Forensic data analytics focuses on detecting and investigating financial fraud by analyzing data patterns and anomalies, while external audit involves examining financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Forensic analytics uses specialized techniques like data mining and predictive modeling, contrasting with the broader financial verification role of external audits. Explore the distinct methodologies and objectives to understand how both contribute to financial integrity.
Why it is important
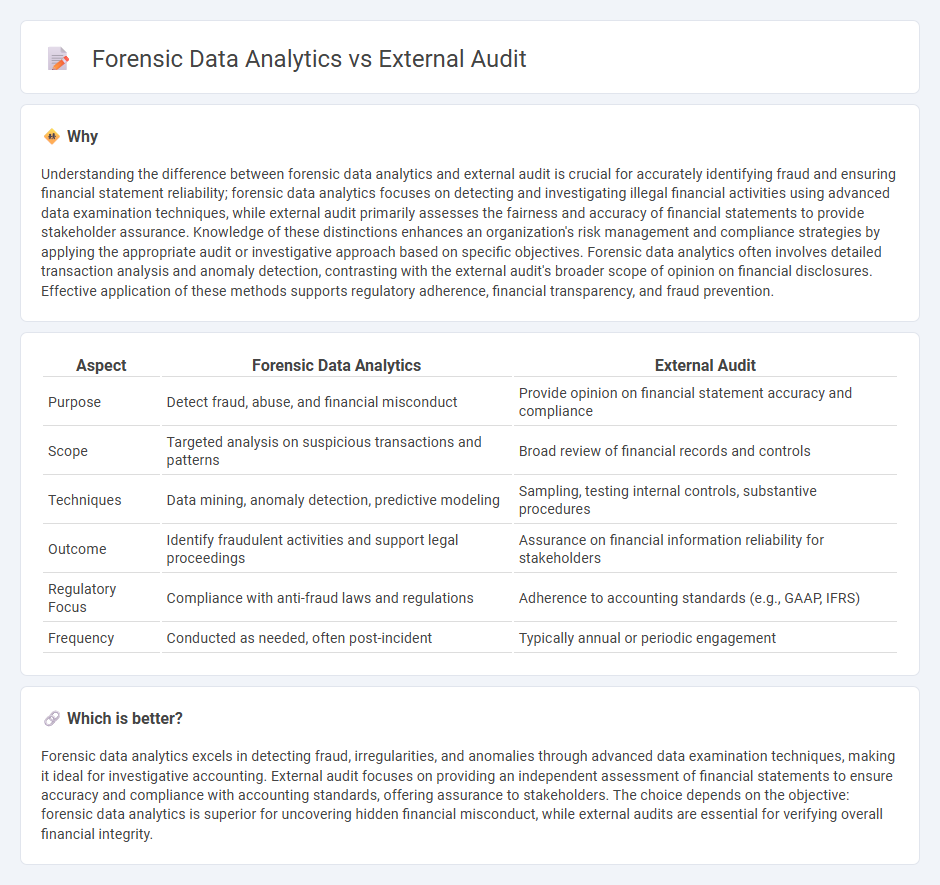
Understanding the difference between forensic data analytics and external audit is crucial for accurately identifying fraud and ensuring financial statement reliability; forensic data analytics focuses on detecting and investigating illegal financial activities using advanced data examination techniques, while external audit primarily assesses the fairness and accuracy of financial statements to provide stakeholder assurance. Knowledge of these distinctions enhances an organization's risk management and compliance strategies by applying the appropriate audit or investigative approach based on specific objectives. Forensic data analytics often involves detailed transaction analysis and anomaly detection, contrasting with the external audit's broader scope of opinion on financial disclosures. Effective application of these methods supports regulatory adherence, financial transparency, and fraud prevention.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Forensic Data Analytics | External Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, abuse, and financial misconduct | Provide opinion on financial statement accuracy and compliance |
| Scope | Targeted analysis on suspicious transactions and patterns | Broad review of financial records and controls |
| Techniques | Data mining, anomaly detection, predictive modeling | Sampling, testing internal controls, substantive procedures |
| Outcome | Identify fraudulent activities and support legal proceedings | Assurance on financial information reliability for stakeholders |
| Regulatory Focus | Compliance with anti-fraud laws and regulations | Adherence to accounting standards (e.g., GAAP, IFRS) |
| Frequency | Conducted as needed, often post-incident | Typically annual or periodic engagement |
Which is better?
Forensic data analytics excels in detecting fraud, irregularities, and anomalies through advanced data examination techniques, making it ideal for investigative accounting. External audit focuses on providing an independent assessment of financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards, offering assurance to stakeholders. The choice depends on the objective: forensic data analytics is superior for uncovering hidden financial misconduct, while external audits are essential for verifying overall financial integrity.
Connection
Forensic data analytics plays a critical role in external audits by enhancing fraud detection and risk assessment through detailed examination of financial transactions and patterns. External auditors leverage forensic data analytics techniques to identify anomalies, ensure compliance with accounting standards, and verify the accuracy of financial statements. Integration of these advanced analytical tools improves the reliability and effectiveness of the audit process, reducing the risk of undetected irregularities.
Key Terms
Assurance
External audit ensures financial statement accuracy through independent examination, focusing on compliance and risk assessment to provide stakeholder assurance. Forensic data analytics targets fraud detection and investigation by analyzing irregularities and anomalies within financial data for legal and regulatory purposes. Discover more about how these methodologies complement assurance objectives in complex financial environments.
Fraud detection
External audits primarily assess financial statements for accuracy and compliance, while forensic data analytics delve deeper into transaction-level data to uncover patterns indicative of fraud. Forensic analytics utilize advanced techniques like anomaly detection, predictive modeling, and data mining to identify suspicious activities often missed in traditional audits. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances fraud detection effectiveness and strengthens organizational controls.
Data integrity
External audit emphasizes verifying data accuracy through systematic review of financial records, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. Forensic data analytics delves deeper, employing advanced techniques to detect fraud, data manipulation, and breaches in data integrity, often uncovering hidden patterns and anomalies in large datasets. Explore how these approaches combine to enhance data reliability and trustworthiness in financial reporting.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Purpose and Benefits of External Audits - Concur - An external audit is an independent process that assesses a company's financial statements and internal controls, providing confidence to management and stakeholders on the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting, and offering recommendations for improvements.
External Audit vs. Internal Audit: What's the Difference? - Hilbert College - External auditors, typically certified public accountants (CPAs), conduct independent reviews to verify the accuracy and integrity of financial statements, ensuring compliance and offering assurance to shareholders and regulatory bodies.
External auditor - Wikipedia - External auditors are independent professionals who audit financial statements in accordance with laws or rules, providing unbiased reports to users such as investors and regulatory agencies, often with mandated requirements differing by jurisdiction.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com