Sustainability assurance evaluates the accuracy and reliability of an organization's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, ensuring compliance with global standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). Internal audit focuses on assessing internal controls, risk management, and governance processes to enhance operational efficiency and safeguard assets. Discover how these distinct yet complementary functions bolster corporate accountability and transparency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between sustainability assurance and internal audit is crucial for accurately evaluating corporate responsibility and operational efficiency. Sustainability assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures to ensure transparency and compliance with global standards like GRI or SASB. Internal audit assesses an organization's internal controls, risk management, and governance processes to improve operational effectiveness. Knowledge of both enables stakeholders to make informed decisions about ethical practices and financial integrity.
Comparison Table
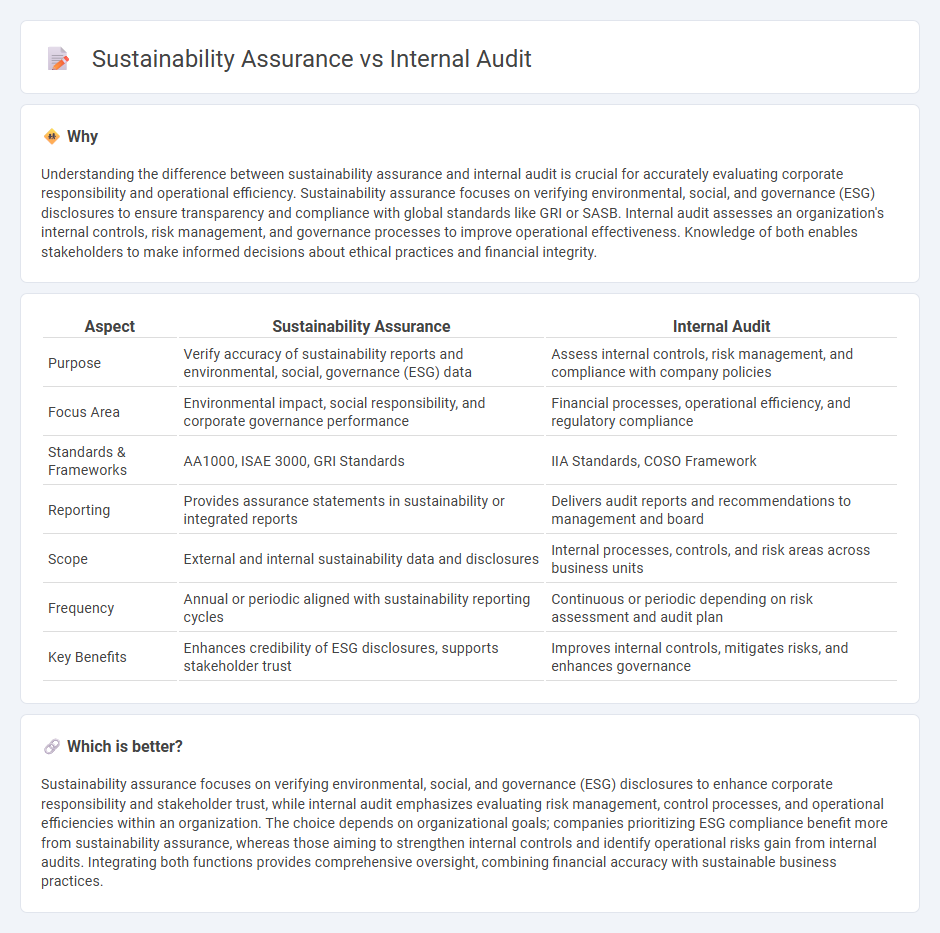
| Aspect | Sustainability Assurance | Internal Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify accuracy of sustainability reports and environmental, social, governance (ESG) data | Assess internal controls, risk management, and compliance with company policies |
| Focus Area | Environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance performance | Financial processes, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance |
| Standards & Frameworks | AA1000, ISAE 3000, GRI Standards | IIA Standards, COSO Framework |
| Reporting | Provides assurance statements in sustainability or integrated reports | Delivers audit reports and recommendations to management and board |
| Scope | External and internal sustainability data and disclosures | Internal processes, controls, and risk areas across business units |
| Frequency | Annual or periodic aligned with sustainability reporting cycles | Continuous or periodic depending on risk assessment and audit plan |
| Key Benefits | Enhances credibility of ESG disclosures, supports stakeholder trust | Improves internal controls, mitigates risks, and enhances governance |
Which is better?
Sustainability assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures to enhance corporate responsibility and stakeholder trust, while internal audit emphasizes evaluating risk management, control processes, and operational efficiencies within an organization. The choice depends on organizational goals; companies prioritizing ESG compliance benefit more from sustainability assurance, whereas those aiming to strengthen internal controls and identify operational risks gain from internal audits. Integrating both functions provides comprehensive oversight, combining financial accuracy with sustainable business practices.
Connection
Sustainability assurance and internal audit are interconnected through their shared focus on risk management, compliance, and enhancing organizational transparency. Internal audit functions incorporate sustainability assurance by evaluating the accuracy and reliability of non-financial reporting, ensuring adherence to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. This integration provides stakeholders with confidence in the integrity of sustainability disclosures, aligning corporate sustainability goals with overall governance frameworks.
Key Terms
**Internal Audit:**
Internal audit systematically evaluates a company's internal controls, risk management, and governance processes to ensure accuracy, compliance, and operational efficiency. It primarily focuses on financial reporting, regulatory adherence, and internal policies, providing stakeholders with confidence in the organization's integrity. Discover how internal audit strengthens organizational resilience and supports strategic decision-making.
Risk Assessment
Internal audit primarily focuses on evaluating financial, operational, and compliance risks within an organization's existing frameworks to ensure accuracy and effectiveness. Sustainability assurance centers on assessing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks, verifying that sustainability claims and disclosures meet regulatory and stakeholder expectations. Explore the distinct methodologies and outcomes of both to enhance your risk management strategy.
Internal Controls
Internal audit primarily concentrates on evaluating the effectiveness and reliability of internal controls, risk management, and governance processes within an organization. Sustainability assurance, however, focuses on verifying the accuracy and completeness of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) disclosures, ensuring that sustainability claims align with established reporting standards. Explore further to understand how internal controls impact both internal audit and sustainability assurance practices.
Source and External Links
What is Internal Audit? Types, Value, Process & Standards - Internal audit is an independent, unbiased review within a company to assess systems, compliance, financial reporting, IT controls, operations, and performance to ensure efficiency, accuracy, and regulatory adherence.
Internal audit - Wikipedia - Internal auditing is an independent assurance and consulting function aimed to add value by evaluating risk management, control, and governance processes through a defined annual audit plan and risk-based procedures.
Internal Audit 101: Everything You Need to Know - AuditBoard - Internal auditing provides independent assurance over operations by objectively assessing the effectiveness of internal controls, risk management, and operational compliance to improve efficiency, uncover risks, and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com