Continuous auditing leverages automated tools and real-time data analysis to provide ongoing assurance and early detection of anomalies in financial processes. Risk-based auditing focuses on identifying and prioritizing high-risk areas to allocate audit resources efficiently and enhance the effectiveness of internal controls. Explore these methodologies to understand how they improve financial accuracy and organizational risk management.
Why it is important
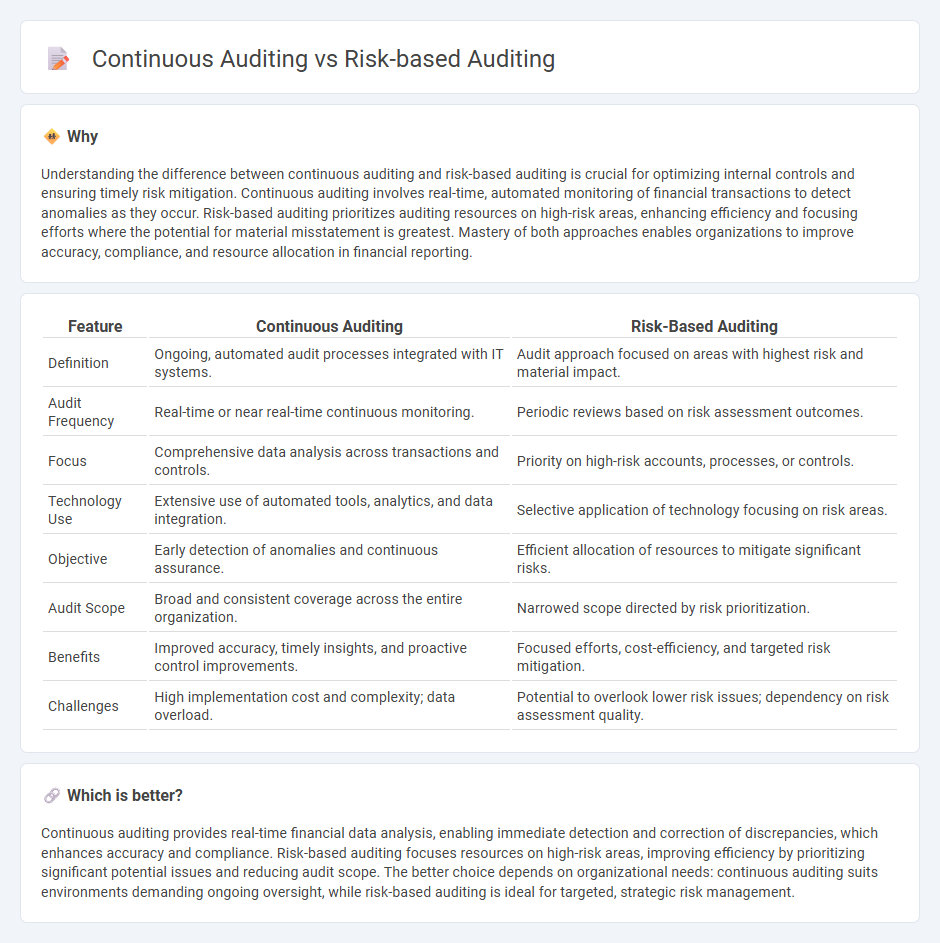
Understanding the difference between continuous auditing and risk-based auditing is crucial for optimizing internal controls and ensuring timely risk mitigation. Continuous auditing involves real-time, automated monitoring of financial transactions to detect anomalies as they occur. Risk-based auditing prioritizes auditing resources on high-risk areas, enhancing efficiency and focusing efforts where the potential for material misstatement is greatest. Mastery of both approaches enables organizations to improve accuracy, compliance, and resource allocation in financial reporting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Continuous Auditing | Risk-Based Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing, automated audit processes integrated with IT systems. | Audit approach focused on areas with highest risk and material impact. |
| Audit Frequency | Real-time or near real-time continuous monitoring. | Periodic reviews based on risk assessment outcomes. |
| Focus | Comprehensive data analysis across transactions and controls. | Priority on high-risk accounts, processes, or controls. |
| Technology Use | Extensive use of automated tools, analytics, and data integration. | Selective application of technology focusing on risk areas. |
| Objective | Early detection of anomalies and continuous assurance. | Efficient allocation of resources to mitigate significant risks. |
| Audit Scope | Broad and consistent coverage across the entire organization. | Narrowed scope directed by risk prioritization. |
| Benefits | Improved accuracy, timely insights, and proactive control improvements. | Focused efforts, cost-efficiency, and targeted risk mitigation. |
| Challenges | High implementation cost and complexity; data overload. | Potential to overlook lower risk issues; dependency on risk assessment quality. |
Which is better?
Continuous auditing provides real-time financial data analysis, enabling immediate detection and correction of discrepancies, which enhances accuracy and compliance. Risk-based auditing focuses resources on high-risk areas, improving efficiency by prioritizing significant potential issues and reducing audit scope. The better choice depends on organizational needs: continuous auditing suits environments demanding ongoing oversight, while risk-based auditing is ideal for targeted, strategic risk management.
Connection
Continuous auditing enhances risk-based auditing by providing real-time data analysis and monitoring, allowing auditors to identify and assess risks more accurately and promptly. Risk-based auditing prioritizes audit activities based on the significance and likelihood of risks, and continuous auditing supplies ongoing assurance through automated controls testing and data analytics. The integration of both approaches improves the detection of anomalies, reduces audit cycle times, and strengthens overall financial governance.
Key Terms
Risk Assessment
Risk-based auditing prioritizes identifying and evaluating risks that could impact financial statements or operational processes, enabling auditors to allocate resources effectively to high-risk areas. Continuous auditing involves real-time monitoring of transactions and controls to detect and respond to risk indicators promptly, enhancing the timeliness of risk assessment. Discover how integrating these approaches improves risk management and audit efficiency.
Audit Frequency
Risk-based auditing prioritizes audit efforts on high-risk areas, conducting reviews at intervals aligned with risk assessment results, which may be quarterly, annually, or according to specific risk events. Continuous auditing involves an ongoing, real-time evaluation of financial transactions and controls, enabled by automated tools to ensure immediate detection of anomalies and compliance issues. Explore the advantages and implementation methods of both audit frequencies to enhance your organization's audit strategy.
Control Monitoring
Risk-based auditing prioritizes high-risk areas to optimize resource allocation and enhance control effectiveness, focusing on identifying and mitigating potential threats before they impact financial statements. Continuous auditing employs automated tools to provide real-time or near real-time control monitoring, enabling timely detection and correction of anomalies. Explore the latest methodologies and benefits of integrating these approaches for robust control monitoring strategies.
Source and External Links
Risk-based auditing - Wikipedia - Risk-based auditing is an audit style focusing on analyzing and managing risks with an emphasis on identifying risks with the greatest potential impact rather than just checking compliance, influenced by standards such as COSO and ISO 31000.
5 Risk-Based Internal Auditing Approaches - AuditBoard - Risk-based auditing involves establishing the organization's risk appetite, conducting regular risk assessments to identify and evaluate high-risk areas, and focusing audit resources on these key risks using frameworks like ISO 31000 and COSO ERM.
Fundamentals of Risk-Based Auditing: A Strategic Framework - Risk-based auditing prioritizes audit activities by assessing the likelihood and impact of risks through approaches such as top-down, bottom-up, hybrid, threat-based, and vulnerability-based methods, with key steps including risk identification, assessment, prioritization, audit planning, execution, and reporting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com