Digital asset taxation focuses on the reporting and payment of taxes related to cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and blockchain-based assets, requiring detailed tracking of gains, losses, and transaction histories. Depreciation expense involves systematically allocating the cost of tangible fixed assets over their useful lives to reflect wear and tear in financial statements. Explore further to understand how these accounting treatments impact financial reporting and tax compliance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital asset taxation and depreciation expense is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with tax laws. Digital asset taxation often involves recognizing capital gains or losses upon sale, whereas depreciation expense systematically allocates the cost of tangible fixed assets over their useful life. Properly distinguishing these ensures optimized tax strategies and avoids legal penalties. Companies handling cryptocurrencies or digital assets must stay updated on evolving tax regulations specific to digital holdings.
Comparison Table
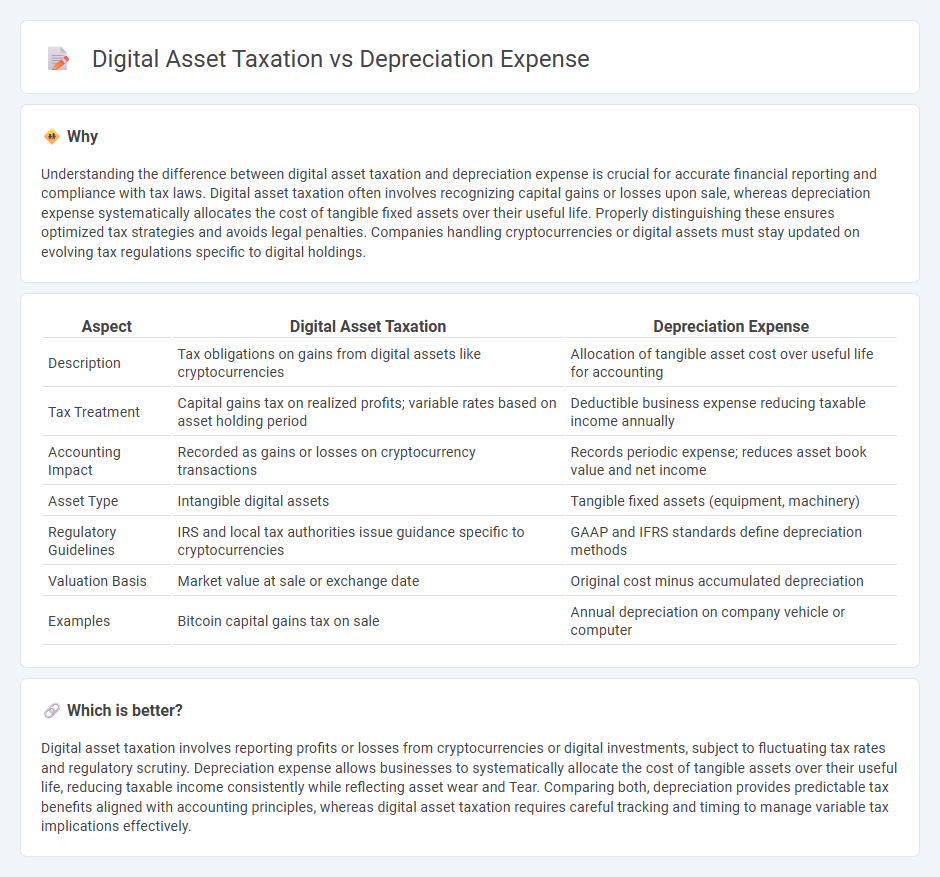
| Aspect | Digital Asset Taxation | Depreciation Expense |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Tax obligations on gains from digital assets like cryptocurrencies | Allocation of tangible asset cost over useful life for accounting |
| Tax Treatment | Capital gains tax on realized profits; variable rates based on asset holding period | Deductible business expense reducing taxable income annually |
| Accounting Impact | Recorded as gains or losses on cryptocurrency transactions | Records periodic expense; reduces asset book value and net income |
| Asset Type | Intangible digital assets | Tangible fixed assets (equipment, machinery) |
| Regulatory Guidelines | IRS and local tax authorities issue guidance specific to cryptocurrencies | GAAP and IFRS standards define depreciation methods |
| Valuation Basis | Market value at sale or exchange date | Original cost minus accumulated depreciation |
| Examples | Bitcoin capital gains tax on sale | Annual depreciation on company vehicle or computer |
Which is better?
Digital asset taxation involves reporting profits or losses from cryptocurrencies or digital investments, subject to fluctuating tax rates and regulatory scrutiny. Depreciation expense allows businesses to systematically allocate the cost of tangible assets over their useful life, reducing taxable income consistently while reflecting asset wear and Tear. Comparing both, depreciation provides predictable tax benefits aligned with accounting principles, whereas digital asset taxation requires careful tracking and timing to manage variable tax implications effectively.
Connection
Digital asset taxation and depreciation expense are interconnected through the requirement to accurately report the amortization or depreciation of digital assets such as cryptocurrencies or NFTs on tax returns. Tax regulations mandate that businesses recognize depreciation expenses to reduce taxable income by accounting for the wear and tear or obsolescence of digital assets over time. Properly calculating depreciation expenses ensures compliance with IRS guidelines and optimizes tax liabilities related to digital asset holdings.
Key Terms
Useful Life
Depreciation expense for tangible assets allocates the cost over the asset's useful life, reflecting wear and usage, while digital asset taxation considers useful life for amortization or impairment, impacting taxable income. Understanding the IRS guidelines on useful life classifications, such as the 3-5 years for software versus indefinite life for certain digital assets, is crucial for accurate financial reporting and tax compliance. Explore detailed comparisons of useful life implications on tax strategy to optimize asset management and minimize liabilities.
Amortization
Depreciation expense applies to tangible assets by allocating their cost over useful life, while digital asset taxation often involves amortization, which spreads intangible asset costs such as software or intellectual property. Amortization for digital assets aligns with IRS guidelines for capitalization and expense recognition, impacting tax reporting and financial statements. Explore detailed strategies and compliance methods for effective digital asset amortization and taxation.
Capital Gains
Depreciation expense reduces the book value of tangible assets over time, impacting financial statements and taxable income, while digital asset taxation primarily involves capital gains calculations based on the difference between the purchase price and sale price of cryptocurrencies or NFTs. Capital gains tax rates vary by holding period, with short-term gains taxed as ordinary income and long-term gains benefiting from lower rates, making the timing of digital asset transactions crucial. Explore more about how depreciation impacts asset management and the nuances of digital asset capital gains taxation.
Source and External Links
Depreciation Expense | Formula + Calculation Tutorial - Depreciation is a non-cash expense that allocates the cost of a fixed asset over its estimated useful life, with common calculation methods including straight-line, double declining balance, and units of production.
Depreciation Expense & Straight-Line Method w/ Example & Journal - The straight-line method is the simplest and most common way to calculate depreciation, spreading the expense evenly over the asset's useful life based on cost, salvage value, and useful life.
Depreciation Expense - Overview and When to Use Various Types - Depreciation expense matches the cost of a long-term asset to the periods it generates revenue, with methods like units-of-production tying expense directly to actual usage.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com