Dark data auditing focuses on uncovering unused or hidden data that can impact financial accuracy and compliance, while internal audit evaluates the overall effectiveness of internal controls and risk management processes. Both practices are essential for improving transparency and safeguarding company assets, but dark data auditing specifically targets data that traditional audits might overlook. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances accounting accuracy and organizational accountability.
Why it is important
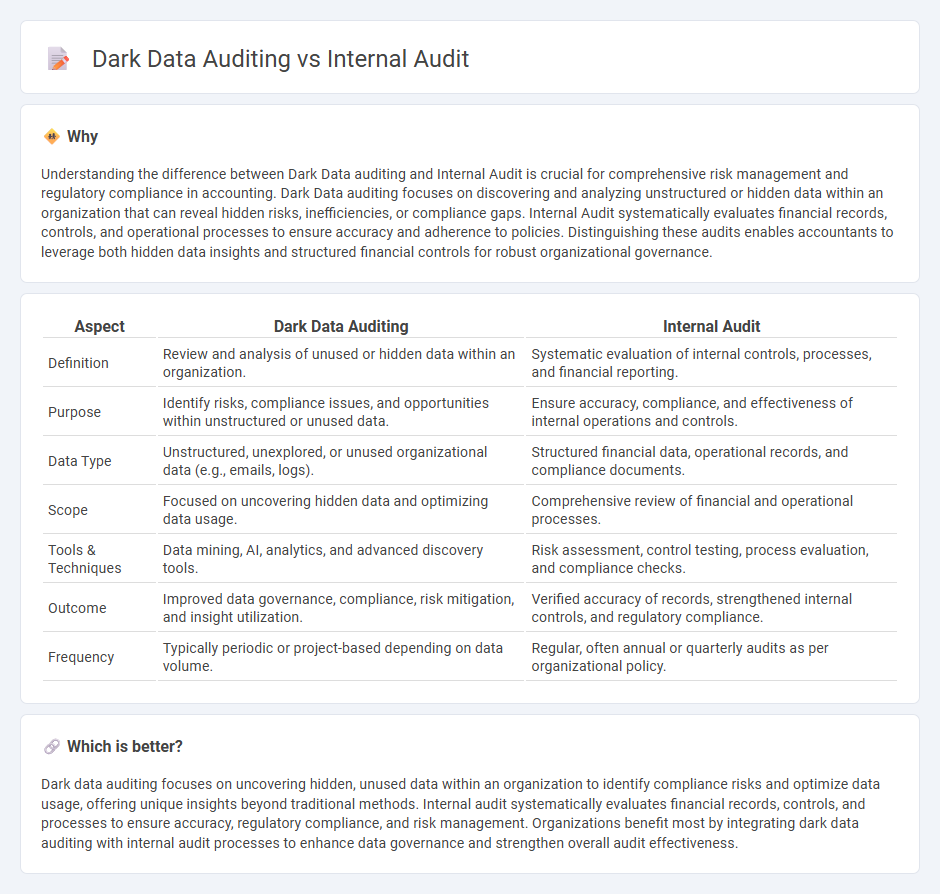
Understanding the difference between Dark Data auditing and Internal Audit is crucial for comprehensive risk management and regulatory compliance in accounting. Dark Data auditing focuses on discovering and analyzing unstructured or hidden data within an organization that can reveal hidden risks, inefficiencies, or compliance gaps. Internal Audit systematically evaluates financial records, controls, and operational processes to ensure accuracy and adherence to policies. Distinguishing these audits enables accountants to leverage both hidden data insights and structured financial controls for robust organizational governance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Dark Data Auditing | Internal Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Review and analysis of unused or hidden data within an organization. | Systematic evaluation of internal controls, processes, and financial reporting. |
| Purpose | Identify risks, compliance issues, and opportunities within unstructured or unused data. | Ensure accuracy, compliance, and effectiveness of internal operations and controls. |
| Data Type | Unstructured, unexplored, or unused organizational data (e.g., emails, logs). | Structured financial data, operational records, and compliance documents. |
| Scope | Focused on uncovering hidden data and optimizing data usage. | Comprehensive review of financial and operational processes. |
| Tools & Techniques | Data mining, AI, analytics, and advanced discovery tools. | Risk assessment, control testing, process evaluation, and compliance checks. |
| Outcome | Improved data governance, compliance, risk mitigation, and insight utilization. | Verified accuracy of records, strengthened internal controls, and regulatory compliance. |
| Frequency | Typically periodic or project-based depending on data volume. | Regular, often annual or quarterly audits as per organizational policy. |
Which is better?
Dark data auditing focuses on uncovering hidden, unused data within an organization to identify compliance risks and optimize data usage, offering unique insights beyond traditional methods. Internal audit systematically evaluates financial records, controls, and processes to ensure accuracy, regulatory compliance, and risk management. Organizations benefit most by integrating dark data auditing with internal audit processes to enhance data governance and strengthen overall audit effectiveness.
Connection
Dark data auditing uncovers hidden or unused data that can reveal compliance risks, financial discrepancies, and operational inefficiencies critical to internal audit processes. Internal audit leverages dark data insights to enhance risk assessment, improve controls, and ensure accurate financial reporting. Integrating dark data auditing into internal audits strengthens fraud detection and regulatory compliance in accounting practices.
Key Terms
**Internal Audit:**
Internal audit systematically evaluates an organization's risk management, control, and governance processes to ensure accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards. It leverages detailed financial, operational, and IT audits to identify inefficiencies and mitigate risks across all departments. Explore comprehensive insights to understand how internal audits optimize organizational performance and safeguard assets.
Risk Assessment
Internal audit primarily concentrates on evaluating organizational processes, controls, and compliance to mitigate operational and financial risks. Dark data auditing targets unstructured, unused data within a company, assessing hidden risks such as data breaches, privacy violations, and regulatory non-compliance. Explore the differences and impacts of these audits on comprehensive risk management by learning more about their methodologies and benefits.
Compliance
Internal audit focuses on evaluating organizational processes and controls to ensure compliance with regulatory standards and internal policies. Dark data auditing addresses the challenge of uncovering and analyzing hidden or unstructured data that may pose compliance risks related to data privacy, security, and regulatory adherence. Explore further to understand how integrating both audits strengthens comprehensive compliance frameworks.
Source and External Links
Internal Audit 101 - This resource provides an overview of internal auditing, including its function, types of audits, and best practices for the auditing process.
Internal audit - This article explains internal auditing as an independent assurance and consulting activity designed to improve an organization's operations.
What is Internal Audit? - This blog post discusses the role of internal audit, its types, process, and standards, highlighting its importance in providing unbiased reviews of systems and processes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com