Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting focuses on measuring and reporting a company's impact on sustainability, social responsibility, and ethical governance, aligning financial performance with environmental and societal goals. Forensic accounting involves investigating financial records to detect fraud, embezzlement, or legal disputes, providing evidence for litigation and regulatory compliance. Explore the distinctive roles and methodologies of ESG and forensic accounting to understand their importance in modern financial management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting and forensic accounting is crucial because ESG accounting focuses on sustainability metrics, ethical impact, and long-term value creation, whereas forensic accounting involves investigating financial fraud, discrepancies, and legal compliance. ESG accounting helps companies meet regulatory requirements and attract socially responsible investors by reporting on environmental impact and social governance. Forensic accounting safeguards organizations by detecting and preventing financial crimes such as embezzlement and fraud, supporting litigation and dispute resolution. Mastery of both disciplines enables businesses to ensure transparency, accountability, and sustainable growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Environmental, Social, Governance (ESG) Accounting | Forensic Accounting |
|---|---|---|
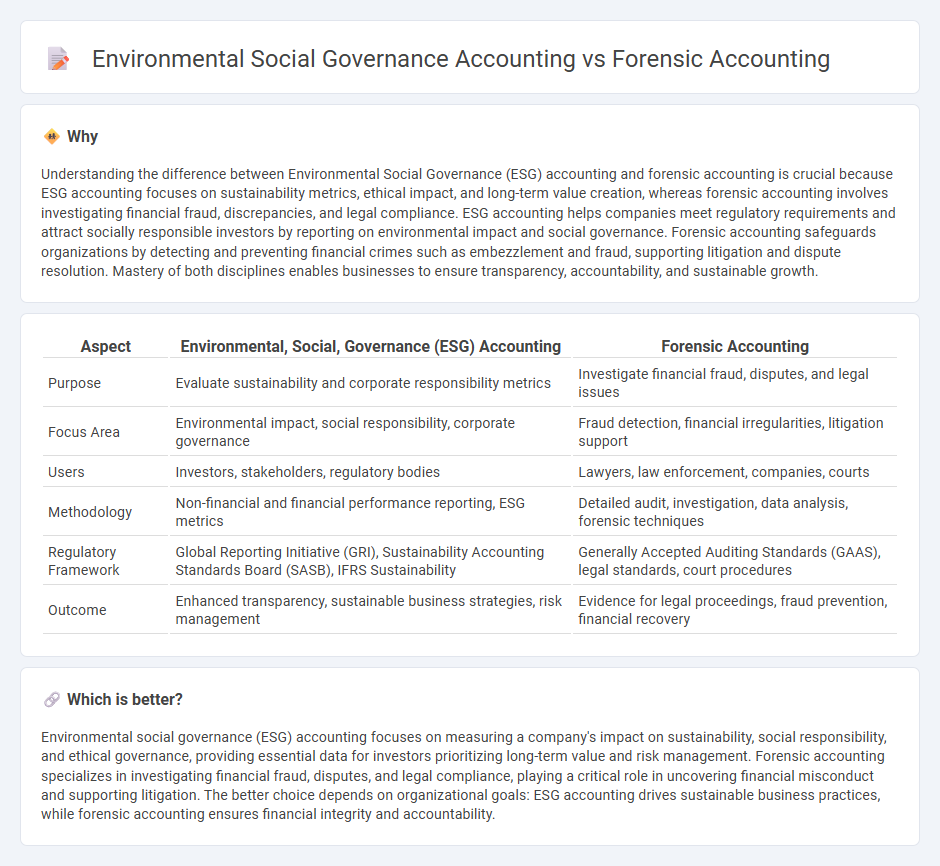
| Purpose | Evaluate sustainability and corporate responsibility metrics | Investigate financial fraud, disputes, and legal issues |
| Focus Area | Environmental impact, social responsibility, corporate governance | Fraud detection, financial irregularities, litigation support |
| Users | Investors, stakeholders, regulatory bodies | Lawyers, law enforcement, companies, courts |
| Methodology | Non-financial and financial performance reporting, ESG metrics | Detailed audit, investigation, data analysis, forensic techniques |
| Regulatory Framework | Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), IFRS Sustainability | Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS), legal standards, court procedures |
| Outcome | Enhanced transparency, sustainable business strategies, risk management | Evidence for legal proceedings, fraud prevention, financial recovery |
Which is better?
Environmental social governance (ESG) accounting focuses on measuring a company's impact on sustainability, social responsibility, and ethical governance, providing essential data for investors prioritizing long-term value and risk management. Forensic accounting specializes in investigating financial fraud, disputes, and legal compliance, playing a critical role in uncovering financial misconduct and supporting litigation. The better choice depends on organizational goals: ESG accounting drives sustainable business practices, while forensic accounting ensures financial integrity and accountability.
Connection
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting integrates sustainability metrics into financial reporting, aiming to measure a company's impact on environmental and social factors. Forensic accounting involves investigating financial discrepancies, fraud, and compliance violations, often uncovering misreported ESG data or sustainability claims. Both fields intersect by enhancing corporate transparency and accountability, ensuring accurate representation of ESG practices within financial statements.
Key Terms
Forensic accounting:
Forensic accounting specializes in investigating financial discrepancies, fraud detection, and legal compliance through detailed audits and analysis of accounting records and transactions. It plays a critical role in legal proceedings, corporate investigations, and insurance claims by providing evidence-based financial insights. Discover how forensic accounting safeguards businesses and supports justice by exploring its methodologies and applications.
Fraud detection
Forensic accounting specializes in identifying, investigating, and preventing financial fraud through detailed examination of financial records, transaction trails, and regulatory compliance. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting integrates sustainability metrics and ethical practices into financial reporting, emphasizing transparency to reduce risks of greenwashing and social misconduct. Explore how combining forensic accounting techniques with ESG principles enhances fraud detection and corporate accountability.
Litigation support
Forensic accounting specializes in investigating financial discrepancies and fraud, providing critical litigation support by uncovering evidence for legal proceedings. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) accounting focuses on evaluating corporate sustainability and ethical impact, playing a growing role in litigation involving regulatory compliance and stakeholder disputes. Explore how these distinct accounting disciplines contribute to litigation support and risk assessment in complex legal environments.
Source and External Links
Forensic Accounting Career Overview - Forensic accountants use accounting and auditing skills to investigate financial crimes such as fraud and embezzlement by analyzing finances, supporting legal cases, and assessing financial risks, requiring strong knowledge of law, auditing standards, and accounting principles.
What Is Forensic Accounting? - MVNU - Forensic accounting involves applying accounting skills to investigate financial crimes, including fraud claims, criminal investigations, and financial dispute resolutions, often providing expert witness testimony and tracing illicit financial activities.
Forensic accounting - Wikipedia - Forensic accounting is a specialty that investigates financial crimes by translating complex financial data for courts, distinguishing itself from internal auditing, and includes methods like public record reviews, interviews, and transaction analysis to uncover fraud.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com