Real-time expense recognition records expenses immediately when they occur, providing an accurate and up-to-date view of financial conditions, while accrual accounting matches expenses to the period in which they are incurred, regardless of cash flow timing. Real-time expense tracking enhances cash management and operational decision-making, whereas accrual accounting ensures compliance with accounting standards and better long-term financial analysis. Explore more to understand which method best suits your business needs and regulatory requirements.
Why it is important
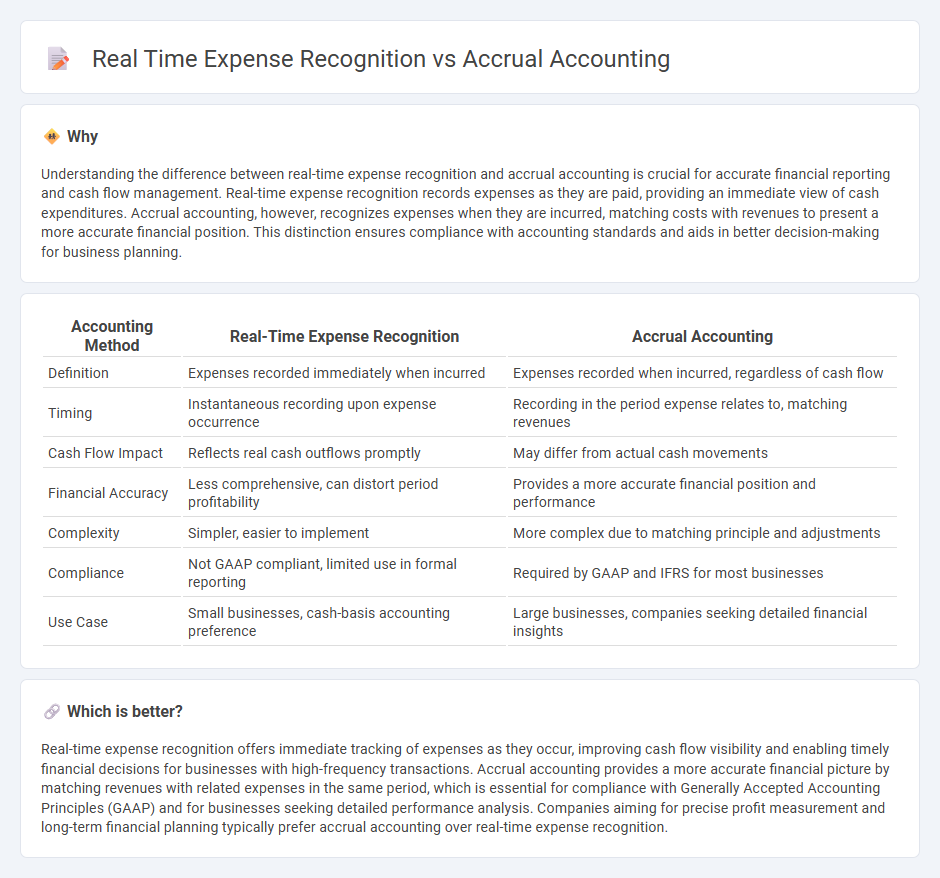
Understanding the difference between real-time expense recognition and accrual accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and cash flow management. Real-time expense recognition records expenses as they are paid, providing an immediate view of cash expenditures. Accrual accounting, however, recognizes expenses when they are incurred, matching costs with revenues to present a more accurate financial position. This distinction ensures compliance with accounting standards and aids in better decision-making for business planning.
Comparison Table
| Accounting Method | Real-Time Expense Recognition | Accrual Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Expenses recorded immediately when incurred | Expenses recorded when incurred, regardless of cash flow |
| Timing | Instantaneous recording upon expense occurrence | Recording in the period expense relates to, matching revenues |
| Cash Flow Impact | Reflects real cash outflows promptly | May differ from actual cash movements |
| Financial Accuracy | Less comprehensive, can distort period profitability | Provides a more accurate financial position and performance |
| Complexity | Simpler, easier to implement | More complex due to matching principle and adjustments |
| Compliance | Not GAAP compliant, limited use in formal reporting | Required by GAAP and IFRS for most businesses |
| Use Case | Small businesses, cash-basis accounting preference | Large businesses, companies seeking detailed financial insights |
Which is better?
Real-time expense recognition offers immediate tracking of expenses as they occur, improving cash flow visibility and enabling timely financial decisions for businesses with high-frequency transactions. Accrual accounting provides a more accurate financial picture by matching revenues with related expenses in the same period, which is essential for compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and for businesses seeking detailed performance analysis. Companies aiming for precise profit measurement and long-term financial planning typically prefer accrual accounting over real-time expense recognition.
Connection
Real-time expense recognition ensures that financial transactions are recorded at the moment they occur, enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of financial statements. Accrual accounting relies on this immediate recognition to match expenses with related revenues within the same accounting period, providing a clearer picture of an organization's financial position. This connection supports compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP and IFRS by promoting transparency and consistency in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Matching Principle
Accrual accounting records expenses and revenues when they are incurred, aligning costs with related income according to the Matching Principle to provide an accurate financial picture. Real-time expense recognition captures expenses immediately when transactions occur, but may not align expenses with corresponding revenues, potentially distorting financial results. Discover how these approaches affect financial statements and decision-making in depth.
Revenue Recognition
Accrual accounting records revenue when earned, matching expenses to corresponding revenues for accurate financial performance, while real-time expense recognition captures costs immediately as transactions occur, enhancing cash flow visibility. Revenue recognition under accrual principles aligns with GAAP and IFRS standards, ensuring reported income reflects economic activity rather than cash movement. Explore how adopting each method impacts financial statements and compliance for informed revenue management.
Timing of Transactions
Accrual accounting records revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of cash flow, ensuring financial statements reflect economic activity within the correct period. Real-time expense recognition captures transactions immediately as they occur, providing an up-to-date financial position at any given moment. Explore the advantages and implications of these timing methods to enhance your accounting strategies.
Source and External Links
Accrual-Based Accounting Explained - Accrual accounting recognizes revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, not when cash is exchanged, providing a more accurate financial picture aligned with GAAP principles and required for publicly traded companies.
Accrual Accounting - Guide, How it Works, Definition - In accrual accounting, revenues earned but not yet received and expenses incurred but unpaid are recorded to track economic transactions accurately, such as an electricity utility recognizing revenue before payment while incurring costs during the period.
Accrual Accounting Explained: Examples, Journal Entries, ... - Accrual accounting involves recording prepaid expenses and accrued revenues or expenses to ensure financial statements reflect the actual economic activity in the appropriate reporting period, e.g., recognizing a prepaid insurance asset that is expensed monthly or accrued salary expenses before payment.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com