Digital twin accounting employs real-time data simulation and digital replicas of financial processes to enhance accuracy and forecasting, while tax accounting focuses on compliance with tax regulations and efficient tax reporting. Digital twin accounting enables dynamic scenario analysis and operational insights, contrasting with tax accounting's emphasis on meeting statutory requirements and minimizing tax liabilities. Discover how integrating digital twin accounting can transform financial management beyond traditional tax accounting practices.
Why it is important
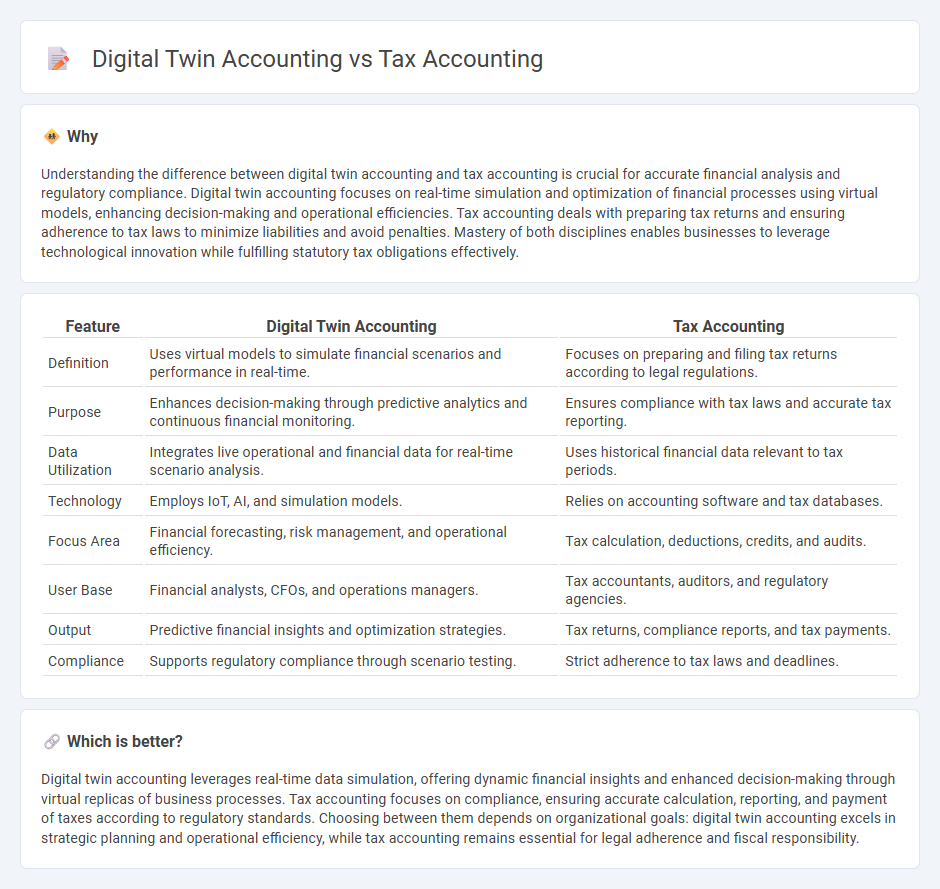
Understanding the difference between digital twin accounting and tax accounting is crucial for accurate financial analysis and regulatory compliance. Digital twin accounting focuses on real-time simulation and optimization of financial processes using virtual models, enhancing decision-making and operational efficiencies. Tax accounting deals with preparing tax returns and ensuring adherence to tax laws to minimize liabilities and avoid penalties. Mastery of both disciplines enables businesses to leverage technological innovation while fulfilling statutory tax obligations effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Twin Accounting | Tax Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses virtual models to simulate financial scenarios and performance in real-time. | Focuses on preparing and filing tax returns according to legal regulations. |
| Purpose | Enhances decision-making through predictive analytics and continuous financial monitoring. | Ensures compliance with tax laws and accurate tax reporting. |
| Data Utilization | Integrates live operational and financial data for real-time scenario analysis. | Uses historical financial data relevant to tax periods. |
| Technology | Employs IoT, AI, and simulation models. | Relies on accounting software and tax databases. |
| Focus Area | Financial forecasting, risk management, and operational efficiency. | Tax calculation, deductions, credits, and audits. |
| User Base | Financial analysts, CFOs, and operations managers. | Tax accountants, auditors, and regulatory agencies. |
| Output | Predictive financial insights and optimization strategies. | Tax returns, compliance reports, and tax payments. |
| Compliance | Supports regulatory compliance through scenario testing. | Strict adherence to tax laws and deadlines. |
Which is better?
Digital twin accounting leverages real-time data simulation, offering dynamic financial insights and enhanced decision-making through virtual replicas of business processes. Tax accounting focuses on compliance, ensuring accurate calculation, reporting, and payment of taxes according to regulatory standards. Choosing between them depends on organizational goals: digital twin accounting excels in strategic planning and operational efficiency, while tax accounting remains essential for legal adherence and fiscal responsibility.
Connection
Digital twin accounting leverages real-time data simulation to enhance accuracy and transparency in tax accounting processes. By mirroring financial transactions and tax obligations virtually, organizations can identify discrepancies, optimize tax strategies, and ensure compliance efficiently. This integration reduces risks of errors and audits while streamlining tax reporting workflows.
Key Terms
**Tax Accounting:**
Tax accounting focuses on the accurate calculation and reporting of tax obligations according to governmental regulations, ensuring compliance with tax laws and minimizing liabilities through strategic planning. It involves detailed record-keeping, preparation of tax returns, and application of tax codes relevant to businesses and individuals. Explore more about tax accounting techniques and benefits in specialized financial resources.
Taxable Income
Tax accounting centers on accurately calculating taxable income by adhering to tax laws and regulations, ensuring compliance and minimizing tax liabilities through deductions and credits. Digital twin accounting leverages real-time data replication to simulate financial scenarios, enhancing precision in forecasting taxable income and optimizing tax strategy decisions. Explore how digital twin accounting transforms tax planning and maximizes taxable income insights.
Deferred Tax
Deferred tax in tax accounting represents temporary differences between accounting profit and taxable profit, creating liabilities or assets for future tax payments or savings. Digital twin accounting enhances this process by simulating real-time financial scenarios, enabling precise tracking and optimization of deferred tax impacts on corporate finance. Explore how integrating digital twin technology revolutionizes deferred tax management and strategic tax planning.
Source and External Links
What Is Tax Accounting? (With Tips and an Example) | Indeed.com - Tax accounting involves methods focused on preparing public financial statements to report tax assets and liabilities, ensuring companies pay correct taxes by considering current and future liabilities and profit and loss reports.
Tax Accounting | Definition, Types & Examples - Study.com - Tax accounting is a specialized field aimed at minimizing tax liabilities and ensuring compliance with tax laws, distinct from financial accounting, with applications including tax return preparation and tax planning.
Tax Accountant Careers - Tax accountants prepare tax filings for individuals and businesses, provide advice on tax strategies to optimize tax exposure, analyze financial data, and stay updated on tax law changes to help clients comply with regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com