strong corporate governance - Internal audit plays a critical role in corporate governance by independently evaluating risk management, internal controls, compliance, and governance processes to ensure transparency, accountability, and ethical operation within an organization.
Corporate governance and its impact on audit practice - ACCA Global - The audit committee, consisting mainly of independent non-executive directors, oversees the integrity of financial statements and the external audit process, ensuring audit independence and effectiveness as a core part of corporate governance.
What is an audit committee? - The Corporate Governance Institute - An audit committee monitors financial reporting, internal control systems, and the work of external auditors, providing crucial accountability and oversight to uphold good corporate governance and prevent financial mismanagement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com