Ledger tokenization enhances accounting accuracy by securely converting assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, ensuring transparent and immutable financial records. Decentralized finance (DeFi) disrupts traditional accounting by enabling peer-to-peer financial transactions and automated smart contracts without intermediaries, fostering real-time auditability and reduced costs. Explore how these innovations redefine financial reporting and asset management in modern accounting.
Why it is important
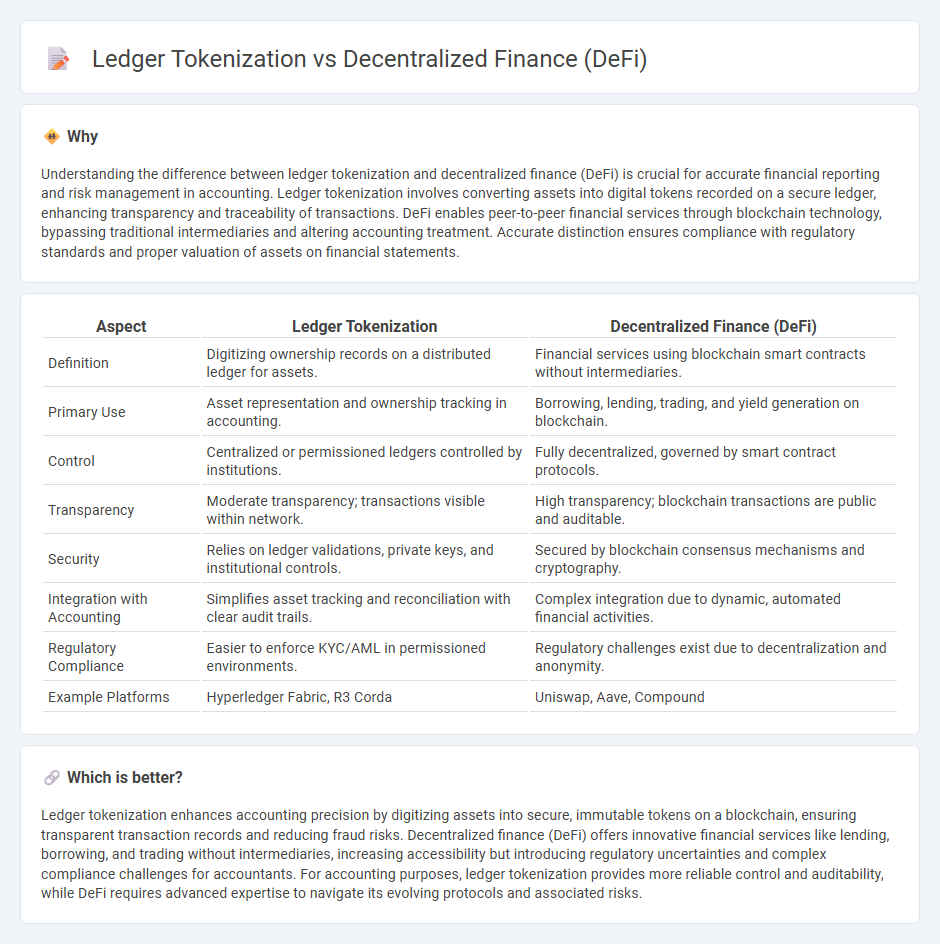
Understanding the difference between ledger tokenization and decentralized finance (DeFi) is crucial for accurate financial reporting and risk management in accounting. Ledger tokenization involves converting assets into digital tokens recorded on a secure ledger, enhancing transparency and traceability of transactions. DeFi enables peer-to-peer financial services through blockchain technology, bypassing traditional intermediaries and altering accounting treatment. Accurate distinction ensures compliance with regulatory standards and proper valuation of assets on financial statements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ledger Tokenization | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitizing ownership records on a distributed ledger for assets. | Financial services using blockchain smart contracts without intermediaries. |
| Primary Use | Asset representation and ownership tracking in accounting. | Borrowing, lending, trading, and yield generation on blockchain. |
| Control | Centralized or permissioned ledgers controlled by institutions. | Fully decentralized, governed by smart contract protocols. |
| Transparency | Moderate transparency; transactions visible within network. | High transparency; blockchain transactions are public and auditable. |
| Security | Relies on ledger validations, private keys, and institutional controls. | Secured by blockchain consensus mechanisms and cryptography. |
| Integration with Accounting | Simplifies asset tracking and reconciliation with clear audit trails. | Complex integration due to dynamic, automated financial activities. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Easier to enforce KYC/AML in permissioned environments. | Regulatory challenges exist due to decentralization and anonymity. |
| Example Platforms | Hyperledger Fabric, R3 Corda | Uniswap, Aave, Compound |
Which is better?
Ledger tokenization enhances accounting precision by digitizing assets into secure, immutable tokens on a blockchain, ensuring transparent transaction records and reducing fraud risks. Decentralized finance (DeFi) offers innovative financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries, increasing accessibility but introducing regulatory uncertainties and complex compliance challenges for accountants. For accounting purposes, ledger tokenization provides more reliable control and auditability, while DeFi requires advanced expertise to navigate its evolving protocols and associated risks.
Connection
Ledger tokenization enables the digitization of assets on a blockchain, facilitating transparent and immutable accounting records crucial for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications. DeFi leverages these tokenized ledgers to execute automated financial transactions, smart contracts, and decentralized auditing without intermediaries. The integration of ledger tokenization with DeFi enhances accuracy, security, and efficiency in financial reporting and asset management within accounting systems.
Key Terms
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts form the backbone of decentralized finance (DeFi) by automating complex financial transactions without intermediaries, ensuring transparency and security on blockchain networks. Ledger tokenization leverages smart contracts to create digital representations of assets, enabling fractional ownership and seamless transferability on distributed ledgers. Explore how smart contracts revolutionize financial systems through DeFi and tokenization innovations.
Asset Backing
Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable peer-to-peer financial services without intermediaries, often using native tokens not always directly backed by physical assets. Ledger tokenization involves creating digital tokens on a blockchain that represent ownership of real-world assets, ensuring a direct asset backing for increased transparency and security. Explore how asset backing in DeFi and ledger tokenization impacts investment trust and market dynamics.
On-chain Auditability
Decentralized finance (DeFi) leverages blockchain technology to enable transparent, trustless financial transactions with on-chain auditability, allowing users to verify and track asset flows directly on the blockchain. Ledger tokenization involves converting real-world assets into digital tokens recorded on a distributed ledger, ensuring immutable ownership records and facilitating seamless audit trails. Explore how these technologies enhance on-chain auditability to transform financial ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Decentralized Finance - Decentralized finance (DeFi) offers financial instruments and services using smart contracts on blockchain platforms, reducing the need for intermediaries.
What is DeFi? - DeFi is an umbrella term for peer-to-peer financial services, primarily on Ethereum, allowing users to perform various financial activities without intermediaries.
The Technology of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) - DeFi leverages distributed ledger technologies to provide services like lending, investing, or exchanging cryptoassets without relying on traditional intermediaries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com