Forensic analytics employs advanced data analysis techniques to detect and investigate fraud, financial discrepancies, and regulatory violations with precision. Internal audit focuses on evaluating internal controls, risk management, and compliance to ensure organizational efficiency and safeguard assets. Explore the distinctive roles and methodologies of forensic analytics and internal audit to enhance your organization's financial integrity.
Why it is important
Knowing the difference between forensic analytics and internal audit is crucial for accurately identifying fraud risks and ensuring regulatory compliance in accounting. Forensic analytics specializes in detecting and investigating financial crimes using detailed data analysis and forensic techniques. Internal audit evaluates the effectiveness of internal controls, risk management, and governance processes to improve organizational performance. Understanding these roles enhances the accuracy of financial reporting and strengthens overall corporate accountability.
Comparison Table
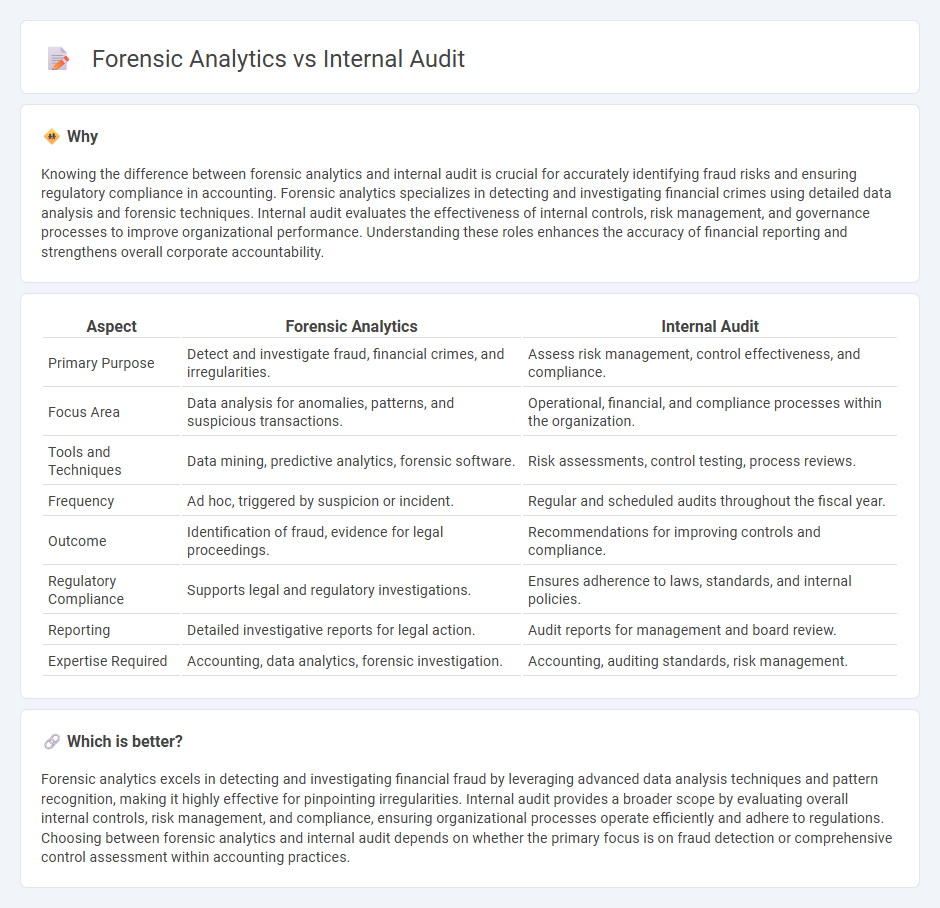
| Aspect | Forensic Analytics | Internal Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Detect and investigate fraud, financial crimes, and irregularities. | Assess risk management, control effectiveness, and compliance. |
| Focus Area | Data analysis for anomalies, patterns, and suspicious transactions. | Operational, financial, and compliance processes within the organization. |
| Tools and Techniques | Data mining, predictive analytics, forensic software. | Risk assessments, control testing, process reviews. |
| Frequency | Ad hoc, triggered by suspicion or incident. | Regular and scheduled audits throughout the fiscal year. |
| Outcome | Identification of fraud, evidence for legal proceedings. | Recommendations for improving controls and compliance. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Supports legal and regulatory investigations. | Ensures adherence to laws, standards, and internal policies. |
| Reporting | Detailed investigative reports for legal action. | Audit reports for management and board review. |
| Expertise Required | Accounting, data analytics, forensic investigation. | Accounting, auditing standards, risk management. |
Which is better?
Forensic analytics excels in detecting and investigating financial fraud by leveraging advanced data analysis techniques and pattern recognition, making it highly effective for pinpointing irregularities. Internal audit provides a broader scope by evaluating overall internal controls, risk management, and compliance, ensuring organizational processes operate efficiently and adhere to regulations. Choosing between forensic analytics and internal audit depends on whether the primary focus is on fraud detection or comprehensive control assessment within accounting practices.
Connection
Forensic analytics enhances internal audit by using advanced data analysis techniques to detect fraud, irregularities, and compliance issues early. Internal audit leverages forensic analytics tools such as data mining, predictive modeling, and anomaly detection to improve risk assessment and ensure financial integrity. Integrating forensic analytics within internal audit processes increases accuracy in identifying suspicious transactions and strengthens overall corporate governance.
Key Terms
Risk assessment
Internal audit emphasizes ongoing risk assessment by systematically evaluating organizational controls, processes, and compliance to identify vulnerabilities and improve governance. Forensic analytics targets risk assessment through detailed examination of transactions, patterns, and anomalies to detect fraud, financial misconduct, or misconduct risks. Explore the distinctions between internal audit and forensic analytics to strengthen your organization's risk management strategies.
Fraud detection
Internal audit focuses on evaluating internal controls and compliance to identify risks, including fraud, through systematic review and testing of financial transactions and processes. Forensic analytics employs advanced data analysis techniques, such as pattern recognition and anomaly detection, to uncover hidden fraud schemes and support investigations. Explore how integrating both approaches enhances fraud detection effectiveness and organizational security.
Evidence gathering
Internal audit focuses on systematic evaluation of financial records and operational processes to ensure compliance and identify risks, while forensic analytics specializes in detecting fraud by analyzing data patterns and anomalies for legal evidence. The forensic approach relies heavily on detailed data extraction and advanced statistical techniques to support investigations and litigation. Explore further to understand how these methods complement each other in strengthening organizational integrity.
Source and External Links
Internal Audit 101: Everything You Need to Know - AuditBoard - Internal audit is an independent, objective review of a company's internal systems, processes, and procedures aimed at ensuring effective risk management, controls, and operational alignment with company goals.
Internal audit - Wikipedia - Internal auditing is a systematic, risk-based assurance activity involving planning, executing, reporting, and follow-up to improve an organization's operations and controls.
What is Internal Audit? Types, Value, Process & Standards - Internal audit provides unbiased reviews of organizational systems, risks, control environments, operational effectiveness, and regulatory compliance, reporting directly to senior leadership or audit committees.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com