Digital asset reporting involves the systematic documentation and disclosure of cryptocurrency transactions and holdings for compliance with financial regulations. Blockchain auditing entails verifying and validating blockchain records to ensure transaction integrity, accuracy, and transparency within decentralized ledgers. Explore the evolving methodologies and tools bridging digital asset reporting and blockchain auditing for comprehensive financial oversight.
Why it is important
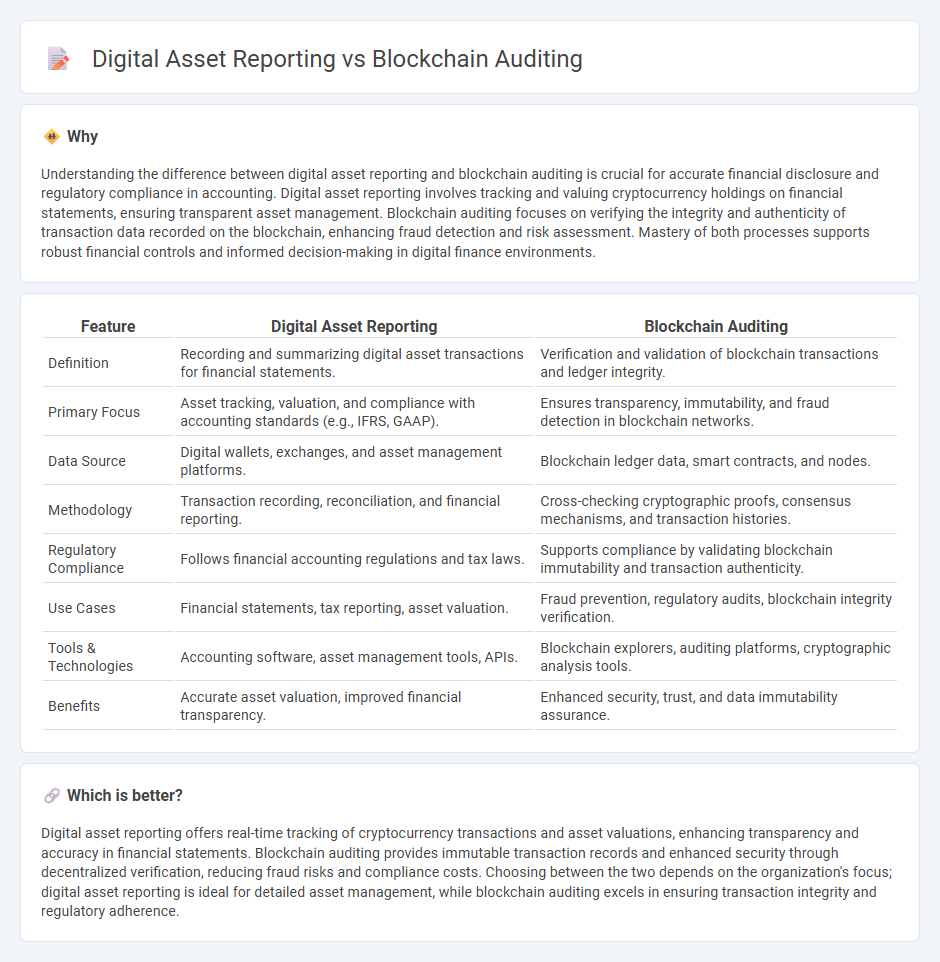
Understanding the difference between digital asset reporting and blockchain auditing is crucial for accurate financial disclosure and regulatory compliance in accounting. Digital asset reporting involves tracking and valuing cryptocurrency holdings on financial statements, ensuring transparent asset management. Blockchain auditing focuses on verifying the integrity and authenticity of transaction data recorded on the blockchain, enhancing fraud detection and risk assessment. Mastery of both processes supports robust financial controls and informed decision-making in digital finance environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Asset Reporting | Blockchain Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recording and summarizing digital asset transactions for financial statements. | Verification and validation of blockchain transactions and ledger integrity. |
| Primary Focus | Asset tracking, valuation, and compliance with accounting standards (e.g., IFRS, GAAP). | Ensures transparency, immutability, and fraud detection in blockchain networks. |
| Data Source | Digital wallets, exchanges, and asset management platforms. | Blockchain ledger data, smart contracts, and nodes. |
| Methodology | Transaction recording, reconciliation, and financial reporting. | Cross-checking cryptographic proofs, consensus mechanisms, and transaction histories. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Follows financial accounting regulations and tax laws. | Supports compliance by validating blockchain immutability and transaction authenticity. |
| Use Cases | Financial statements, tax reporting, asset valuation. | Fraud prevention, regulatory audits, blockchain integrity verification. |
| Tools & Technologies | Accounting software, asset management tools, APIs. | Blockchain explorers, auditing platforms, cryptographic analysis tools. |
| Benefits | Accurate asset valuation, improved financial transparency. | Enhanced security, trust, and data immutability assurance. |
Which is better?
