Dynamic allocation tracing identifies overhead costs by tracking resource consumption in real-time, enhancing accuracy in complex production environments. Activity-based costing allocates expenses based on predefined activities, offering detailed insights into cost drivers and product profitability. Explore deeper to understand which method suits your business needs for precise cost management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dynamic allocation tracing and Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is important because dynamic allocation tracing tracks resource usage in real time for precise cost assignment, while ABC allocates overhead based on multiple cost drivers to improve cost accuracy. Knowing these distinctions enables accountants to select the most suitable method for accurate product costing and resource optimization. This knowledge directly impacts financial reporting, budgeting, and strategic decision-making by providing clearer insights into cost behavior. Accurate cost allocation ensures better pricing strategies and profitability analysis in complex business environments.
Comparison Table
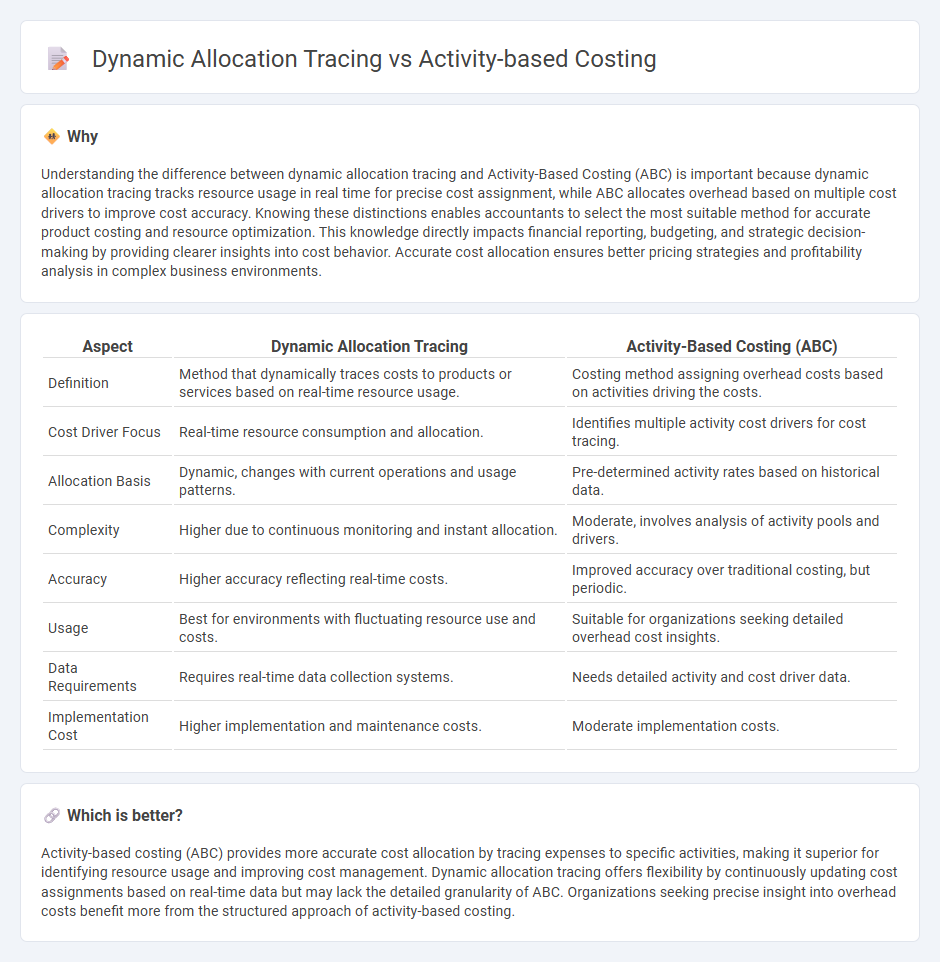
| Aspect | Dynamic Allocation Tracing | Activity-Based Costing (ABC) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Method that dynamically traces costs to products or services based on real-time resource usage. | Costing method assigning overhead costs based on activities driving the costs. |
| Cost Driver Focus | Real-time resource consumption and allocation. | Identifies multiple activity cost drivers for cost tracing. |
| Allocation Basis | Dynamic, changes with current operations and usage patterns. | Pre-determined activity rates based on historical data. |
| Complexity | Higher due to continuous monitoring and instant allocation. | Moderate, involves analysis of activity pools and drivers. |
| Accuracy | Higher accuracy reflecting real-time costs. | Improved accuracy over traditional costing, but periodic. |
| Usage | Best for environments with fluctuating resource use and costs. | Suitable for organizations seeking detailed overhead cost insights. |
| Data Requirements | Requires real-time data collection systems. | Needs detailed activity and cost driver data. |
| Implementation Cost | Higher implementation and maintenance costs. | Moderate implementation costs. |
Which is better?
Activity-based costing (ABC) provides more accurate cost allocation by tracing expenses to specific activities, making it superior for identifying resource usage and improving cost management. Dynamic allocation tracing offers flexibility by continuously updating cost assignments based on real-time data but may lack the detailed granularity of ABC. Organizations seeking precise insight into overhead costs benefit more from the structured approach of activity-based costing.
Connection
Dynamic allocation tracing enhances Activity-Based Costing (ABC) by providing detailed insights into resource consumption patterns, enabling more accurate cost driver identification. This method tracks resource usage dynamically across various activities, improving the precision of cost allocation in ABC systems. Integrating dynamic allocation tracing with ABC supports more effective cost management and strategic decision-making in accounting.
Key Terms
Cost Driver
Activity-based costing (ABC) identifies specific cost drivers linked to activities, enabling precise tracing of overhead costs based on consumption patterns. Dynamic allocation tracing adjusts cost drivers continuously to reflect real-time changes in resource usage, improving accuracy in fluctuating production environments. Explore these methods in depth to optimize cost management strategies effectively.
Resource Consumption
Activity-based costing (ABC) allocates overhead costs based on specific activities that drive resource consumption, providing a detailed view of cost drivers within business processes. Dynamic allocation tracing continuously monitors and assigns costs in real-time by tracking the usage of resources across multiple activities and time frames, enabling more precise cost management. Explore the nuances and applications of these costing methods to enhance resource consumption analysis.
Allocation Basis
Activity-based costing (ABC) allocates overhead costs based on multiple cost drivers linked to specific activities, enhancing accuracy in product or service costing. Dynamic allocation tracing continuously adjusts cost assignments in real-time, reflecting changes in resource consumption and operational processes. Explore further to understand how allocation bases impact cost management effectiveness.
Source and External Links
Activity Based Costing (ABC) : A Detailed Definition and Explanation - Activity-based costing assigns overhead and indirect costs to products by identifying activities as cost drivers and measuring them by transaction frequency and duration to allocate costs more accurately than traditional methods.
Activity-Based Costing - Overview, Approach, Benefits - ABC allocates overhead costs based on specific activities that cause costs, enabling more accurate product costing and informed pricing strategies, especially in manufacturing.
Activity-Based Costing (ABC): Advantages and When To Use - ABC tracks resource use by identifying activities causing production costs, assigning costs via cost drivers, and calculating overhead rates for precise product costing and management decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com