Digital ledger technology (DLT) revolutionizes accounting by enabling decentralized, secure record-keeping across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risks. Blockchain accounting, a subset of DLT, leverages cryptographic hashing and immutability to create tamper-proof transaction histories, improving auditability and trust in financial data. Explore the distinctions and advantages of these technologies to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
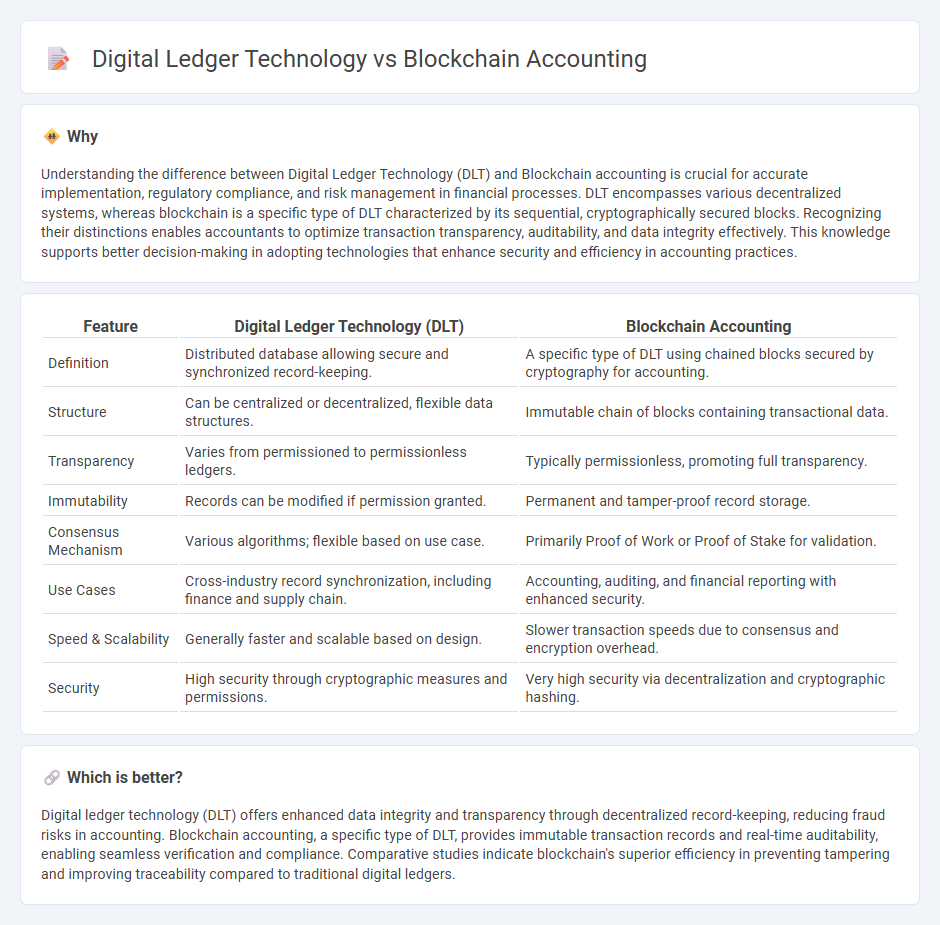
Understanding the difference between Digital Ledger Technology (DLT) and Blockchain accounting is crucial for accurate implementation, regulatory compliance, and risk management in financial processes. DLT encompasses various decentralized systems, whereas blockchain is a specific type of DLT characterized by its sequential, cryptographically secured blocks. Recognizing their distinctions enables accountants to optimize transaction transparency, auditability, and data integrity effectively. This knowledge supports better decision-making in adopting technologies that enhance security and efficiency in accounting practices.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Ledger Technology (DLT) | Blockchain Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Distributed database allowing secure and synchronized record-keeping. | A specific type of DLT using chained blocks secured by cryptography for accounting. |
| Structure | Can be centralized or decentralized, flexible data structures. | Immutable chain of blocks containing transactional data. |
| Transparency | Varies from permissioned to permissionless ledgers. | Typically permissionless, promoting full transparency. |
| Immutability | Records can be modified if permission granted. | Permanent and tamper-proof record storage. |
| Consensus Mechanism | Various algorithms; flexible based on use case. | Primarily Proof of Work or Proof of Stake for validation. |
| Use Cases | Cross-industry record synchronization, including finance and supply chain. | Accounting, auditing, and financial reporting with enhanced security. |
| Speed & Scalability | Generally faster and scalable based on design. | Slower transaction speeds due to consensus and encryption overhead. |
| Security | High security through cryptographic measures and permissions. | Very high security via decentralization and cryptographic hashing. |
Which is better?
Digital ledger technology (DLT) offers enhanced data integrity and transparency through decentralized record-keeping, reducing fraud risks in accounting. Blockchain accounting, a specific type of DLT, provides immutable transaction records and real-time auditability, enabling seamless verification and compliance. Comparative studies indicate blockchain's superior efficiency in preventing tampering and improving traceability compared to traditional digital ledgers.
Connection
Digital ledger technology (DLT) serves as the foundational framework for blockchain accounting by providing a decentralized, immutable record-keeping system that enhances transparency and security. Blockchain accounting utilizes this technology to automate transaction verification, reduce errors, and streamline audits through cryptographic validation and consensus mechanisms. This connection transforms traditional accounting practices by enabling real-time data access and fostering trust among stakeholders.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Blockchain accounting ensures decentralization by distributing transaction records across a network of nodes, making data tampering nearly impossible and enhancing transparency. Digital ledger technology (DLT), while also decentralized, may operate with varying degrees of central control depending on the implementation, influencing security and trust levels. Explore the nuances of decentralization in blockchain accounting versus DLT to understand their impact on financial integrity.
Immutability
Blockchain accounting ensures immutability by recording transactions in a decentralized, tamper-proof ledger where each block is cryptographically linked, preventing data alteration. Digital ledger technology (DLT) offers a broader range of architectures, but not all guarantee the same level of immutability as blockchain's consensus mechanisms and cryptographic proofs. Explore the nuances of how immutability impacts financial auditing and data integrity in blockchain and other DLT systems to deepen your understanding.
Smart contracts
Blockchain accounting integrates digital ledger technology (DLT) to create immutable transaction records, leveraging smart contracts to automate and enforce financial agreements without intermediaries. Smart contracts within blockchain systems enable real-time auditing, enhanced transparency, and reduce manual errors by executing programmable rules on decentralized ledgers. Explore the advantages and practical applications of smart contracts in blockchain accounting to understand their transformative impact.
Source and External Links
How Blockchain is Changing Accounting Practices - Paystand - Blockchain transforms accounting by providing a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger that enhances transaction recording, audit trails, automated reconciliations, fraud detection, inventory management, financial reporting, taxation, smart contracts, and data security.
What is Blockchain Accounting? - FreshBooks - Blockchain accounting supports auditors and accountants by verifying transactions securely, reducing the need for manual paper trails, but it does not replace traditional accounting as it lacks detail like transaction purpose or categorization.
Blockchain Accounting - Guide & Use Cases - Blockchain accounting uses immutable, shared ledgers and smart contracts to automate accounting tasks, reduce fraud, simplify audits via triple entry accounting, and enable cost reductions through AI and automation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com