Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying digital asset transactions, wallet security, and blockchain integrity, whereas IT auditing evaluates information systems, data processing, and cybersecurity controls. Both disciplines require expertise in technology and regulatory compliance, but cryptocurrency auditing demands specialized knowledge of blockchain mechanisms and cryptographic principles. Explore the key differences and synergies between cryptocurrency and IT auditing to enhance your financial assurance strategies.
Why it is important
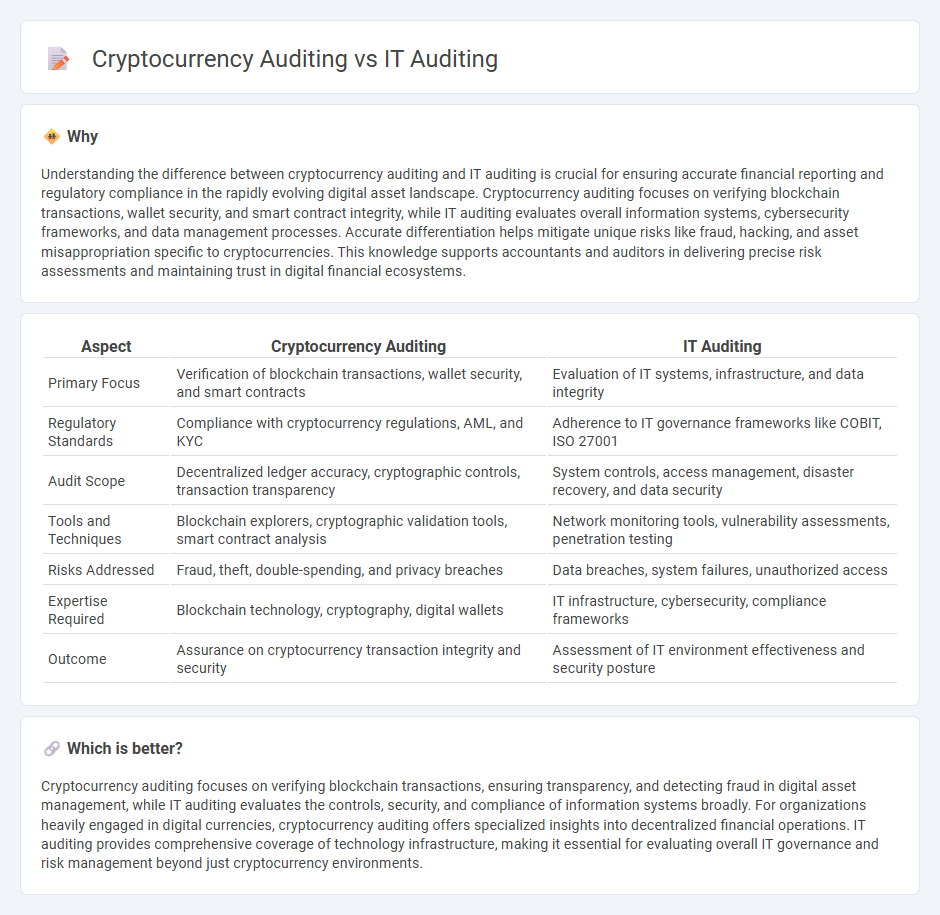
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency auditing and IT auditing is crucial for ensuring accurate financial reporting and regulatory compliance in the rapidly evolving digital asset landscape. Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying blockchain transactions, wallet security, and smart contract integrity, while IT auditing evaluates overall information systems, cybersecurity frameworks, and data management processes. Accurate differentiation helps mitigate unique risks like fraud, hacking, and asset misappropriation specific to cryptocurrencies. This knowledge supports accountants and auditors in delivering precise risk assessments and maintaining trust in digital financial ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Auditing | IT Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Verification of blockchain transactions, wallet security, and smart contracts | Evaluation of IT systems, infrastructure, and data integrity |
| Regulatory Standards | Compliance with cryptocurrency regulations, AML, and KYC | Adherence to IT governance frameworks like COBIT, ISO 27001 |
| Audit Scope | Decentralized ledger accuracy, cryptographic controls, transaction transparency | System controls, access management, disaster recovery, and data security |
| Tools and Techniques | Blockchain explorers, cryptographic validation tools, smart contract analysis | Network monitoring tools, vulnerability assessments, penetration testing |
| Risks Addressed | Fraud, theft, double-spending, and privacy breaches | Data breaches, system failures, unauthorized access |
| Expertise Required | Blockchain technology, cryptography, digital wallets | IT infrastructure, cybersecurity, compliance frameworks |
| Outcome | Assurance on cryptocurrency transaction integrity and security | Assessment of IT environment effectiveness and security posture |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying blockchain transactions, ensuring transparency, and detecting fraud in digital asset management, while IT auditing evaluates the controls, security, and compliance of information systems broadly. For organizations heavily engaged in digital currencies, cryptocurrency auditing offers specialized insights into decentralized financial operations. IT auditing provides comprehensive coverage of technology infrastructure, making it essential for evaluating overall IT governance and risk management beyond just cryptocurrency environments.
Connection
Cryptocurrency auditing and IT auditing intersect through their focus on verifying digital asset transactions and assessing information systems' security protocols to ensure accuracy and compliance. Both rely on blockchain technology expertise and cybersecurity measures to detect fraud, inconsistencies, and vulnerabilities within financial records and IT infrastructure. The integration of advanced analytics and automated tools in these audits enhances transparency and reduces risks in digital financial ecosystems.
Key Terms
**IT Auditing:**
IT auditing evaluates an organization's information systems, ensuring data integrity, security protocols, and compliance with regulatory standards such as SOX and GDPR. It focuses on risk assessment, system controls, and process efficiencies to mitigate cybersecurity threats and operational vulnerabilities. Discover detailed methodologies and industry best practices in IT auditing for enhanced organizational governance.
Access Controls
IT auditing emphasizes evaluating access controls to ensure system security, data integrity, and compliance with regulatory standards through user authentication, authorization, and regular access reviews. Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying access controls related to digital wallets, private keys management, and blockchain permissions to prevent unauthorized transactions and maintain trust in decentralized networks. Explore comprehensive insights to understand the critical differences and best practices in access control auditing for IT and cryptocurrency environments.
Data Integrity
IT auditing ensures data integrity by systematically evaluating an organization's information systems, emphasizing accuracy, consistency, and reliability of digital records. Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying blockchain transactions and wallets to maintain transparency, immutability, and security against fraud or cyber threats. Explore more to understand the critical differences and methodologies in auditing data integrity within both domains.
Source and External Links
What is IT audit (information technology audit)? - An IT audit is the examination and evaluation of an organization's information technology, operations, and controls to ensure data integrity, security, and compliance with laws and standards.
What is an IT Audit? A Beginner's Guide - IT audits inspect and assess an organization's IT infrastructure, applications, data management, and compliance with internal and external standards to evaluate efficiency and security.
IT Audit & Compliance Guide: Types & Best Practices - The IT audit process involves planning, risk assessment, controls evaluation, compliance review, vulnerability testing, and reporting to identify risks and improve IT governance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com