Digital asset reporting offers real-time tracking of cryptocurrency transactions and asset valuations, enhancing transparency and accuracy in financial statements. Blockchain auditing provides immutable transaction records and enhanced security through decentralized verification, reducing fraud risks and compliance costs. Choosing between the two depends on the organization's focus; digital asset reporting is ideal for detailed asset management, while blockchain auditing excels in ensuring transaction integrity and regulatory adherence.
Connection
Digital asset reporting relies on blockchain auditing to ensure transparency, accuracy, and immutability of financial records related to cryptocurrencies and tokenized assets. Blockchain auditing uses decentralized ledger technology to verify transactions, providing a secure and verifiable trail that enhances the reliability of digital asset reports. This integration helps accountants and auditors efficiently track ownership, valuation, and compliance within digital ecosystems.
Key Terms
**Blockchain Auditing:**
Blockchain auditing involves verifying the integrity and security of blockchain transactions by examining cryptographic records and consensus mechanisms to ensure transparency and compliance with regulatory standards. This process helps identify fraud, errors, and vulnerabilities within decentralized networks, enhancing trust among stakeholders and supporting accurate financial reporting. Explore more to understand how blockchain auditing strengthens digital trust and regulatory adherence in blockchain ecosystems.
Immutable Ledger
Blockchain auditing leverages the immutable ledger to verify transaction accuracy and ensure compliance by tracing asset flows without alteration. Digital asset reporting utilizes the same ledger to generate transparent, real-time financial statements reflecting the current state of digital holdings. Explore how integrating immutable ledger technology transforms transparency and trust in financial ecosystems.
Smart Contracts
Blockchain auditing involves systematically verifying the integrity and security of smart contracts by analyzing their code and transaction history to detect vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with established protocols. Digital asset reporting centers on generating transparent, accurate reports of smart contract interactions and asset movements to satisfy regulatory requirements and enhance stakeholder trust. Explore how these processes complement each other to optimize the management and security of blockchain-based smart contracts.
Source and External Links
What is a Blockchain Audit and How Does It Work? - CertiK - Blockchain auditing evaluates a blockchain's security, functionality, and compliance by reviewing technical specs, code, data accuracy, and security measures, involving planning, review, testing, reporting, and follow-up stages to ensure system integrity and mitigate risks.
Top 15 Blockchain Audit Companies: Your Guide for 2025 - Webisoft - Blockchain auditing is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities in smart contracts and protocols, ensuring compliance, reducing risk, and fostering investor confidence and trust in blockchain-based systems and applications.
Auditing in the blockchain: a literature review - Frontiers - Blockchain auditing improves audit efficacy through automated authentication and anomaly detection but faces challenges like technical vulnerabilities, regulatory gaps, and skill shortages, emphasizing the need for harmonized regulations and interdisciplinary training to advance cryptographic trust systems.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com