Data lake reconciliation involves matching and validating vast, unstructured data sets stored in data lakes to ensure accuracy and consistency across financial systems. Receivables reconciliation focuses on verifying customer accounts and payments to confirm outstanding balances and detect discrepancies in accounts receivable. Explore the key differences and benefits of each reconciliation method to enhance your accounting processes.
Why it is important
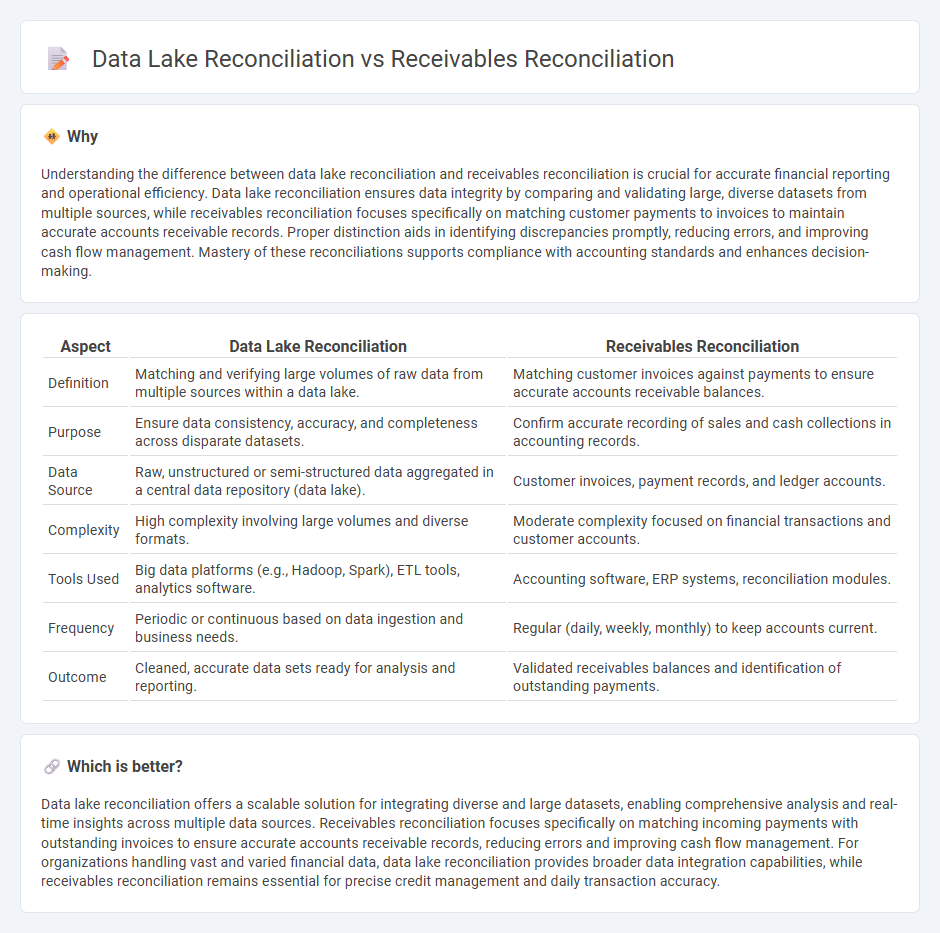
Understanding the difference between data lake reconciliation and receivables reconciliation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and operational efficiency. Data lake reconciliation ensures data integrity by comparing and validating large, diverse datasets from multiple sources, while receivables reconciliation focuses specifically on matching customer payments to invoices to maintain accurate accounts receivable records. Proper distinction aids in identifying discrepancies promptly, reducing errors, and improving cash flow management. Mastery of these reconciliations supports compliance with accounting standards and enhances decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Data Lake Reconciliation | Receivables Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Matching and verifying large volumes of raw data from multiple sources within a data lake. | Matching customer invoices against payments to ensure accurate accounts receivable balances. |
| Purpose | Ensure data consistency, accuracy, and completeness across disparate datasets. | Confirm accurate recording of sales and cash collections in accounting records. |
| Data Source | Raw, unstructured or semi-structured data aggregated in a central data repository (data lake). | Customer invoices, payment records, and ledger accounts. |
| Complexity | High complexity involving large volumes and diverse formats. | Moderate complexity focused on financial transactions and customer accounts. |
| Tools Used | Big data platforms (e.g., Hadoop, Spark), ETL tools, analytics software. | Accounting software, ERP systems, reconciliation modules. |
| Frequency | Periodic or continuous based on data ingestion and business needs. | Regular (daily, weekly, monthly) to keep accounts current. |
| Outcome | Cleaned, accurate data sets ready for analysis and reporting. | Validated receivables balances and identification of outstanding payments. |
Which is better?
Data lake reconciliation offers a scalable solution for integrating diverse and large datasets, enabling comprehensive analysis and real-time insights across multiple data sources. Receivables reconciliation focuses specifically on matching incoming payments with outstanding invoices to ensure accurate accounts receivable records, reducing errors and improving cash flow management. For organizations handling vast and varied financial data, data lake reconciliation provides broader data integration capabilities, while receivables reconciliation remains essential for precise credit management and daily transaction accuracy.
Connection
Data lake reconciliation enhances receivables reconciliation by consolidating diverse financial data sources into a centralized repository, enabling more accurate matching of invoices and payments. Machine learning algorithms applied within data lakes identify discrepancies and anomalies in accounts receivable, improving error detection and reducing reconciliation time. This integration streamlines financial reporting and optimizes cash flow management for businesses.
Key Terms
Aging Schedule
Receivables reconciliation involves matching outstanding invoices to payment records to ensure accurate aging schedules, highlighting overdue accounts and cash flow status. Data lake reconciliation aggregates varied financial data sources, providing a comprehensive, real-time aging analysis across complex datasets with enhanced accuracy and scalability. Explore more to understand how these methods optimize aging schedule management and improve financial reporting.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)
Receivables reconciliation typically relies on ETL processes to extract transaction data from accounting systems, transform it to align with ledger formats, and load it into reconciliation platforms for accurate matching. Data lake reconciliation involves ETL workflows that ingest diverse, large-scale data sources into centralized repositories, transforming raw data into structured formats to enable comprehensive analysis and correlation. Explore how optimized ETL strategies enhance accuracy and efficiency in both receivables and data lake reconciliations.
Subledger
Receivables reconciliation ensures accurate alignment between customer invoices and payments within the subledger, maintaining financial integrity and reducing discrepancies. Data lake reconciliation consolidates diverse financial data, including subledger entries, into a centralized repository for enhanced analytics and reporting. Discover the detailed processes and benefits of each reconciliation method in relation to subledger management.
Source and External Links
How to reconcile accounts receivable - Accounts receivable reconciliation involves matching detailed unpaid customer billings to the accounts receivable balance in the general ledger to ensure the ledger figure is accurate and justified.
Accounts receivable (AR) reconciliation tips - The AR reconciliation process includes gathering invoices and receipts, comparing those with ledger balances, investigating discrepancies, making adjustments, and ensuring both records match for accurate accounting.
Ultimate Guide to Accounts Receivable Reconciliation - Effective receivables reconciliation at month-end involves reviewing previous balances, cross-referencing general ledger balances with unpaid billings from sales ledgers or invoicing systems, and resolving any discrepancies to confirm proper recording of all AR activity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com