Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying misleading claims companies make about their environmental practices through financial statements and marketing reports. Ethical auditing examines broader aspects of corporate responsibility, including social, environmental, and governance factors, to ensure transparency and accountability. Explore how these methodologies enhance corporate integrity and inform investment decisions.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between greenwashing detection and ethical auditing is crucial for accurately assessing a company's environmental claims versus its overall ethical practices. Greenwashing detection focuses specifically on identifying misleading environmental statements, while ethical auditing evaluates broader ethical business conduct, including labor practices and financial transparency. Accurately distinguishing these processes ensures stakeholders can trust sustainability reports and corporate social responsibility disclosures. This knowledge is essential for accountants, auditors, and investors committed to genuine corporate accountability and ethical compliance.
Comparison Table
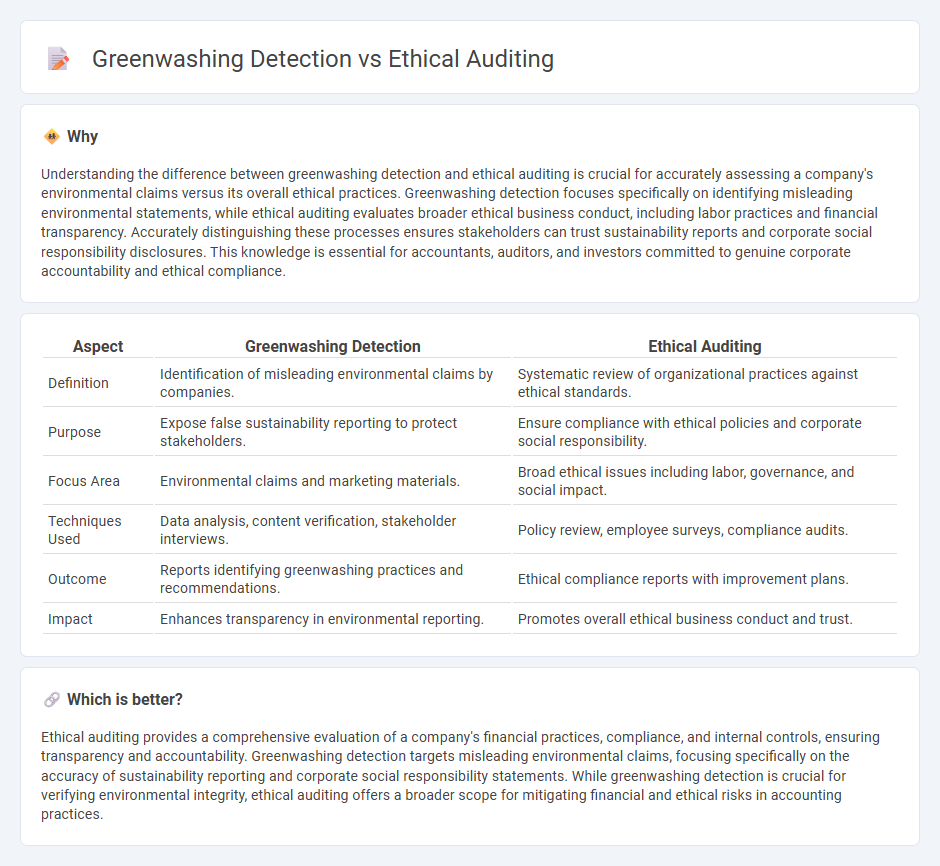
| Aspect | Greenwashing Detection | Ethical Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identification of misleading environmental claims by companies. | Systematic review of organizational practices against ethical standards. |
| Purpose | Expose false sustainability reporting to protect stakeholders. | Ensure compliance with ethical policies and corporate social responsibility. |
| Focus Area | Environmental claims and marketing materials. | Broad ethical issues including labor, governance, and social impact. |
| Techniques Used | Data analysis, content verification, stakeholder interviews. | Policy review, employee surveys, compliance audits. |
| Outcome | Reports identifying greenwashing practices and recommendations. | Ethical compliance reports with improvement plans. |
| Impact | Enhances transparency in environmental reporting. | Promotes overall ethical business conduct and trust. |
Which is better?
Ethical auditing provides a comprehensive evaluation of a company's financial practices, compliance, and internal controls, ensuring transparency and accountability. Greenwashing detection targets misleading environmental claims, focusing specifically on the accuracy of sustainability reporting and corporate social responsibility statements. While greenwashing detection is crucial for verifying environmental integrity, ethical auditing offers a broader scope for mitigating financial and ethical risks in accounting practices.
Connection
Greenwashing detection and ethical auditing intersect in accounting by ensuring transparency in financial and sustainability reports, preventing companies from misleading stakeholders about their environmental practices. Ethical auditing incorporates verification of environmental claims, strengthening corporate accountability and compliance with regulatory standards. This integration helps investors and regulators assess the authenticity of green initiatives, promoting responsible business conduct.
Key Terms
Independence
Ethical auditing emphasizes strict independence to ensure unbiased evaluation of corporate practices, while greenwashing detection requires autonomous assessment to identify misleading environmental claims. Both rely on transparent methodologies and external verification to maintain credibility and public trust. Explore further to understand how independence shapes the integrity of sustainability assessments.
Materiality
Ethical auditing emphasizes thorough examination of corporate practices against established social, environmental, and governance standards, prioritizing material issues that significantly impact stakeholders and long-term sustainability. Greenwashing detection specifically targets misleading claims about environmental efforts, scrutinizing how companies might exaggerate their positive impact or hide significant negative effects, with materiality guiding the assessment of what truly matters to consumers and regulators. Discover more about leveraging materiality to enhance transparency and accountability in corporate reporting.
Transparency
Ethical auditing assesses corporate practices against established standards to ensure genuine transparency and accountability in social and environmental performance. Greenwashing detection identifies misleading claims that companies use to appear more sustainable than they truly are, emphasizing the importance of verifying authenticity in disclosed information. Explore these methodologies further to understand how transparency shapes trust in sustainability reporting.
Source and External Links
9 Steps to Audit and Monitor an Ethical Culture - This guide outlines steps to implement and monitor ethical culture within organizations, including reviewing codes of ethics and conducting risk assessments.
Ethical Audit: Guide for Businesses in the UK - This guide explains why ethical audits are essential for detecting impropriety and ensuring compliance with ethics-related requirements in businesses.
Ethical Audits for Supply Chains - This explains the importance of ethical audits in maintaining social responsibility throughout supply chains and complying with international labor laws and environmental regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com