Cryptocurrency taxation involves reporting taxable events such as sales or exchanges of digital assets to tax authorities, while crypto-to-crypto transactions are treated as taxable events where one cryptocurrency is traded for another, triggering capital gains or losses. Accurate tracking of transaction dates, fair market values, and cost basis is essential for compliance with IRS guidelines. Explore the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation and crypto-to-crypto transaction reporting to ensure proper accounting practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency taxation and crypto-to-crypto transactions is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with tax laws. Cryptocurrency taxation involves tracking taxable events such as sales or exchanges for fiat currency, which may trigger capital gains or losses. Crypto-to-crypto transactions require detailed record-keeping of fair market values at the time of exchange to properly calculate tax liabilities. Proper differentiation prevents legal penalties and ensures optimized tax obligations for individuals and businesses.
Comparison Table
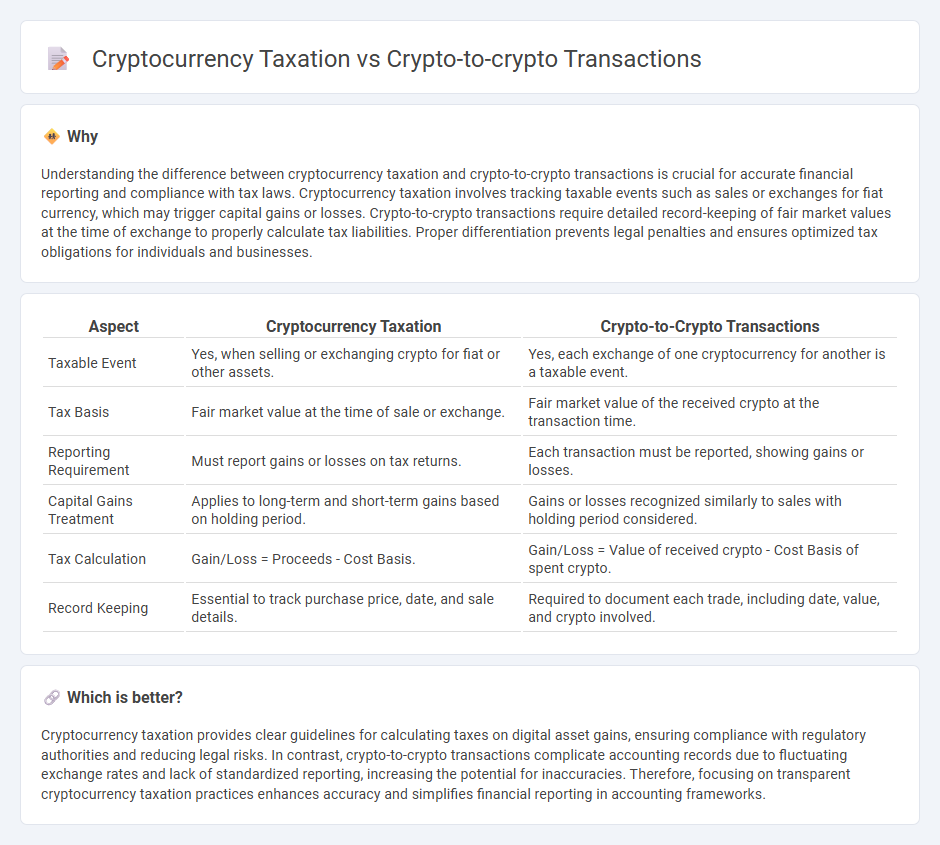
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Taxation | Crypto-to-Crypto Transactions |
|---|---|---|
| Taxable Event | Yes, when selling or exchanging crypto for fiat or other assets. | Yes, each exchange of one cryptocurrency for another is a taxable event. |
| Tax Basis | Fair market value at the time of sale or exchange. | Fair market value of the received crypto at the transaction time. |
| Reporting Requirement | Must report gains or losses on tax returns. | Each transaction must be reported, showing gains or losses. |
| Capital Gains Treatment | Applies to long-term and short-term gains based on holding period. | Gains or losses recognized similarly to sales with holding period considered. |
| Tax Calculation | Gain/Loss = Proceeds - Cost Basis. | Gain/Loss = Value of received crypto - Cost Basis of spent crypto. |
| Record Keeping | Essential to track purchase price, date, and sale details. | Required to document each trade, including date, value, and crypto involved. |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency taxation provides clear guidelines for calculating taxes on digital asset gains, ensuring compliance with regulatory authorities and reducing legal risks. In contrast, crypto-to-crypto transactions complicate accounting records due to fluctuating exchange rates and lack of standardized reporting, increasing the potential for inaccuracies. Therefore, focusing on transparent cryptocurrency taxation practices enhances accuracy and simplifies financial reporting in accounting frameworks.
Connection
Cryptocurrency taxation requires reporting all taxable events, including crypto-to-crypto transactions, where exchanging one cryptocurrency for another triggers a taxable disposition. The IRS treats each crypto-to-crypto trade as a sale, necessitating calculation of capital gains or losses based on the fair market value at the time of the transaction. Accurate record-keeping of transaction dates, amounts, and values is essential to ensure compliance with tax regulations and avoid penalties.
Key Terms
Cost Basis
Crypto-to-crypto transactions require meticulous tracking of the cost basis to accurately calculate capital gains or losses for tax purposes. The IRS treats each swap as a taxable event, where the fair market value of the received cryptocurrency at the transaction date determines the cost basis for future tax reporting. Explore detailed strategies for managing cost basis effectively in cryptocurrency taxation to ensure compliance and optimize your tax outcomes.
Capital Gains/Losses
Crypto-to-crypto transactions trigger capital gains or losses calculations based on the fair market value at the time of each trade, impacting taxable income. The IRS treats each trade as a taxable event, requiring detailed record-keeping of acquisition costs and proceeds for accurate capital gains reporting. Explore comprehensive guidelines to optimize tax reporting and compliance in cryptocurrency trading.
Like-Kind Exchange (IRS Section 1031)
Crypto-to-crypto transactions involve exchanging one cryptocurrency directly for another, which the IRS treats as taxable events subject to capital gains tax, complicating tax reporting for digital asset traders. Unlike traditional like-kind exchanges under IRS Section 1031, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 explicitly excludes cryptocurrencies from Section 1031 benefits, meaning crypto trades cannot defer taxes through like-kind exchange rules. Explore detailed guidance on cryptocurrency taxation and compliance strategies for crypto-to-crypto transactions to optimize your tax outcomes.
Source and External Links
Understanding crypto taxes - Trading one cryptocurrency for another is considered a taxable event, subject to capital gains tax if a profit is realized.
Crypto Taxes: The Complete Guide - Profits from crypto-to-crypto trades are taxed as capital gains, with losses potentially offsetting gains.
Crypto tax guide - Exchanging one cryptocurrency for another at a loss may allow for tax deductions to offset realized gains.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com