Continuous assurance involves ongoing monitoring and real-time verification of financial data throughout the fiscal year, enhancing accuracy and early detection of discrepancies. Year-end audit is a comprehensive examination conducted after the fiscal period to validate the integrity of financial statements and compliance with accounting standards. Explore the benefits and differences between continuous assurance and year-end audit to optimize your financial reporting processes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between continuous assurance and year-end audit is crucial for maintaining accurate financial oversight and timely risk identification. Continuous assurance involves real-time monitoring of financial processes, enabling early detection of errors or fraud. Year-end audit provides a comprehensive, retrospective examination of financial statements, ensuring compliance with accounting standards. Leveraging both approaches enhances organizational transparency and strengthens stakeholder confidence.
Comparison Table
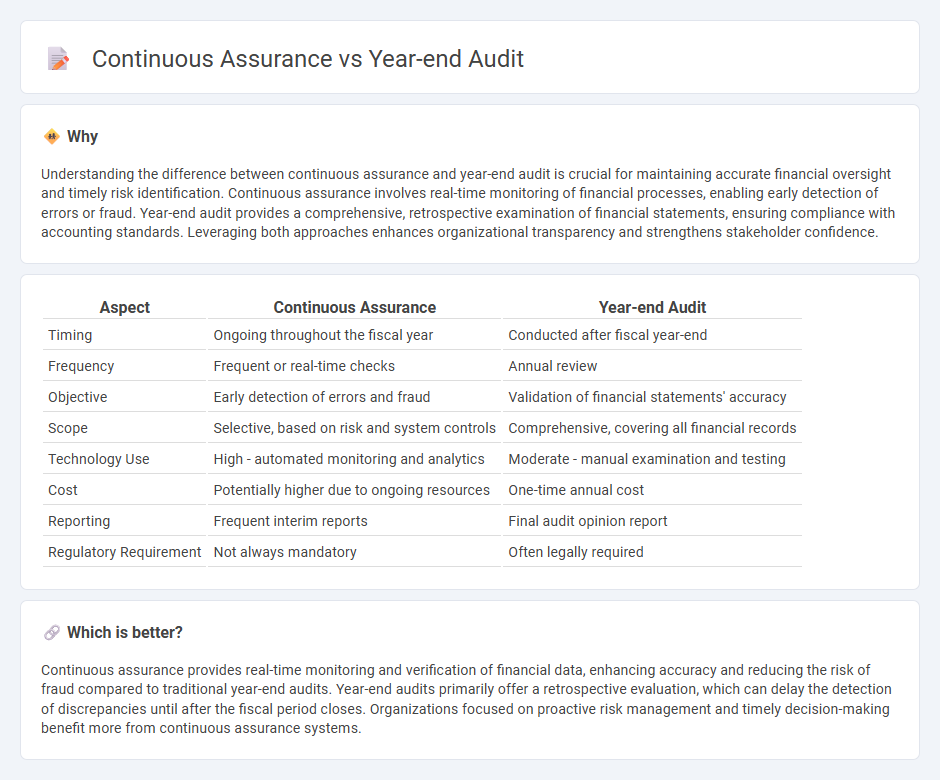
| Aspect | Continuous Assurance | Year-end Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Timing | Ongoing throughout the fiscal year | Conducted after fiscal year-end |
| Frequency | Frequent or real-time checks | Annual review |
| Objective | Early detection of errors and fraud | Validation of financial statements' accuracy |
| Scope | Selective, based on risk and system controls | Comprehensive, covering all financial records |
| Technology Use | High - automated monitoring and analytics | Moderate - manual examination and testing |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to ongoing resources | One-time annual cost |
| Reporting | Frequent interim reports | Final audit opinion report |
| Regulatory Requirement | Not always mandatory | Often legally required |
Which is better?
Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring and verification of financial data, enhancing accuracy and reducing the risk of fraud compared to traditional year-end audits. Year-end audits primarily offer a retrospective evaluation, which can delay the detection of discrepancies until after the fiscal period closes. Organizations focused on proactive risk management and timely decision-making benefit more from continuous assurance systems.
Connection
Continuous assurance integrates real-time data analysis and monitoring throughout the fiscal year, enhancing the accuracy and reliability of financial information. Year-end audits utilize insights from continuous assurance processes to streamline verification and reduce risk of misstatements. This connection improves overall financial transparency and compliance with accounting standards.
Key Terms
**Year-end audit:**
Year-end audit provides a comprehensive review of an organization's financial statements at the end of the fiscal year, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and detecting material misstatements. This process relies on retrospective examination and sampling of transactions to form an opinion on the overall financial health of the company. Explore more about the detailed procedures and benefits of year-end audit to enhance financial transparency.
Financial Statements
Year-end audits provide a comprehensive evaluation of financial statements at a specific point in time, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Continuous assurance offers ongoing monitoring and real-time verification of financial data, enhancing transparency and timely risk detection throughout the fiscal year. Discover how integrating continuous assurance with traditional audits can improve financial statement reliability and decision-making processes.
Audit Report
Year-end audit primarily concentrates on validating financial statements at a specific closing date, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Continuous assurance employs real-time data monitoring and automated controls, providing ongoing validation and early detection of discrepancies throughout the fiscal period. Discover how integrating continuous assurance can transform audit report reliability and timeliness.
Source and External Links
Preparing For Year-End Audits: A Comprehensive Guide - NOW CFO - Year-end audits verify financial accuracy, ensure compliance with standards like GAAP or IFRS, detect fraud, and enhance credibility with investors and stakeholders, making them essential for business transparency and regulatory adherence.
How to Prepare for the Year-End Audit | FloQast - A year-end audit involves external auditors reviewing and verifying financial records to boost transparency, identify issues missed internally, and prevent fraud through an independent assessment.
Year End Audit Preparation - How to Ace Your Year End Audit? - Year-end audits are conducted by third-party auditors examining financial statements and supporting documents to assess authenticity and provide insights for optimizing company financial performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com