Cryptocurrency taxation requires precise calculation of capital gains and losses based on transaction history, while reporting requirements mandate disclosure of digital asset holdings and activities to tax authorities. Compliance involves understanding varying tax treatments for different types of crypto transactions, such as trading, mining, and staking. Explore detailed guidance to ensure accurate accounting and regulatory adherence in the evolving cryptocurrency landscape.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency taxation and reporting requirements is crucial for accurate financial compliance and avoiding legal penalties. Cryptocurrency taxation involves calculating and paying taxes on gains or income derived from digital assets, while reporting requirements mandate disclosure of transactions to tax authorities. Proper knowledge ensures timely filing, minimizes audit risks, and maximizes tax benefits. Clear differentiation supports strategic tax planning and adherence to regulations like the IRS's Form 8949 and FinCEN's FBAR.
Comparison Table
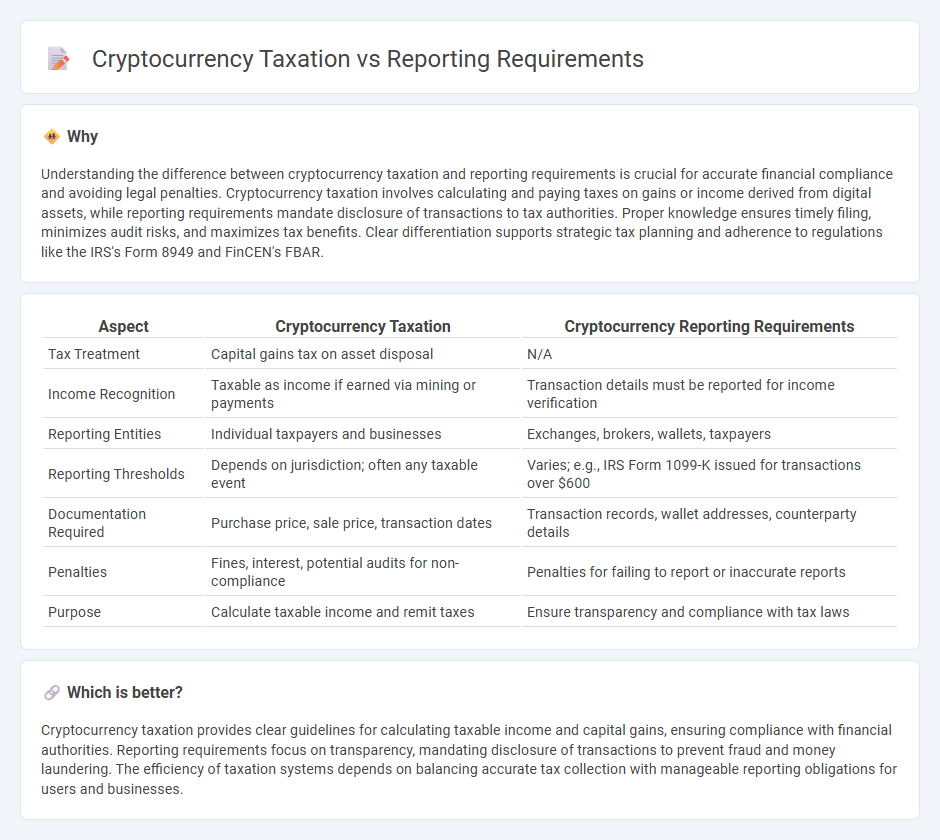
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Taxation | Cryptocurrency Reporting Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Treatment | Capital gains tax on asset disposal | N/A |
| Income Recognition | Taxable as income if earned via mining or payments | Transaction details must be reported for income verification |
| Reporting Entities | Individual taxpayers and businesses | Exchanges, brokers, wallets, taxpayers |
| Reporting Thresholds | Depends on jurisdiction; often any taxable event | Varies; e.g., IRS Form 1099-K issued for transactions over $600 |
| Documentation Required | Purchase price, sale price, transaction dates | Transaction records, wallet addresses, counterparty details |
| Penalties | Fines, interest, potential audits for non-compliance | Penalties for failing to report or inaccurate reports |
| Purpose | Calculate taxable income and remit taxes | Ensure transparency and compliance with tax laws |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency taxation provides clear guidelines for calculating taxable income and capital gains, ensuring compliance with financial authorities. Reporting requirements focus on transparency, mandating disclosure of transactions to prevent fraud and money laundering. The efficiency of taxation systems depends on balancing accurate tax collection with manageable reporting obligations for users and businesses.
Connection
Cryptocurrency taxation and reporting requirements are interconnected through regulatory frameworks that mandate accurate tracking and disclosure of digital asset transactions for tax compliance. Tax authorities require detailed records of cryptocurrency gains, losses, and income to calculate taxable amounts and prevent tax evasion. Compliance with reporting standards such as IRS Form 8949 in the U.S. ensures transparent financial documentation and adherence to tax laws involving virtual currencies.
Key Terms
Financial Statements
Financial statements must accurately reflect cryptocurrency holdings, requiring detailed reporting of transactions, valuations, and impairments according to accounting standards such as IFRS or GAAP. Regulatory bodies increasingly demand comprehensive disclosures to ensure transparency in tax obligations related to digital assets, emphasizing the need for precise documentation of gains, losses, and taxable events. Explore the complexities of cryptocurrency taxation and reporting requirements to enhance financial compliance and strategic planning.
Taxable Events
Taxable events in cryptocurrency taxation often trigger specific reporting requirements, including capital gains declarations, income realization, and transaction disclosures. Examples include selling crypto assets, trading between different cryptocurrencies, or using crypto for purchases, each necessitating accurate records and compliance with IRS guidelines. Explore further to understand how these taxable events impact your cryptocurrency reporting obligations.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance in cryptocurrency taxation mandates precise reporting requirements to ensure transparent transaction disclosures and accurate tax obligations. The IRS requires detailed records of digital asset transactions, including dates, amounts, and fair market values to prevent tax evasion and facilitate audits. Explore comprehensive guidelines and updates to stay compliant with evolving cryptocurrency tax regulations.
Source and External Links
4.1703 Reporting requirements. - Acquisition.GOV - Reporting requirements for service contracts and subcontracts depend on contract type and estimated values, with detailed thresholds for cost-reimbursement, time-and-materials, labor-hour, and fixed-price contracts starting at $500,000 in recent fiscal years.
Reporting Requirements: Meaning & Examples - StudySmarter - Reporting requirements are regulatory obligations that organizations must follow to disclose financial, operational, and compliance information, often analyzed using theories like Agency, Stakeholder, and Legitimacy theories to understand their purpose and impact.
Information return reporting | Internal Revenue Service - Businesses and self-employed individuals must file information returns such as Form 1099 to report payments made during the tax year, with specific forms and electronic filing options detailed by the IRS.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com