Data lake reconciliation involves comparing and validating large volumes of diverse financial data stored in centralized repositories to ensure accuracy and consistency across multiple systems. Payment reconciliation focuses specifically on matching outgoing payments with corresponding invoices or transaction records to verify correct disbursement and prevent discrepancies. Explore the differences and applications of these reconciliation methods to enhance your accounting processes.
Why it is important
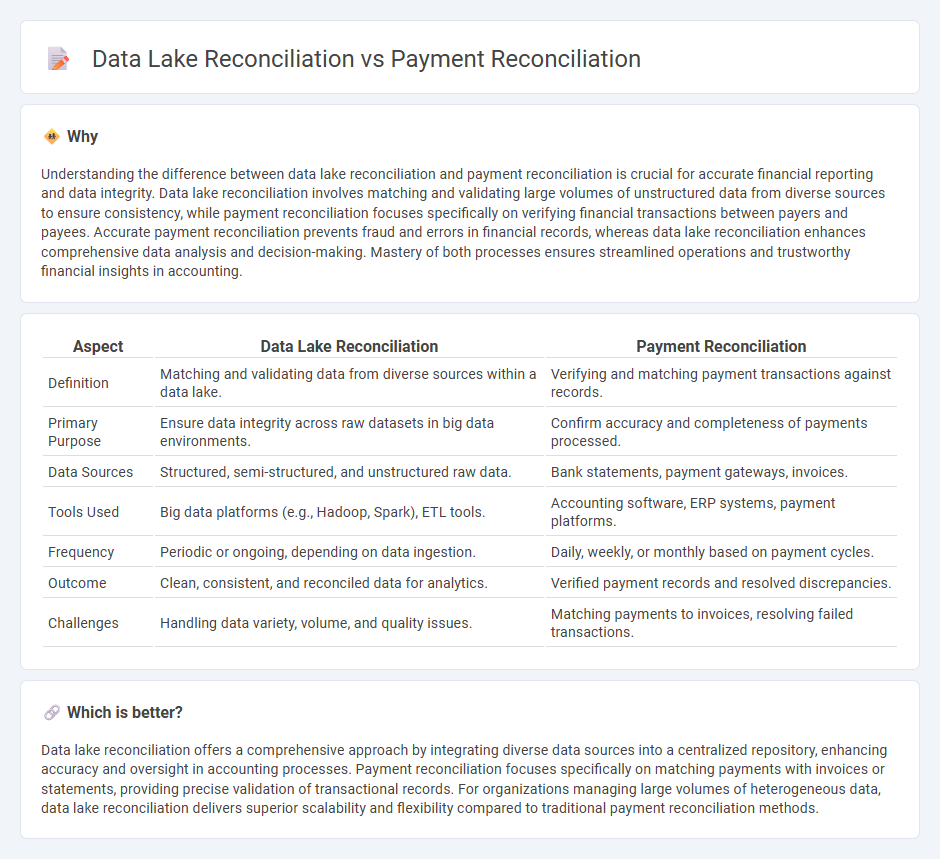
Understanding the difference between data lake reconciliation and payment reconciliation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and data integrity. Data lake reconciliation involves matching and validating large volumes of unstructured data from diverse sources to ensure consistency, while payment reconciliation focuses specifically on verifying financial transactions between payers and payees. Accurate payment reconciliation prevents fraud and errors in financial records, whereas data lake reconciliation enhances comprehensive data analysis and decision-making. Mastery of both processes ensures streamlined operations and trustworthy financial insights in accounting.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Data Lake Reconciliation | Payment Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Matching and validating data from diverse sources within a data lake. | Verifying and matching payment transactions against records. |
| Primary Purpose | Ensure data integrity across raw datasets in big data environments. | Confirm accuracy and completeness of payments processed. |
| Data Sources | Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured raw data. | Bank statements, payment gateways, invoices. |
| Tools Used | Big data platforms (e.g., Hadoop, Spark), ETL tools. | Accounting software, ERP systems, payment platforms. |
| Frequency | Periodic or ongoing, depending on data ingestion. | Daily, weekly, or monthly based on payment cycles. |
| Outcome | Clean, consistent, and reconciled data for analytics. | Verified payment records and resolved discrepancies. |
| Challenges | Handling data variety, volume, and quality issues. | Matching payments to invoices, resolving failed transactions. |
Which is better?
Data lake reconciliation offers a comprehensive approach by integrating diverse data sources into a centralized repository, enhancing accuracy and oversight in accounting processes. Payment reconciliation focuses specifically on matching payments with invoices or statements, providing precise validation of transactional records. For organizations managing large volumes of heterogeneous data, data lake reconciliation delivers superior scalability and flexibility compared to traditional payment reconciliation methods.
Connection
Data lake reconciliation and payment reconciliation intersect by ensuring comprehensive financial data integrity and accuracy across diverse sources. Data lake reconciliation consolidates unstructured and structured payment data from various systems into a unified repository, enabling a granular audit trail. Payment reconciliation leverages this unified dataset to match transactions, identify discrepancies, and validate financial records efficiently, enhancing operational transparency and compliance.
Key Terms
Matching criteria
Payment reconciliation emphasizes matching transactional attributes such as invoice numbers, payment amounts, and dates to ensure financial accuracy. Data lake reconciliation involves aligning and validating large, heterogeneous datasets using schema mapping, key identifiers, and timestamp correlation to maintain data integrity. Explore how advanced matching criteria enhance both reconciliation processes for optimized data and financial management.
Transaction records
Payment reconciliation involves matching transaction records from payments made against accounting entries to ensure accuracy and completeness in financial reporting. Data lake reconciliation focuses on integrating and verifying vast, diverse datasets, including transaction records, within a centralized repository for comprehensive analysis and auditing. Explore our detailed guide to understand the specific methodologies and tools used in each reconciliation process.
Data integrity
Payment reconciliation ensures transactional accuracy by comparing payment records against invoices and bank statements, maintaining financial data integrity through precise matching algorithms. Data lake reconciliation focuses on validating data consistency and completeness across vast, diverse datasets stored in centralized repositories to uphold data integrity within analytics-driven environments. Explore how optimizing both processes enhances organizational trust in financial and operational data.
Source and External Links
What is Payment Reconciliation & How Does it Work? - BillingPlatform - Payment reconciliation is the process of verifying that all payments are accounted for by comparing internal financial records with external statements, matching transactions, resolving discrepancies, and updating accounts to ensure accuracy.
Payment reconciliation: What it is and how it's done - Stripe - Payment reconciliation involves gathering financial data, matching transaction records, identifying and resolving discrepancies, recording adjustments, and verifying that accounting balances align with actual bank statements to maintain accurate financial records.
What is Payment Reconciliation? - DealHub - Payment reconciliation is an accounting process where businesses collect, match, and verify payment records against bank and internal statements, ensuring all transactions are correctly recorded and any inconsistencies are investigated and resolved.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com