Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double entry systems by incorporating a third entry recorded on a decentralized ledger, ensuring transaction transparency and immutability. This method leverages blockchain technology to provide a secure, tamper-proof record that promotes trust among parties. Explore how integrating triple entry bookkeeping with decentralized ledgers revolutionizes accounting accuracy and accountability.
Why it is important
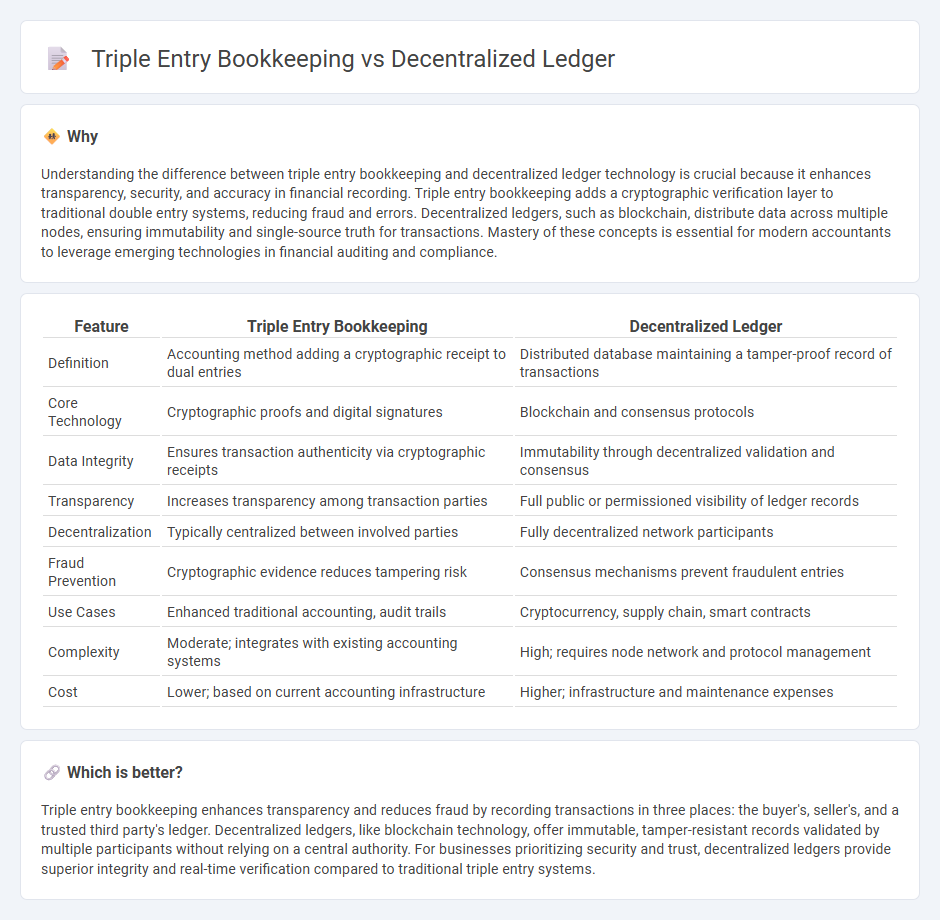
Understanding the difference between triple entry bookkeeping and decentralized ledger technology is crucial because it enhances transparency, security, and accuracy in financial recording. Triple entry bookkeeping adds a cryptographic verification layer to traditional double entry systems, reducing fraud and errors. Decentralized ledgers, such as blockchain, distribute data across multiple nodes, ensuring immutability and single-source truth for transactions. Mastery of these concepts is essential for modern accountants to leverage emerging technologies in financial auditing and compliance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Triple Entry Bookkeeping | Decentralized Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting method adding a cryptographic receipt to dual entries | Distributed database maintaining a tamper-proof record of transactions |
| Core Technology | Cryptographic proofs and digital signatures | Blockchain and consensus protocols |
| Data Integrity | Ensures transaction authenticity via cryptographic receipts | Immutability through decentralized validation and consensus |
| Transparency | Increases transparency among transaction parties | Full public or permissioned visibility of ledger records |
| Decentralization | Typically centralized between involved parties | Fully decentralized network participants |
| Fraud Prevention | Cryptographic evidence reduces tampering risk | Consensus mechanisms prevent fraudulent entries |
| Use Cases | Enhanced traditional accounting, audit trails | Cryptocurrency, supply chain, smart contracts |
| Complexity | Moderate; integrates with existing accounting systems | High; requires node network and protocol management |
| Cost | Lower; based on current accounting infrastructure | Higher; infrastructure and maintenance expenses |
Which is better?
Triple entry bookkeeping enhances transparency and reduces fraud by recording transactions in three places: the buyer's, seller's, and a trusted third party's ledger. Decentralized ledgers, like blockchain technology, offer immutable, tamper-resistant records validated by multiple participants without relying on a central authority. For businesses prioritizing security and trust, decentralized ledgers provide superior integrity and real-time verification compared to traditional triple entry systems.
Connection
Triple entry bookkeeping integrates with decentralized ledger technology by creating immutable, cryptographically secured transaction records visible to all network participants. This system enhances transparency and trust in accounting by providing a real-time, tamper-resistant ledger shared across multiple parties. Blockchain platforms, which embody decentralized ledgers, enable this innovative approach, revolutionizing traditional double-entry bookkeeping practices.
Key Terms
Transparency
Decentralized ledger technology enhances transparency by providing an immutable, publicly accessible record of transactions that all participants can verify in real-time. Triple entry bookkeeping integrates cryptographic receipts into traditional double-entry accounting, ensuring that each transaction is independently verifiable and tamper-proof. Explore how these innovations redefine transparency in financial systems and improve trustworthiness.
Immutability
Decentralized ledgers ensure data immutability by distributing transaction records across multiple nodes, making unauthorized changes virtually impossible. Triple entry bookkeeping enhances immutability through cryptographic verification, linking entries in a tamper-evident manner that introduces an additional layer of trust beyond traditional double-entry systems. Explore how combining decentralized ledger technology with triple entry bookkeeping can revolutionize financial transparency and security.
Verification
Decentralized ledgers utilize cryptographic verification and consensus mechanisms to ensure transaction authenticity and data integrity across a distributed network, eliminating the need for a central authority. Triple-entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double-entry accounting by embedding cryptographically sealed third entries, allowing real-time verification and immutable audit trails between parties. Explore the distinct verification advantages of these systems to understand their impact on finance and auditing.
Source and External Links
Decentralized Ledger - River - A decentralized ledger is a network-wide record of all transactions maintained by many independent nodes, enabling anyone to read, write, and verify transactions without a central authority, ensuring security and trust through protocols like blockchain and proof-of-work.
Distributed ledger - Wikipedia - A distributed ledger is a shared, replicated digital database spread across multiple geographic sites that operates without a central administrator, relying on peer-to-peer networks and consensus algorithms to securely update and synchronize data among many nodes.
Blockchain: Decentralized Ledgers Enabling Peer to Peer Payments - SGR Law - Blockchain technology uses decentralized ledgers to enable trustless, peer-to-peer transactions by recording digital blocks of information linked in a secure chain, eliminating intermediaries and allowing tracking of nearly any asset or value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com