Triple entry accounting enhances financial transparency by incorporating cryptographic verification alongside traditional debit and credit records, fostering trust and accuracy. Environmental accounting integrates ecological costs and benefits into financial statements, enabling organizations to measure and report their environmental impact effectively. Explore how these innovative accounting methods transform corporate accountability and sustainability reporting.
Why it is important
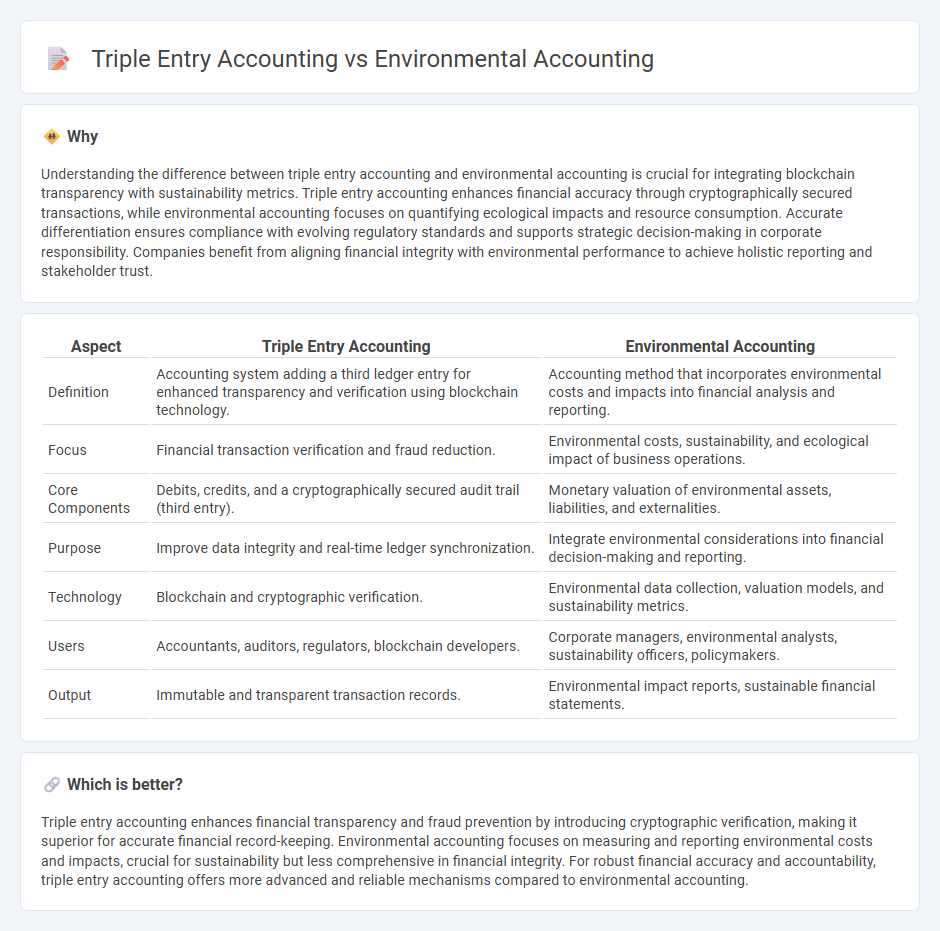
Understanding the difference between triple entry accounting and environmental accounting is crucial for integrating blockchain transparency with sustainability metrics. Triple entry accounting enhances financial accuracy through cryptographically secured transactions, while environmental accounting focuses on quantifying ecological impacts and resource consumption. Accurate differentiation ensures compliance with evolving regulatory standards and supports strategic decision-making in corporate responsibility. Companies benefit from aligning financial integrity with environmental performance to achieve holistic reporting and stakeholder trust.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Triple Entry Accounting | Environmental Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting system adding a third ledger entry for enhanced transparency and verification using blockchain technology. | Accounting method that incorporates environmental costs and impacts into financial analysis and reporting. |
| Focus | Financial transaction verification and fraud reduction. | Environmental costs, sustainability, and ecological impact of business operations. |
| Core Components | Debits, credits, and a cryptographically secured audit trail (third entry). | Monetary valuation of environmental assets, liabilities, and externalities. |
| Purpose | Improve data integrity and real-time ledger synchronization. | Integrate environmental considerations into financial decision-making and reporting. |
| Technology | Blockchain and cryptographic verification. | Environmental data collection, valuation models, and sustainability metrics. |
| Users | Accountants, auditors, regulators, blockchain developers. | Corporate managers, environmental analysts, sustainability officers, policymakers. |
| Output | Immutable and transparent transaction records. | Environmental impact reports, sustainable financial statements. |
Which is better?
Triple entry accounting enhances financial transparency and fraud prevention by introducing cryptographic verification, making it superior for accurate financial record-keeping. Environmental accounting focuses on measuring and reporting environmental costs and impacts, crucial for sustainability but less comprehensive in financial integrity. For robust financial accuracy and accountability, triple entry accounting offers more advanced and reliable mechanisms compared to environmental accounting.
Connection
Triple entry accounting enhances transparency by incorporating cryptographic verification of transactions, which can be applied to environmental accounting to track and verify sustainability efforts accurately. Environmental accounting measures the ecological impact of business activities and benefits from the immutable records provided by triple entry systems to ensure reliable reporting of carbon footprints and resource usage. Integrating these methods supports comprehensive accountability and promotes sustainable financial practices.
Key Terms
Environmental accounting:
Environmental accounting quantifies and reports the environmental costs and benefits associated with business activities, integrating ecological impacts into financial decision-making processes. It involves tracking resource consumption, waste generation, and environmental liabilities to enhance sustainability and regulatory compliance. Explore detailed insights on how environmental accounting drives corporate responsibility and long-term value creation.
Sustainability reporting
Environmental accounting integrates ecological costs and benefits into financial analysis, enabling organizations to quantify their environmental impact. Triple entry accounting enhances transparency by recording transactions in a shared ledger, promoting accountability in sustainability reporting frameworks such as GRI and SASB. Discover how combining these methods advances comprehensive sustainability assessments.
Environmental costs
Environmental accounting specifically tracks and monetizes environmental costs such as waste management, carbon emissions, and resource depletion, integrating these expenses into financial statements to highlight sustainability impacts. Triple entry accounting extends traditional double-entry bookkeeping by incorporating a cryptographically secured third entry, enhancing transparency and accountability, but it does not inherently focus on environmental cost capture. For a deeper understanding of how these accounting methods impact environmental cost management, explore detailed financial frameworks and case studies.
Source and External Links
Environmental accounting - Wikipedia - Environmental accounting is a field that identifies, measures, and communicates the economic and environmental costs incurred by companies or national economies due to their activities, aiming to integrate both financial and ecological information into decision-making.
Environmental accounting - EBSCO Research Starters - Environmental accounting evaluates and analyzes the costs organizations incur from their impact on the natural environment, helping them reduce risks, improve sustainability, and strengthen corporate social responsibility.
An Introduction to Environmental Accounting - US EPA - Environmental accounting serves as a management tool to track environmental costs, improve performance, control expenses, and support decisions related to cleaner technologies, greener processes, and product strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com