Decentralized ledger accounting employs blockchain technology to create transparent, immutable records distributed across multiple nodes, minimizing the risk of data tampering. Double-entry bookkeeping is a traditional method where each financial transaction affects at least two accounts, maintaining a balanced ledger that ensures accuracy and error detection. Explore the detailed differences and benefits of each system to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
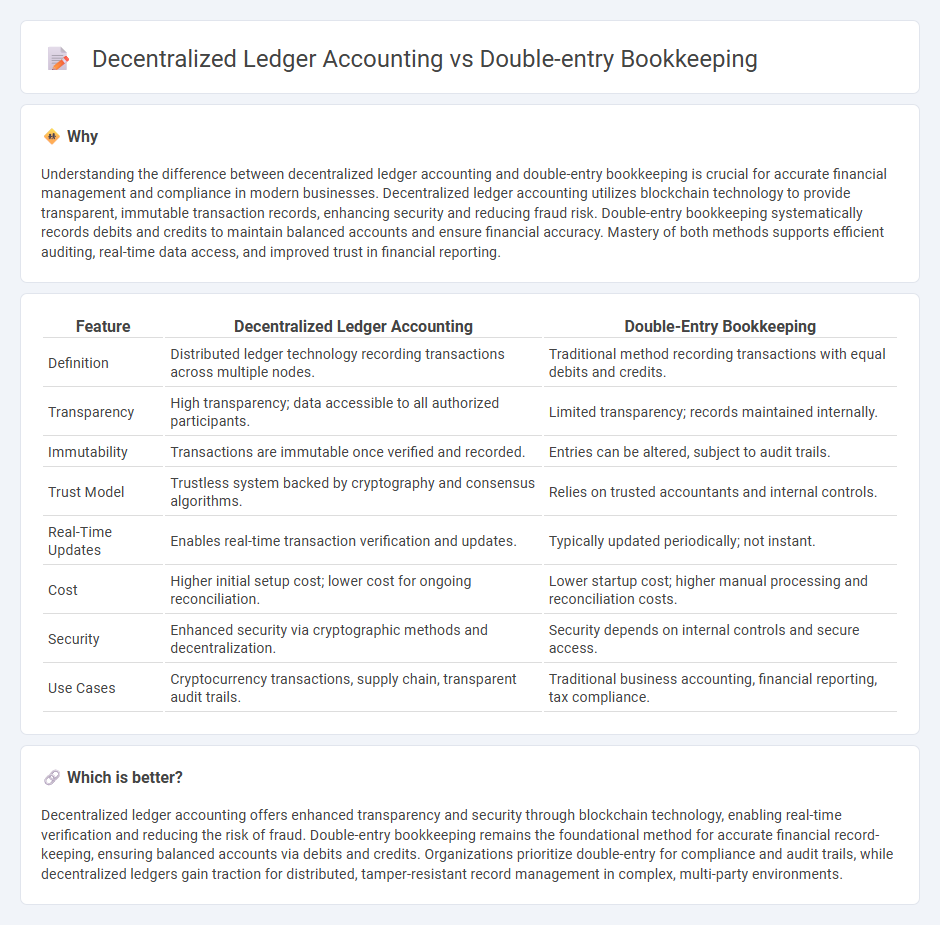
Understanding the difference between decentralized ledger accounting and double-entry bookkeeping is crucial for accurate financial management and compliance in modern businesses. Decentralized ledger accounting utilizes blockchain technology to provide transparent, immutable transaction records, enhancing security and reducing fraud risk. Double-entry bookkeeping systematically records debits and credits to maintain balanced accounts and ensure financial accuracy. Mastery of both methods supports efficient auditing, real-time data access, and improved trust in financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Ledger Accounting | Double-Entry Bookkeeping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed ledger technology recording transactions across multiple nodes. | Traditional method recording transactions with equal debits and credits. |
| Transparency | High transparency; data accessible to all authorized participants. | Limited transparency; records maintained internally. |
| Immutability | Transactions are immutable once verified and recorded. | Entries can be altered, subject to audit trails. |
| Trust Model | Trustless system backed by cryptography and consensus algorithms. | Relies on trusted accountants and internal controls. |
| Real-Time Updates | Enables real-time transaction verification and updates. | Typically updated periodically; not instant. |
| Cost | Higher initial setup cost; lower cost for ongoing reconciliation. | Lower startup cost; higher manual processing and reconciliation costs. |
| Security | Enhanced security via cryptographic methods and decentralization. | Security depends on internal controls and secure access. |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrency transactions, supply chain, transparent audit trails. | Traditional business accounting, financial reporting, tax compliance. |
Which is better?
Decentralized ledger accounting offers enhanced transparency and security through blockchain technology, enabling real-time verification and reducing the risk of fraud. Double-entry bookkeeping remains the foundational method for accurate financial record-keeping, ensuring balanced accounts via debits and credits. Organizations prioritize double-entry for compliance and audit trails, while decentralized ledgers gain traction for distributed, tamper-resistant record management in complex, multi-party environments.
Connection
Decentralized ledger accounting enhances transparency and security by recording transactions across multiple nodes, while double-entry bookkeeping ensures each transaction affects two accounts, maintaining balanced financial records. The integration of double-entry principles into decentralized ledgers allows real-time verification of debits and credits, reducing errors and fraud. This connection streamlines audit processes and improves trustworthiness in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Debits and Credits
Double-entry bookkeeping records financial transactions in two accounts, ensuring that debits equal credits to maintain balanced ledgers and accurate financial statements. Decentralized ledger accounting uses blockchain technology to record transactions across multiple nodes, providing transparency, immutability, and real-time verification without the need for traditional debit and credit entries. Explore the advantages and applications of these accounting methods to optimize your financial management strategy.
Distributed Ledger
Double-entry bookkeeping records financial transactions through debits and credits, ensuring accuracy in centralized accounting systems. Distributed ledger technology enables decentralized accounting by storing transaction data across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and security without relying on a central authority. Discover how integrating distributed ledger technology can revolutionize traditional financial record-keeping.
Journal Entries
Double-entry bookkeeping systematically records financial transactions in two accounts, ensuring credits equal debits for balanced accounts and error detection. Decentralized ledger accounting distributes journal entries across multiple nodes using blockchain technology, enhancing transparency, security, and immutability of financial data. Explore the benefits and challenges of both methods to optimize accounting accuracy and integrity.
Source and External Links
What is Double-Entry Bookkeeping? - Double-entry bookkeeping records every transaction twice, in debits and credits, so the books balance by reflecting how assets, liabilities, and equity change with each transaction.
Double-Entry Accounting: What It Is and Why It Matters - This method requires two entries per transaction, a debit and a credit, which keeps the ledger balanced and offers a comprehensive view of financial activity including assets, liabilities, and equity.
What Is Double-Entry Bookkeeping? A Simple Guide for ... - Double-entry bookkeeping ensures total debits equal total credits and maintains the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity, with transactions recorded in at least two accounts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com