Digital asset reporting leverages blockchain technology and automated software to ensure real-time accuracy, enhanced traceability, and reduced risk of errors in financial record-keeping. Physical inventory reporting relies on traditional methods such as manual counting and barcode scanning, which can be time-consuming and prone to discrepancies. Discover the key differences and best practices for optimizing your accounting processes with digital asset integration.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital asset reporting and physical inventory reporting is crucial for accurate financial statements and regulatory compliance in accounting. Digital asset reporting often involves intangible items like cryptocurrencies or software licenses, requiring specialized valuation methods and recognition standards. Physical inventory reporting deals with tangible goods, focusing on cost flow assumptions and stock tracking accuracy. Precise differentiation ensures proper asset management, risk assessment, and audit readiness.
Comparison Table
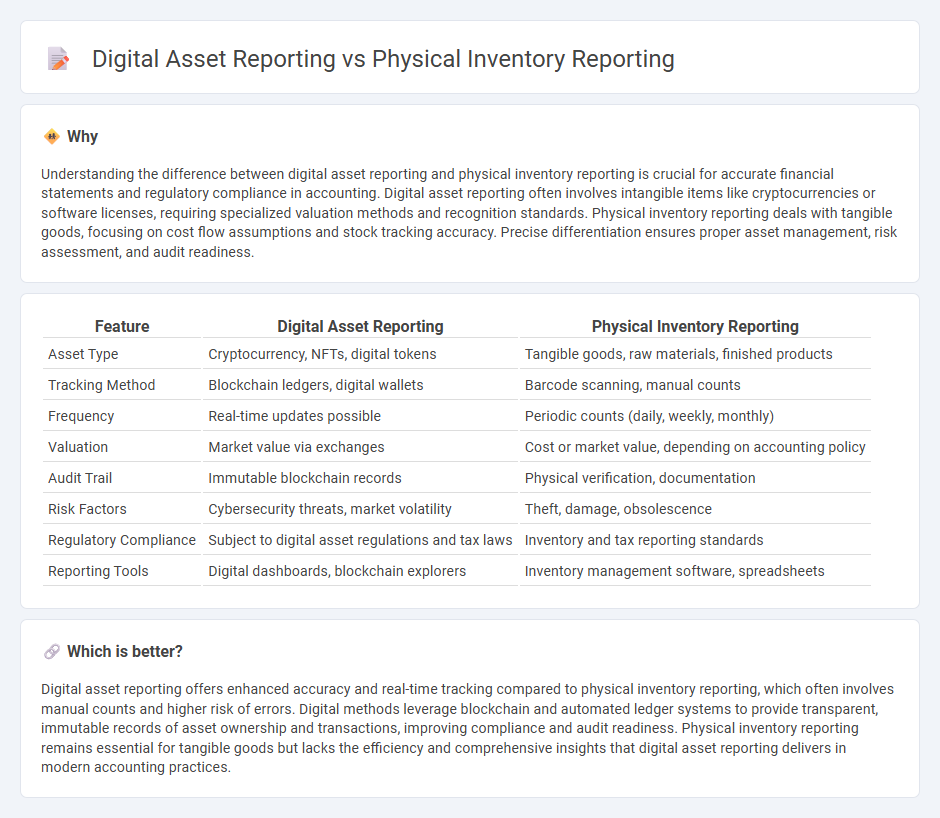
| Feature | Digital Asset Reporting | Physical Inventory Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Asset Type | Cryptocurrency, NFTs, digital tokens | Tangible goods, raw materials, finished products |
| Tracking Method | Blockchain ledgers, digital wallets | Barcode scanning, manual counts |
| Frequency | Real-time updates possible | Periodic counts (daily, weekly, monthly) |
| Valuation | Market value via exchanges | Cost or market value, depending on accounting policy |
| Audit Trail | Immutable blockchain records | Physical verification, documentation |
| Risk Factors | Cybersecurity threats, market volatility | Theft, damage, obsolescence |
| Regulatory Compliance | Subject to digital asset regulations and tax laws | Inventory and tax reporting standards |
| Reporting Tools | Digital dashboards, blockchain explorers | Inventory management software, spreadsheets |
Which is better?
Digital asset reporting offers enhanced accuracy and real-time tracking compared to physical inventory reporting, which often involves manual counts and higher risk of errors. Digital methods leverage blockchain and automated ledger systems to provide transparent, immutable records of asset ownership and transactions, improving compliance and audit readiness. Physical inventory reporting remains essential for tangible goods but lacks the efficiency and comprehensive insights that digital asset reporting delivers in modern accounting practices.
Connection
Digital asset reporting enhances physical inventory reporting by providing real-time data accuracy and streamlined tracking of inventory levels through integrated accounting systems. This connection enables precise reconciliation of digital records with actual stock, reducing discrepancies and improving financial transparency. Advanced software tools automate updates across both reports, facilitating efficient audit trails and regulatory compliance.
Key Terms
Inventory Valuation
Physical inventory reporting involves tracking tangible goods and materials, directly impacting inventory valuation through cost accounting methods such as FIFO, LIFO, or weighted average cost. Digital asset reporting, on the other hand, centers on intangible assets like cryptocurrencies, software licenses, or digital media, where valuation often relies on market value, usage rights, or amortization schedules. Explore the distinct methodologies and implications of inventory valuation in both physical and digital asset contexts to enhance your financial accuracy.
Asset Tracking
Physical inventory reporting relies on manual counting and barcode scanning to track tangible assets in warehouses or retail environments, often resulting in time-consuming processes and potential human error. Digital asset reporting leverages RFID, IoT sensors, and cloud-based systems to provide real-time tracking, automated updates, and enhanced accuracy for both physical and intangible assets. Explore the latest technologies and strategies to optimize asset tracking in your organization.
Reconciliation
Physical inventory reporting involves verifying and reconciling tangible assets through manual counts and documentation, ensuring accuracy between recorded and actual stock levels. Digital asset reporting centers on tracking intangible resources like cryptocurrencies or intellectual property via automated systems that reconcile blockchain or usage data with ledger entries. Explore in-depth methods and tools for effective reconciliation in both physical and digital asset management.
Source and External Links
What is Physical Inventory? How to and Tips (2024) - Shopify - Physical inventory reporting involves counting and verifying actual stock in store or warehouse and reconciling any discrepancies with recorded inventory to maintain accuracy in the POS system, measuring accuracy via shrinkage rate.
A Guide to Conducting Physical Inventory Counts - HBK CPA - Physical inventory count verifies quantity and condition of inventory items such as raw materials and finished goods, ensuring records in the inventory management system are accurate, which is crucial for financial reporting, operational efficiency, and reducing inventory costs.
Physical Inventory Reports - Oracle Help Center - Physical inventory reporting includes detailed reports on inventory tag counts, adjustments, accuracy analysis, and summary reports that help monitor inventory accuracy and determine if recounts or adjustments are needed before final processing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com