Zero knowledge proofs in accounting enable verification of financial data without revealing sensitive details, enhancing privacy and security in audits. Cost accounting focuses on tracking, analyzing, and controlling costs to improve financial efficiency and decision-making within organizations. Explore how these innovative approaches transform accuracy and confidentiality in financial management.
Why it is important
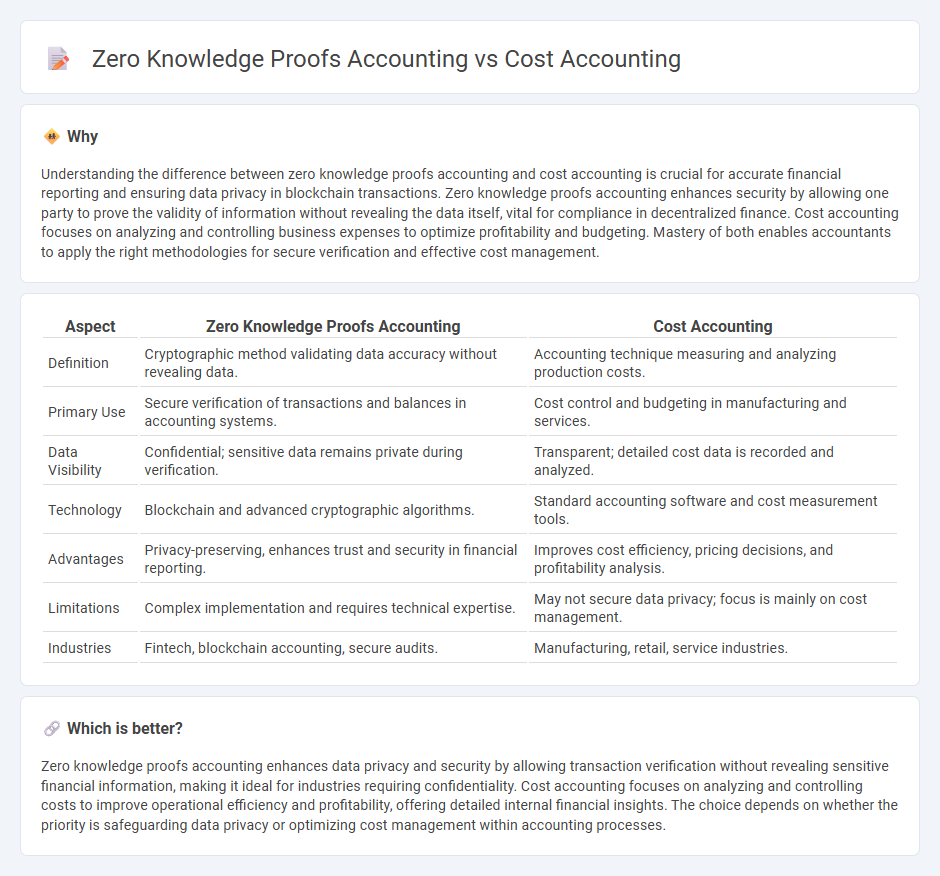
Understanding the difference between zero knowledge proofs accounting and cost accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and ensuring data privacy in blockchain transactions. Zero knowledge proofs accounting enhances security by allowing one party to prove the validity of information without revealing the data itself, vital for compliance in decentralized finance. Cost accounting focuses on analyzing and controlling business expenses to optimize profitability and budgeting. Mastery of both enables accountants to apply the right methodologies for secure verification and effective cost management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Knowledge Proofs Accounting | Cost Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptographic method validating data accuracy without revealing data. | Accounting technique measuring and analyzing production costs. |
| Primary Use | Secure verification of transactions and balances in accounting systems. | Cost control and budgeting in manufacturing and services. |
| Data Visibility | Confidential; sensitive data remains private during verification. | Transparent; detailed cost data is recorded and analyzed. |
| Technology | Blockchain and advanced cryptographic algorithms. | Standard accounting software and cost measurement tools. |
| Advantages | Privacy-preserving, enhances trust and security in financial reporting. | Improves cost efficiency, pricing decisions, and profitability analysis. |
| Limitations | Complex implementation and requires technical expertise. | May not secure data privacy; focus is mainly on cost management. |
| Industries | Fintech, blockchain accounting, secure audits. | Manufacturing, retail, service industries. |
Which is better?
Zero knowledge proofs accounting enhances data privacy and security by allowing transaction verification without revealing sensitive financial information, making it ideal for industries requiring confidentiality. Cost accounting focuses on analyzing and controlling costs to improve operational efficiency and profitability, offering detailed internal financial insights. The choice depends on whether the priority is safeguarding data privacy or optimizing cost management within accounting processes.
Connection
Zero-knowledge proofs enhance cost accounting by enabling secure verification of financial data without revealing sensitive information, thus improving transparency and trust in internal audits. Implementing cryptographic protocols ensures accurate cost allocation and fraud prevention while maintaining confidentiality. This integration supports efficient resource management and compliance with regulatory standards.
Key Terms
**Cost Accounting:**
Cost accounting involves tracking, recording, and analyzing costs associated with production to optimize budgeting and improve financial efficiency in businesses. It uses detailed data on direct materials, labor, and overhead to provide actionable insights for decision-making and cost control. Explore more to understand how cost accounting drives profitability and resource management in various industries.
Cost Allocation
Cost accounting allocates expenses to products or departments based on resource consumption, enabling detailed financial analysis for budgeting and cost control. Zero knowledge proofs accounting uses cryptographic methods to verify transaction accuracy and allocation without revealing sensitive financial data, enhancing privacy and security. Explore how zero knowledge proofs transform traditional cost allocation by safeguarding information while maintaining transparency.
Overhead
Cost accounting allocates overhead costs based on predefined cost drivers to measure product profitability and improve operational efficiency, relying heavily on historical data accuracy. Zero knowledge proofs (ZKPs) accounting uses cryptographic methods to verify overhead cost calculations without revealing sensitive financial details, enhancing privacy and security in financial audits. Explore the benefits and applications of integrating zero knowledge proofs into traditional overhead cost accounting for robust financial management.
Source and External Links
Cost Accounting Defined: What It Is & Why It Matters - Cost accounting is the process of tracking, analyzing, and summarizing all fixed and variable costs related to the production of a product or service to help management control costs and make pricing decisions, and it is used internally rather than for external reporting.
Cost Accounting: Everything You Need to Know - Cost accounting is a branch of managerial accounting focused on analyzing production costs using methods like job costing or activity-based costing, enabling businesses to optimize pricing and budgeting through systematic cost tracking and review.
How to Become a Cost Accountant - Cost accountants manage and evaluate a company's operating expenses to increase profits by tracking budgets, setting standard costs, and working mainly with internal departments across various industries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com