Continuous audit involves automated, real-time examination of financial data throughout the accounting period, enabling timely detection of anomalies and enhancing internal controls. External audit, performed periodically by independent auditors, focuses on providing an objective assessment of financial statements' accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Explore further to understand the distinct benefits and methodologies of continuous and external audits.
Why it is important
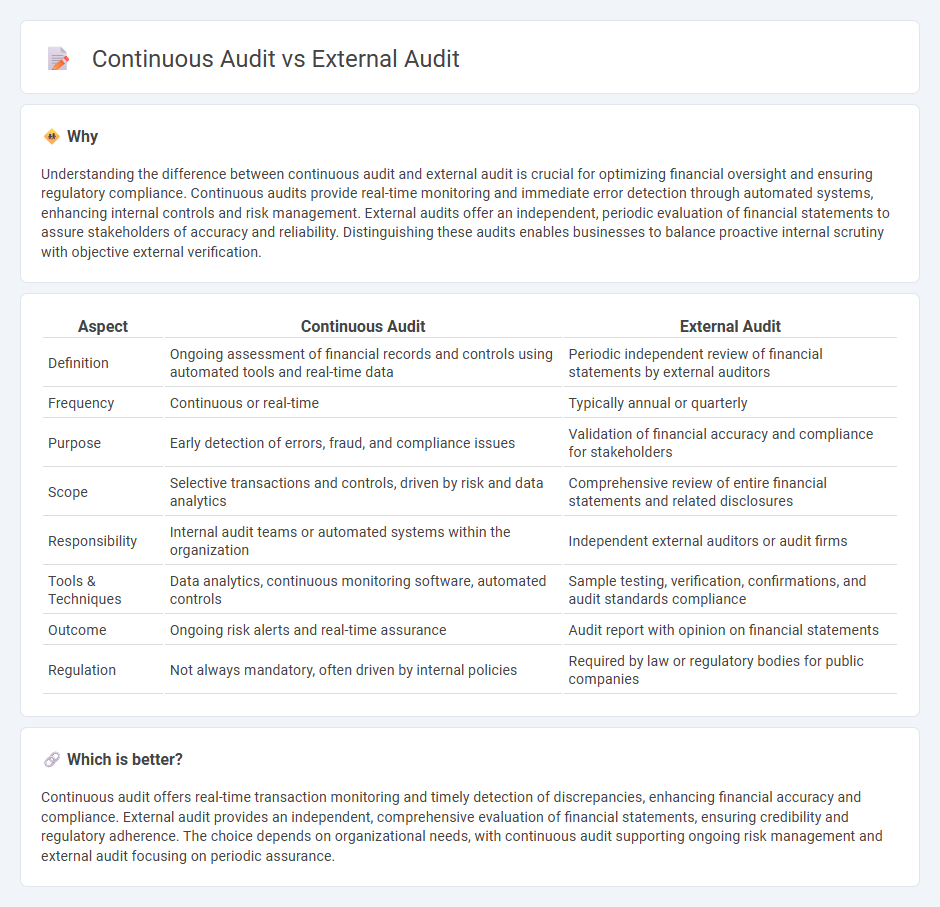
Understanding the difference between continuous audit and external audit is crucial for optimizing financial oversight and ensuring regulatory compliance. Continuous audits provide real-time monitoring and immediate error detection through automated systems, enhancing internal controls and risk management. External audits offer an independent, periodic evaluation of financial statements to assure stakeholders of accuracy and reliability. Distinguishing these audits enables businesses to balance proactive internal scrutiny with objective external verification.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Audit | External Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing assessment of financial records and controls using automated tools and real-time data | Periodic independent review of financial statements by external auditors |
| Frequency | Continuous or real-time | Typically annual or quarterly |
| Purpose | Early detection of errors, fraud, and compliance issues | Validation of financial accuracy and compliance for stakeholders |
| Scope | Selective transactions and controls, driven by risk and data analytics | Comprehensive review of entire financial statements and related disclosures |
| Responsibility | Internal audit teams or automated systems within the organization | Independent external auditors or audit firms |
| Tools & Techniques | Data analytics, continuous monitoring software, automated controls | Sample testing, verification, confirmations, and audit standards compliance |
| Outcome | Ongoing risk alerts and real-time assurance | Audit report with opinion on financial statements |
| Regulation | Not always mandatory, often driven by internal policies | Required by law or regulatory bodies for public companies |
Which is better?
Continuous audit offers real-time transaction monitoring and timely detection of discrepancies, enhancing financial accuracy and compliance. External audit provides an independent, comprehensive evaluation of financial statements, ensuring credibility and regulatory adherence. The choice depends on organizational needs, with continuous audit supporting ongoing risk management and external audit focusing on periodic assurance.
Connection
Continuous audit leverages automated tools and real-time data analysis to provide ongoing assurance of financial records, enhancing the external audit process by delivering up-to-date information. External audits rely on insights from continuous audits to identify anomalies, reduce sampling risk, and improve the accuracy of financial statement evaluations. Integration of continuous audit data enables external auditors to focus on high-risk areas and enhance overall audit efficiency and effectiveness.
Key Terms
Independence
External audit emphasizes strict independence as auditors must remain impartial and free from conflicts of interest to ensure unbiased financial reporting. Continuous audit integrates ongoing monitoring within an organization, often involving internal auditors who maintain a degree of independence but work more closely with management to provide timely insights. Explore the key differences in independence and their impact on audit effectiveness to deepen your understanding.
Real-time Monitoring
External audit primarily involves periodic, independent evaluations of financial statements to ensure compliance and accuracy, typically conducted annually or quarterly. Continuous audit leverages real-time monitoring technologies and automated tools to provide ongoing assurance by analyzing transaction data instantly, allowing immediate identification of anomalies or risks. Explore how real-time monitoring in continuous audits transforms risk management and compliance effectiveness.
Audit Frequency
External audits are typically conducted annually or at specific intervals, providing a periodic, snapshot assessment of an organization's financial statements and internal controls. Continuous audits leverage technology and data analytics to monitor transactions and controls in real-time or near real-time, enabling ongoing assurance and quicker identification of risks. Explore more about how audit frequency impacts organizational governance and compliance effectiveness.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Purpose and Benefits of External Audits - This article outlines the purpose and benefits of external audits, including validating internal controls and enhancing decision-making through reliable financial information.
External Audit vs. Internal Audit - This resource explains the differences between external and internal audits, highlighting the role of external auditors in verifying financial statement accuracy for stakeholders.
Three Differences Between External and Internal Audits - This page discusses the key differences between external audits (independent assessments of financial information) and internal audits (reviews of operations and processes).
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com