Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, requiring specialized tracking of transaction flows and third-party payment processing fees. Neobank accounting focuses on digital-only banking operations, emphasizing real-time balance management, regulatory compliance, and efficient handling of virtual accounts. Explore the key differences and accounting practices that define these innovative financial models.
Why it is important
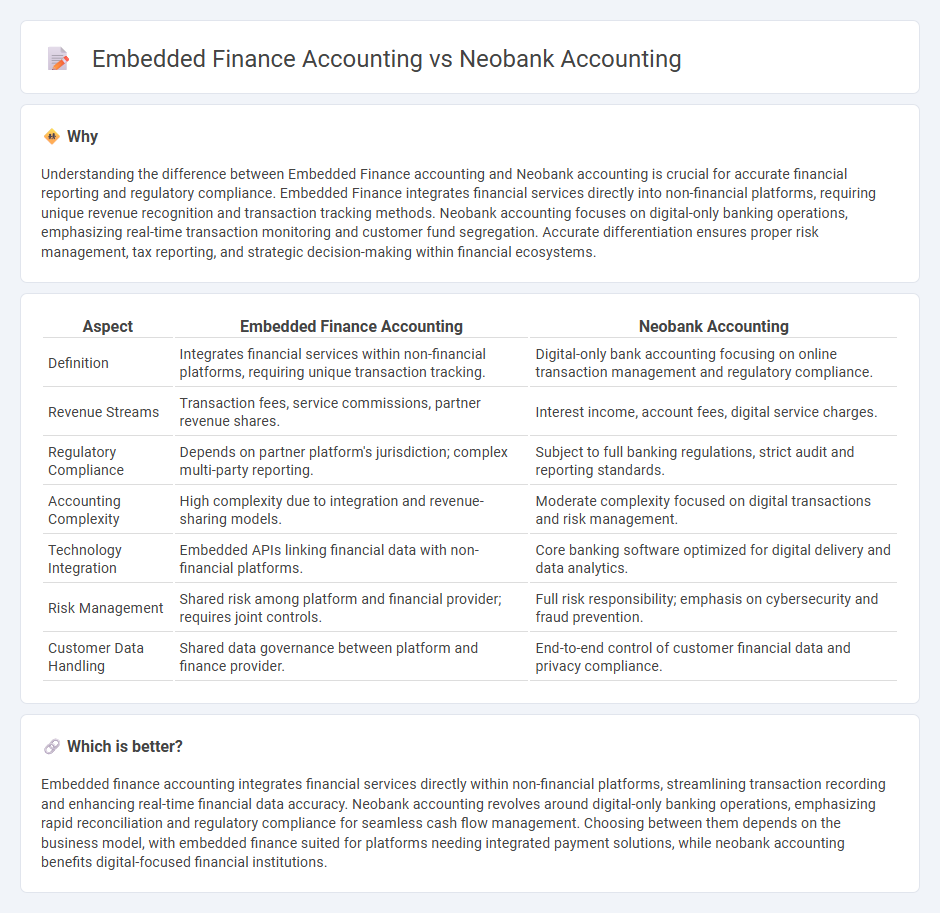
Understanding the difference between Embedded Finance accounting and Neobank accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and regulatory compliance. Embedded Finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, requiring unique revenue recognition and transaction tracking methods. Neobank accounting focuses on digital-only banking operations, emphasizing real-time transaction monitoring and customer fund segregation. Accurate differentiation ensures proper risk management, tax reporting, and strategic decision-making within financial ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Embedded Finance Accounting | Neobank Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates financial services within non-financial platforms, requiring unique transaction tracking. | Digital-only bank accounting focusing on online transaction management and regulatory compliance. |
| Revenue Streams | Transaction fees, service commissions, partner revenue shares. | Interest income, account fees, digital service charges. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Depends on partner platform's jurisdiction; complex multi-party reporting. | Subject to full banking regulations, strict audit and reporting standards. |
| Accounting Complexity | High complexity due to integration and revenue-sharing models. | Moderate complexity focused on digital transactions and risk management. |
| Technology Integration | Embedded APIs linking financial data with non-financial platforms. | Core banking software optimized for digital delivery and data analytics. |
| Risk Management | Shared risk among platform and financial provider; requires joint controls. | Full risk responsibility; emphasis on cybersecurity and fraud prevention. |
| Customer Data Handling | Shared data governance between platform and finance provider. | End-to-end control of customer financial data and privacy compliance. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services directly within non-financial platforms, streamlining transaction recording and enhancing real-time financial data accuracy. Neobank accounting revolves around digital-only banking operations, emphasizing rapid reconciliation and regulatory compliance for seamless cash flow management. Choosing between them depends on the business model, with embedded finance suited for platforms needing integrated payment solutions, while neobank accounting benefits digital-focused financial institutions.
Connection
Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, requiring seamless tracking of transactions and revenue recognition within those ecosystems. Neobank accounting focuses on digital-only banking operations, emphasizing real-time data processing, regulatory compliance, and accurate reporting of virtual accounts and payment activities. The connection lies in their reliance on advanced financial technologies to automate accounting processes, enhance transparency, and support scalable financial management across digital platforms.
Key Terms
Revenue Recognition
Neobank accounting emphasizes direct revenue recognition from digital banking services such as transaction fees, interest income, and subscription models, adhering to IFRS 15 principles for clarity and compliance. In contrast, embedded finance accounting deals with revenue streams integrated within third-party platforms, often requiring nuanced allocation and timing methods to accurately recognize fees, commissions, and shared income. Explore deeper insights into how these accounting frameworks impact financial reporting and operational transparency.
Regulatory Compliance
Neobank accounting emphasizes adherence to banking regulations such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) standards, ensuring transparent financial reporting under frameworks like IFRS and GAAP. Embedded finance accounting must navigate compliance complexities across various sectors, integrating financial services within non-banking platforms while meeting regulatory requirements like PCI DSS for secure payments. Explore the nuances of regulatory compliance in neobank and embedded finance accounting to optimize your financial operations efficiently.
Risk Management
Neobank accounting emphasizes real-time transaction monitoring and fraud detection to mitigate financial risks, leveraging AI-driven analytics for enhanced accuracy. Embedded finance accounting integrates third-party financial services within platforms, necessitating robust compliance controls to manage operational and third-party risks effectively. Explore detailed strategies for optimizing risk management approaches in these innovative financial models.
Source and External Links
What is a Neobank? How It Works, Examples, Pros & Cons - Neobank accounting involves managing online-only financial services through digital platforms, usually in partnership with traditional banks for regulatory compliance; neobanks earn revenue mainly via subscription fees, transaction fees, interchange fees, and commissions from financial services partnerships.
What is a Neobank? How fintech is transforming banking - Neobanks' accounting typically reflects revenue from interchange fees, interest on loans and credit cards, small fees for transactions, and subscription fees--all streamlined due to their low physical overhead costs.
Neobanks: Definition, examples, trends and challenges - Neobank accounting has to address the particular regulatory challenges they face as financial institutions rather than traditional banks, focusing on digital-only service accounting, lower fee structures, and integration with partner banks where applicable.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com