Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration in accounting focuses on embedding sustainability criteria into financial reporting and decision-making frameworks, ensuring transparency and accountability in corporate behavior. Green finance specifically channels investments into projects and initiatives that generate environmental benefits, such as renewable energy or pollution reduction, promoting sustainable economic growth. Explore the distinctions and synergies between ESG integration and green finance to enhance sustainable business strategies.
Why it is important
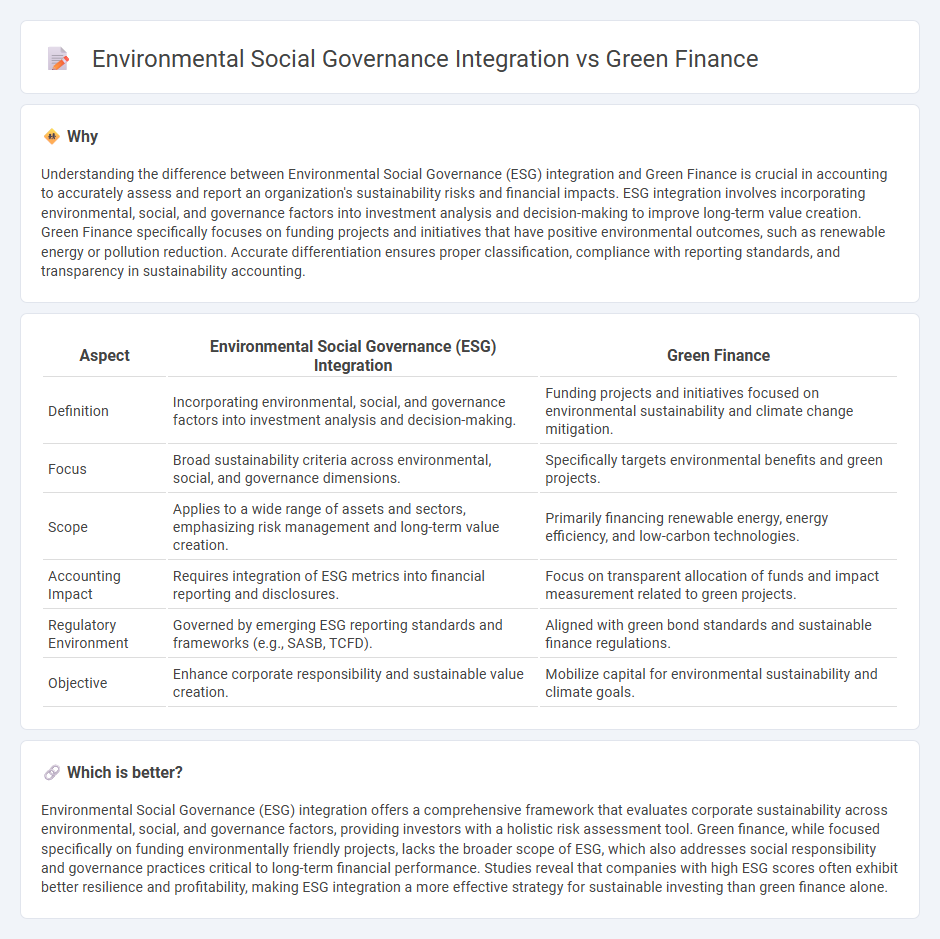
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration and Green Finance is crucial in accounting to accurately assess and report an organization's sustainability risks and financial impacts. ESG integration involves incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into investment analysis and decision-making to improve long-term value creation. Green Finance specifically focuses on funding projects and initiatives that have positive environmental outcomes, such as renewable energy or pollution reduction. Accurate differentiation ensures proper classification, compliance with reporting standards, and transparency in sustainability accounting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Integration | Green Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating environmental, social, and governance factors into investment analysis and decision-making. | Funding projects and initiatives focused on environmental sustainability and climate change mitigation. |
| Focus | Broad sustainability criteria across environmental, social, and governance dimensions. | Specifically targets environmental benefits and green projects. |
| Scope | Applies to a wide range of assets and sectors, emphasizing risk management and long-term value creation. | Primarily financing renewable energy, energy efficiency, and low-carbon technologies. |
| Accounting Impact | Requires integration of ESG metrics into financial reporting and disclosures. | Focus on transparent allocation of funds and impact measurement related to green projects. |
| Regulatory Environment | Governed by emerging ESG reporting standards and frameworks (e.g., SASB, TCFD). | Aligned with green bond standards and sustainable finance regulations. |
| Objective | Enhance corporate responsibility and sustainable value creation. | Mobilize capital for environmental sustainability and climate goals. |
Which is better?
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration offers a comprehensive framework that evaluates corporate sustainability across environmental, social, and governance factors, providing investors with a holistic risk assessment tool. Green finance, while focused specifically on funding environmentally friendly projects, lacks the broader scope of ESG, which also addresses social responsibility and governance practices critical to long-term financial performance. Studies reveal that companies with high ESG scores often exhibit better resilience and profitability, making ESG integration a more effective strategy for sustainable investing than green finance alone.
Connection
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration in accounting involves incorporating sustainability metrics into financial reporting and decision-making processes, which directly supports the principles of Green Finance by promoting investments in environmentally responsible projects. Accurate ESG data enables accountants to assess risks and opportunities related to climate change and social responsibility, enhancing transparency and attracting Green Finance capital that prioritizes low-carbon and sustainable initiatives. This synergy ensures that financial statements reflect the true impact of corporate sustainability efforts, facilitating long-term value creation and compliance with emerging regulatory standards.
Key Terms
Sustainable Investment
Green finance centers on funding projects that deliver measurable environmental benefits, such as renewable energy and pollution reduction initiatives. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration involves embedding environmental, social, and governance criteria into investment analysis and decision-making to mitigate risk and enhance sustainable returns. Explore further to understand how sustainable investment strategies balance both green finance and ESG frameworks for long-term impact.
ESG Reporting
Green finance emphasizes allocating capital to projects with positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy and sustainable infrastructure, while Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration involves embedding ESG factors into overall corporate strategy and investment decisions. ESG reporting provides transparency on a company's performance in environmental responsibility, social impact, and governance practices, enhancing investor confidence and driving sustainable growth. Explore how ESG reporting bridges green finance goals with comprehensive ESG integration for more effective sustainability outcomes.
Green Bonds
Green finance emphasizes funding projects that deliver measurable environmental benefits, with green bonds serving as a primary instrument to channel capital into renewable energy, clean transportation, and sustainable infrastructure. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration incorporates green finance principles within broader corporate strategies, evaluating companies based on environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices to foster sustainable business models. Explore the evolving role of green bonds in bridging green finance and ESG frameworks for sustainable investment opportunities.
Source and External Links
What is green finance and why is it important? - Green finance refers to any structured financial activity designed to ensure better environmental outcomes, including various loans, debt mechanisms, and investments aimed at supporting green projects or reducing climate impacts, with the green bond market expected to reach $2.36 trillion by 2023.
Driving a virtuous cycle of inclusive green finance - Inclusive green finance integrates policies such as green credit guarantee schemes, climate-responsive insurance, and information systems to enhance access and resilience, promoting sustainable financial inclusion alongside climate goals.
Green Finance and Investment - Green finance supports the transition to a low-carbon, climate-resilient economy by mobilizing private and public investment in sustainable technologies and infrastructure, requiring aligned policy frameworks that remove barriers to green growth.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com