Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration involves incorporating sustainability factors directly into financial analysis and decision-making processes, reflecting a company's commitment to responsible business practices. Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial information, including ESG metrics, into a unified report to provide a holistic view of an organization's performance. Explore how these approaches transform accounting practices for enhanced transparency and long-term value creation.
Why it is important
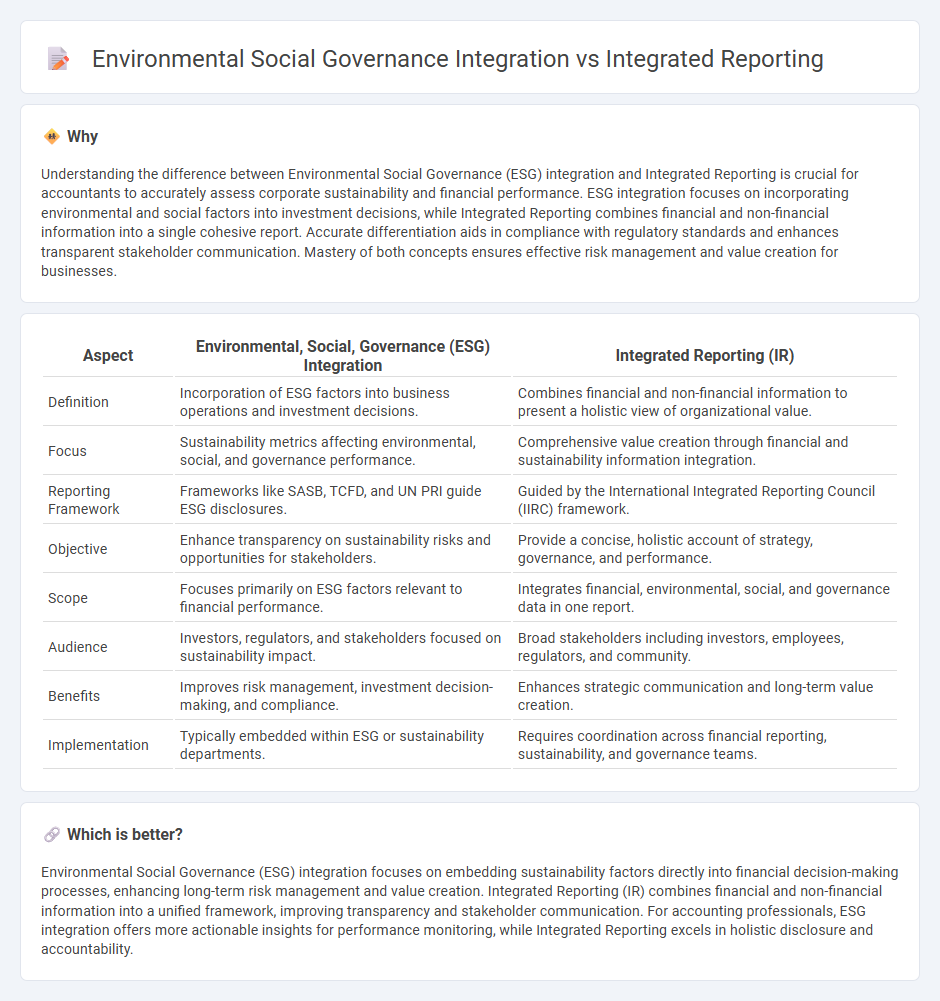
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration and Integrated Reporting is crucial for accountants to accurately assess corporate sustainability and financial performance. ESG integration focuses on incorporating environmental and social factors into investment decisions, while Integrated Reporting combines financial and non-financial information into a single cohesive report. Accurate differentiation aids in compliance with regulatory standards and enhances transparent stakeholder communication. Mastery of both concepts ensures effective risk management and value creation for businesses.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Integration | Integrated Reporting (IR) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporation of ESG factors into business operations and investment decisions. | Combines financial and non-financial information to present a holistic view of organizational value. |
| Focus | Sustainability metrics affecting environmental, social, and governance performance. | Comprehensive value creation through financial and sustainability information integration. |
| Reporting Framework | Frameworks like SASB, TCFD, and UN PRI guide ESG disclosures. | Guided by the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) framework. |
| Objective | Enhance transparency on sustainability risks and opportunities for stakeholders. | Provide a concise, holistic account of strategy, governance, and performance. |
| Scope | Focuses primarily on ESG factors relevant to financial performance. | Integrates financial, environmental, social, and governance data in one report. |
| Audience | Investors, regulators, and stakeholders focused on sustainability impact. | Broad stakeholders including investors, employees, regulators, and community. |
| Benefits | Improves risk management, investment decision-making, and compliance. | Enhances strategic communication and long-term value creation. |
| Implementation | Typically embedded within ESG or sustainability departments. | Requires coordination across financial reporting, sustainability, and governance teams. |
Which is better?
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration focuses on embedding sustainability factors directly into financial decision-making processes, enhancing long-term risk management and value creation. Integrated Reporting (IR) combines financial and non-financial information into a unified framework, improving transparency and stakeholder communication. For accounting professionals, ESG integration offers more actionable insights for performance monitoring, while Integrated Reporting excels in holistic disclosure and accountability.
Connection
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) integration in accounting enhances transparency by incorporating non-financial metrics into financial reports, driving sustainable business practices. Integrated reporting combines financial and ESG disclosures into a unified document, providing a holistic view of organizational performance and value creation. This connection encourages accountability and informed decision-making among stakeholders by aligning financial outcomes with ESG impacts.
Key Terms
Triple Bottom Line
Integrated reporting combines financial, social, and environmental performance into a single comprehensive framework, enhancing transparency and accountability. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration emphasizes incorporating sustainability factors into investment decisions and corporate strategies, aligning with the Triple Bottom Line approach that balances profit, people, and planet. Discover how these approaches drive sustainable business practices and stakeholder value.
Materiality Assessment
Integrated reporting centers on combining financial and non-financial data to provide a comprehensive view of organizational performance, emphasizing materiality assessment to identify critical issues impacting value creation. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration prioritizes embedding sustainable practices into core business strategies, with materiality assessment guiding focus on ESG factors most relevant to stakeholders and long-term risks. Explore how materiality assessment bridges integrated reporting and ESG integration to drive strategic decision-making and transparency.
Non-Financial Disclosure
Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data to provide a holistic view of an organization's performance, emphasizing transparency and value creation over time. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) integration specifically targets non-financial disclosure related to sustainability practices, social responsibility, and ethical governance criteria, often aligning with regulatory frameworks and investor expectations. Explore how these approaches complement each other to enhance corporate transparency and stakeholder engagement in sustainable business practices.
Source and External Links
Integrated reporting - Integrated reporting is a process that produces a concise report explaining how an organization's strategy, governance, and performance create value over time, integrating financial and non-financial information to support decision-making primarily for providers of financial capital.
What is Integrated Reporting? - Integrated reporting communicates a company's financial and non-financial factors, including environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues, to provide a holistic view of how a company creates sustainable value and influences long-term performance and stakeholder trust.
Integrated Reporting Explained - Integrated reporting combines a company's sustainability practices with its financial outcomes and long-term strategy, focusing on integrated thinking that considers multiple resources and capitals to explain value creation over short, medium, and long terms beyond traditional financial reports.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com