ESG assurance evaluates a company's environmental, social, and governance practices to ensure accurate, transparent reporting aligned with stakeholder expectations. Environmental audits specifically assess compliance with environmental laws, regulations, and internal policies focused on ecological impacts. Explore the distinctions and benefits of each approach to enhance your organization's sustainability strategy.
Why it is important
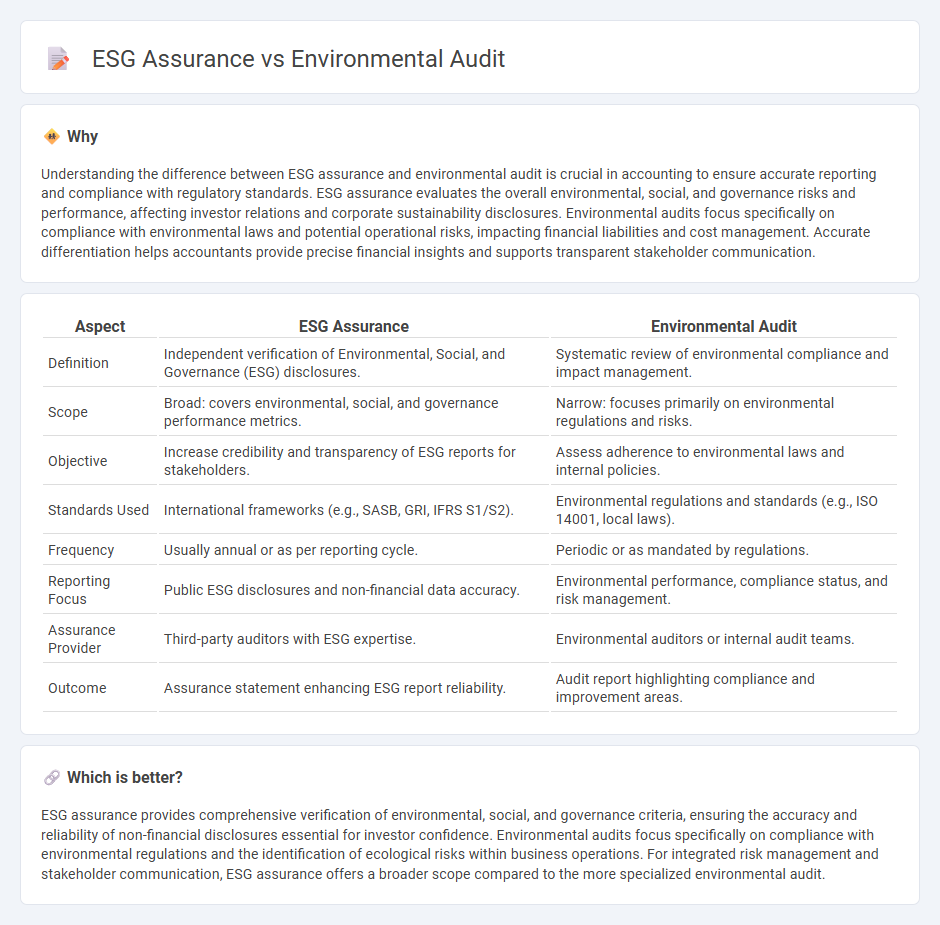
Understanding the difference between ESG assurance and environmental audit is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with regulatory standards. ESG assurance evaluates the overall environmental, social, and governance risks and performance, affecting investor relations and corporate sustainability disclosures. Environmental audits focus specifically on compliance with environmental laws and potential operational risks, impacting financial liabilities and cost management. Accurate differentiation helps accountants provide precise financial insights and supports transparent stakeholder communication.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Assurance | Environmental Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Independent verification of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) disclosures. | Systematic review of environmental compliance and impact management. |
| Scope | Broad: covers environmental, social, and governance performance metrics. | Narrow: focuses primarily on environmental regulations and risks. |
| Objective | Increase credibility and transparency of ESG reports for stakeholders. | Assess adherence to environmental laws and internal policies. |
| Standards Used | International frameworks (e.g., SASB, GRI, IFRS S1/S2). | Environmental regulations and standards (e.g., ISO 14001, local laws). |
| Frequency | Usually annual or as per reporting cycle. | Periodic or as mandated by regulations. |
| Reporting Focus | Public ESG disclosures and non-financial data accuracy. | Environmental performance, compliance status, and risk management. |
| Assurance Provider | Third-party auditors with ESG expertise. | Environmental auditors or internal audit teams. |
| Outcome | Assurance statement enhancing ESG report reliability. | Audit report highlighting compliance and improvement areas. |
Which is better?
ESG assurance provides comprehensive verification of environmental, social, and governance criteria, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of non-financial disclosures essential for investor confidence. Environmental audits focus specifically on compliance with environmental regulations and the identification of ecological risks within business operations. For integrated risk management and stakeholder communication, ESG assurance offers a broader scope compared to the more specialized environmental audit.
Connection
ESG assurance evaluates the accuracy and reliability of environmental, social, and governance disclosures, while environmental audits focus specifically on assessing an organization's compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability practices. Both processes provide critical insights into environmental performance, helping stakeholders verify data integrity and identify risks. Together, ESG assurance and environmental audits enhance transparency and accountability in corporate sustainability reporting.
Key Terms
Compliance
Environmental audits systematically evaluate a company's adherence to legal environmental regulations, ensuring compliance with national and international standards such as ISO 14001 and EPA guidelines. ESG assurance encompasses a broader scope by validating the reliability and accuracy of a company's Environmental, Social, and Governance disclosures in sustainability reports, often aligned with frameworks like GRI, SASB, and TCFD. Explore how integrating environmental audits with ESG assurance enhances regulatory compliance and stakeholder trust.
Materiality
Environmental audits primarily assess compliance with environmental regulations and identify potential risks related to a company's environmental impact, focusing on tangible data and operational processes. ESG assurance emphasizes materiality by evaluating how environmental, social, and governance factors influence a company's long-term value and stakeholder interests, often prioritizing broader sustainability goals beyond regulatory requirements. Explore in-depth insights on how materiality shapes environmental audits and ESG assurance to enhance corporate accountability and strategic decision-making.
Reporting standards
Environmental audits primarily assess compliance with regulatory requirements and the accuracy of environmental data within established reporting frameworks such as ISO 14001 or the EPA standards. ESG assurance extends beyond environmental factors to evaluate Environmental, Social, and Governance disclosures, aligning with comprehensive frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). Explore how integrating these reporting standards enhances transparency and stakeholder trust in sustainability performance.
Source and External Links
How to Prepare for and Conduct Environmental Audits - This article discusses the types of environmental audits, including compliance, management, and functional audits, and their role in ensuring environmental compliance and management.
Environmental Audit and its Importance - This resource explains the importance of environmental audits in ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and identifying areas for improvement in environmental management.
Environmental audit - This Wikipedia page provides an overview of environmental audits, focusing on compliance and management systems audits, which are crucial for identifying gaps in environmental compliance and management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com