Ledger tokenization transforms traditional accounting entries into digital tokens, enhancing transaction traceability and security. Blockchain recordkeeping decentralizes financial data, ensuring immutable and transparent transaction history across distributed networks. Discover more about how these innovative approaches revolutionize accounting accuracy and efficiency.
Why it is important
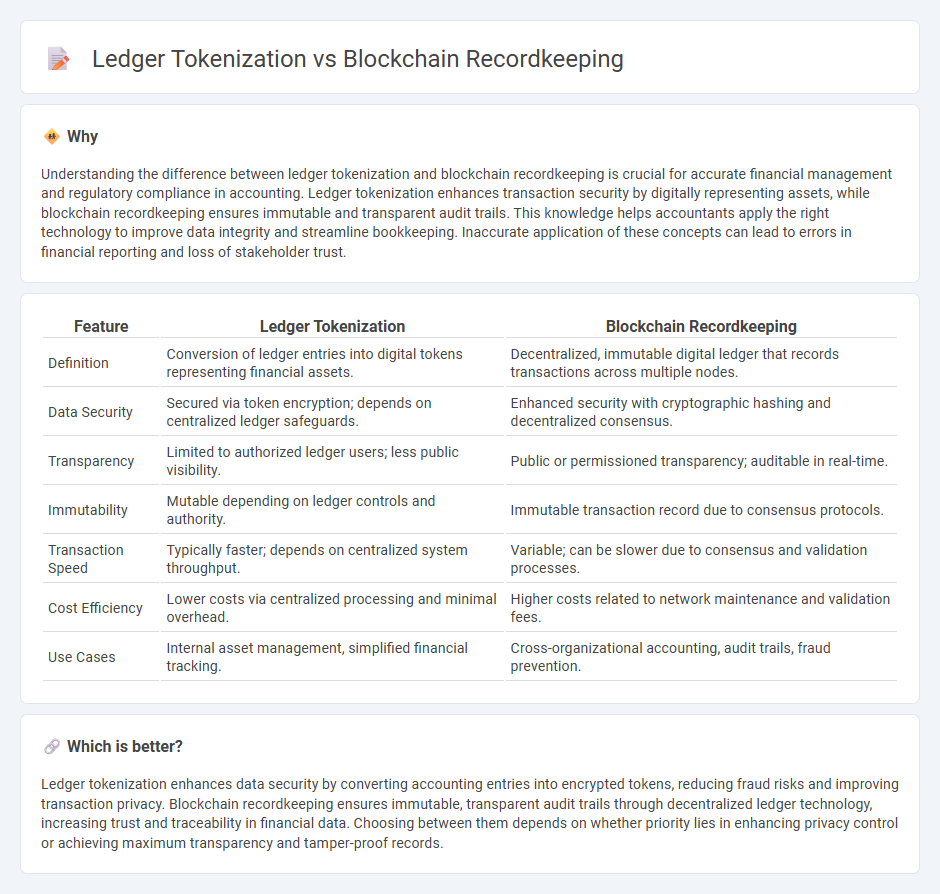
Understanding the difference between ledger tokenization and blockchain recordkeeping is crucial for accurate financial management and regulatory compliance in accounting. Ledger tokenization enhances transaction security by digitally representing assets, while blockchain recordkeeping ensures immutable and transparent audit trails. This knowledge helps accountants apply the right technology to improve data integrity and streamline bookkeeping. Inaccurate application of these concepts can lead to errors in financial reporting and loss of stakeholder trust.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ledger Tokenization | Blockchain Recordkeeping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Conversion of ledger entries into digital tokens representing financial assets. | Decentralized, immutable digital ledger that records transactions across multiple nodes. |
| Data Security | Secured via token encryption; depends on centralized ledger safeguards. | Enhanced security with cryptographic hashing and decentralized consensus. |
| Transparency | Limited to authorized ledger users; less public visibility. | Public or permissioned transparency; auditable in real-time. |
| Immutability | Mutable depending on ledger controls and authority. | Immutable transaction record due to consensus protocols. |
| Transaction Speed | Typically faster; depends on centralized system throughput. | Variable; can be slower due to consensus and validation processes. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower costs via centralized processing and minimal overhead. | Higher costs related to network maintenance and validation fees. |
| Use Cases | Internal asset management, simplified financial tracking. | Cross-organizational accounting, audit trails, fraud prevention. |
Which is better?
Ledger tokenization enhances data security by converting accounting entries into encrypted tokens, reducing fraud risks and improving transaction privacy. Blockchain recordkeeping ensures immutable, transparent audit trails through decentralized ledger technology, increasing trust and traceability in financial data. Choosing between them depends on whether priority lies in enhancing privacy control or achieving maximum transparency and tamper-proof records.
Connection
Ledger tokenization enhances blockchain recordkeeping by converting physical and digital assets into secure, tradable tokens recorded on an immutable ledger. This integration ensures transparent, tamper-proof accounting records, improving auditability and reducing fraud risks. Blockchain's decentralized nature supports real-time synchronization of tokenized assets across multiple stakeholders, streamlining verification and reconciliation processes in accounting systems.
Key Terms
Immutable Ledger
Immutable ledger technology ensures tamper-proof recordkeeping by securely logging transactions on a blockchain, making historical data unalterable and transparent. Ledger tokenization enhances this by converting asset ownership into digital tokens recorded on the same immutable ledger, facilitating efficient asset transfers without compromising data integrity. Explore the transformative benefits of combining blockchain recordkeeping with ledger tokenization for resilient digital asset management.
Smart Contracts
Blockchain recordkeeping ensures immutability and transparency by securely storing transaction data in decentralized ledgers, while ledger tokenization leverages smart contracts to represent real-world assets as digital tokens with programmable features. Smart contracts automate transactions and enforce rules without intermediaries, enhancing efficiency and reducing settlement times in tokenized ledgers. Explore how integrating smart contracts revolutionizes asset management and transaction processing in blockchain ecosystems.
Asset Tokenization
Asset tokenization transforms physical assets into digital tokens on a blockchain, enabling fractional ownership, enhanced liquidity, and seamless trading across decentralized platforms. Blockchain recordkeeping ensures transparent, immutable data storage, providing a secure audit trail that underpins the trustworthiness of asset tokens. Explore how asset tokenization revolutionizes ownership models and investment opportunities in the digital economy.
Source and External Links
Expert Guide: Implementing Blockchain for Secure Record-Keeping - Blockchain acts as an immutable digital ledger, enhancing record-keeping by providing security, transparency, and decentralization that prevent tampering and enable trustworthy data management across organizations.
Blockchain in Recordkeeping - Blockchain offers encrypted, decentralized, and transparent record-keeping solutions ideal for sensitive data such as government and land registries, enabling secure and unalterable record storage accessible only to authorized users.
BLOCKCHAIN RECORDKEEPING: A SWOT ANALYSIS - While blockchain provides immutable and verifiable records, private permissioned blockchains are preferable for many organizations to maintain control and governance over record integrity, mitigating risks from forks or ledger edits found in public blockchains.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com