Cryptocurrency valuation involves assessing digital assets at fair value based on market prices, reflecting real-time demand and supply fluctuations. Amortized cost accounting records assets at their initial purchase price minus principal repayments and amortization, providing a stable, historical cost perspective. Explore detailed methods and implications of each approach to optimize financial reporting accuracy.
Why it is important
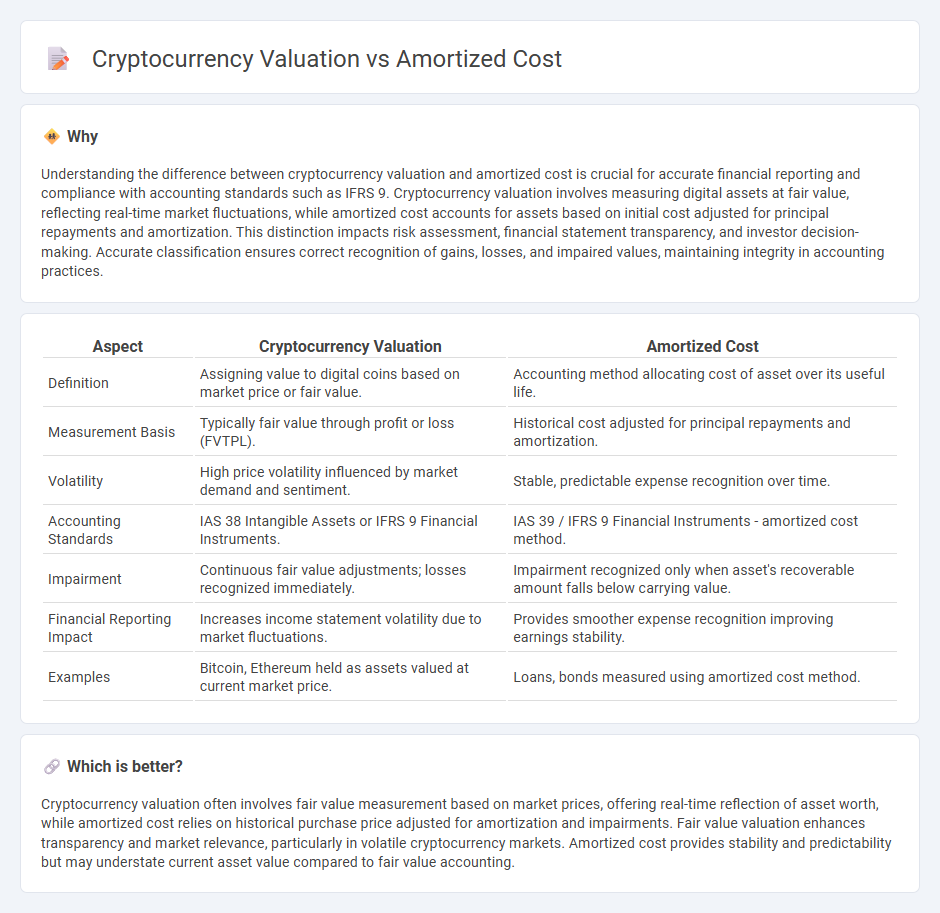
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency valuation and amortized cost is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards such as IFRS 9. Cryptocurrency valuation involves measuring digital assets at fair value, reflecting real-time market fluctuations, while amortized cost accounts for assets based on initial cost adjusted for principal repayments and amortization. This distinction impacts risk assessment, financial statement transparency, and investor decision-making. Accurate classification ensures correct recognition of gains, losses, and impaired values, maintaining integrity in accounting practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Valuation | Amortized Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assigning value to digital coins based on market price or fair value. | Accounting method allocating cost of asset over its useful life. |
| Measurement Basis | Typically fair value through profit or loss (FVTPL). | Historical cost adjusted for principal repayments and amortization. |
| Volatility | High price volatility influenced by market demand and sentiment. | Stable, predictable expense recognition over time. |
| Accounting Standards | IAS 38 Intangible Assets or IFRS 9 Financial Instruments. | IAS 39 / IFRS 9 Financial Instruments - amortized cost method. |
| Impairment | Continuous fair value adjustments; losses recognized immediately. | Impairment recognized only when asset's recoverable amount falls below carrying value. |
| Financial Reporting Impact | Increases income statement volatility due to market fluctuations. | Provides smoother expense recognition improving earnings stability. |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Ethereum held as assets valued at current market price. | Loans, bonds measured using amortized cost method. |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency valuation often involves fair value measurement based on market prices, offering real-time reflection of asset worth, while amortized cost relies on historical purchase price adjusted for amortization and impairments. Fair value valuation enhances transparency and market relevance, particularly in volatile cryptocurrency markets. Amortized cost provides stability and predictability but may understate current asset value compared to fair value accounting.
Connection
Cryptocurrency valuation relies heavily on the amortized cost method to record and report digital assets on financial statements, ensuring consistent measurement over time. Amortized cost reflects the initial acquisition price adjusted for any impairments or related expenses, providing a reliable basis for valuing cryptocurrencies held for investment or operational purposes. This connection enables accurate tracking of asset value fluctuations and compliance with accounting standards such as IFRS 9 or ASC 326.
Key Terms
Historical Cost
Historical cost accounting records cryptocurrency assets based on their original purchase price, offering a stable valuation method amid market volatility. This approach contrasts with fair value accounting, which fluctuates with real-time market prices, potentially causing significant value swings in financial statements. Explore more about how amortized cost impacts cryptocurrency investment strategies and risk assessment.
Fair Value
Amortized cost in cryptocurrency valuation reflects the systematic allocation of an asset's cost over its useful life, offering a grounded approach compared to volatile market prices. Fair value measurement prioritizes current market conditions, providing a transparent snapshot that aligns with investors' real-time expectations. Explore the nuances between amortized cost and fair value to enhance your understanding of cryptocurrency asset valuation.
Volatility
Amortized cost accounting smooths out asset value fluctuations by spreading expenses evenly over time, providing a stable representation of investment worth. Cryptocurrency valuation, however, is directly impacted by market volatility, causing rapid and significant price swings that reflect real-time investor sentiment and market dynamics. Explore how these contrasting approaches affect financial reporting and investment strategies in the volatile crypto market.
Source and External Links
What is Amortized Cost? - Amortized cost refers to the purchase price of an asset adjusted for factors like interest rates and payments over its lifetime.
How To Calculate Amortization Cost Basis - This guide explains how to calculate the amortization cost basis, particularly for investments purchased at a premium, and its relevance in financial reporting and tax purposes.
Amortized Costs - In the context of FinOps and cloud computing, amortized cost is a method for spreading asset expenses over their expected useful life to accurately allocate costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com