Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to promote transparency and environmental responsibility, while creative accounting involves manipulating financial information to mislead stakeholders. Accurate carbon accounting supports sustainable business practices and regulatory compliance, contrasting with the unethical nature of creative accounting that distorts financial reality. Explore the distinctions between these accounting approaches to enhance your understanding of corporate ethics and sustainability.
Why it is important
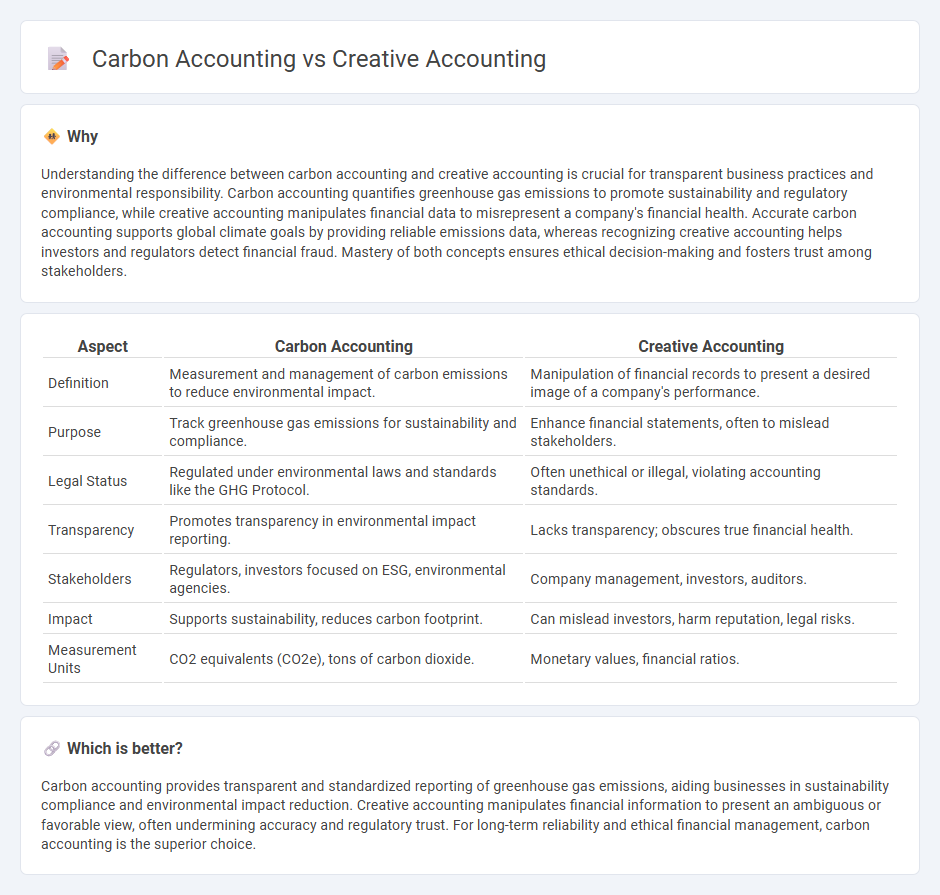
Understanding the difference between carbon accounting and creative accounting is crucial for transparent business practices and environmental responsibility. Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to promote sustainability and regulatory compliance, while creative accounting manipulates financial data to misrepresent a company's financial health. Accurate carbon accounting supports global climate goals by providing reliable emissions data, whereas recognizing creative accounting helps investors and regulators detect financial fraud. Mastery of both concepts ensures ethical decision-making and fosters trust among stakeholders.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Accounting | Creative Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement and management of carbon emissions to reduce environmental impact. | Manipulation of financial records to present a desired image of a company's performance. |
| Purpose | Track greenhouse gas emissions for sustainability and compliance. | Enhance financial statements, often to mislead stakeholders. |
| Legal Status | Regulated under environmental laws and standards like the GHG Protocol. | Often unethical or illegal, violating accounting standards. |
| Transparency | Promotes transparency in environmental impact reporting. | Lacks transparency; obscures true financial health. |
| Stakeholders | Regulators, investors focused on ESG, environmental agencies. | Company management, investors, auditors. |
| Impact | Supports sustainability, reduces carbon footprint. | Can mislead investors, harm reputation, legal risks. |
| Measurement Units | CO2 equivalents (CO2e), tons of carbon dioxide. | Monetary values, financial ratios. |
Which is better?
Carbon accounting provides transparent and standardized reporting of greenhouse gas emissions, aiding businesses in sustainability compliance and environmental impact reduction. Creative accounting manipulates financial information to present an ambiguous or favorable view, often undermining accuracy and regulatory trust. For long-term reliability and ethical financial management, carbon accounting is the superior choice.
Connection
Carbon accounting and creative accounting both involve the systematic recording and reporting of data, with carbon accounting focusing on quantifying greenhouse gas emissions to support environmental sustainability. Creative accounting employs maneuvers within legal frameworks to present financial statements in a more favorable light, which may sometimes obscure accurate carbon footprint disclosures. The integrity of carbon accounting relies on transparent and ethical accounting practices, highlighting the risk that creative accounting techniques can undermine environmental reporting accuracy.
Key Terms
Creative Accounting:
Creative accounting involves manipulating financial statements and accounting practices to present a misleadingly favorable view of a company's financial position, often bending accounting rules without outright fraud. It contrasts with carbon accounting, which objectively measures and reports greenhouse gas emissions to enhance environmental transparency and regulatory compliance. Explore how creative accounting impacts corporate governance and financial integrity for deeper insights.
Earnings Management
Creative accounting manipulates financial statements to enhance reported earnings, often obscuring true financial performance through aggressive revenue recognition or expense deferrals. Carbon accounting tracks greenhouse gas emissions and associated costs, integrating environmental impact into financial reports to support sustainable earnings management. Explore how aligning carbon accounting with earnings management can promote transparency and responsible corporate practices.
Off-Balance Sheet
Creative accounting often involves off-balance sheet tactics to manipulate financial statements, hiding liabilities or inflating assets to present a healthier corporate financial position. Carbon accounting uses off-balance sheet reporting to transparently track greenhouse gas emissions and environmental liabilities that traditional financial statements may overlook. Discover how off-balance sheet approaches differ in financial manipulation versus environmental accountability.
Source and External Links
Creative Accounting: What it is, Types, and Methods - This article explains creative accounting, its types, and methods, including manipulating financial statements using accounting loopholes.
Creative Accounting: Definition, Types & Methods - FreshBooks - This page provides a definition of creative accounting, discussing its methods and how it involves taking advantage of accounting loopholes.
Creative Accounting - Wikipedia - This Wikipedia article defines creative accounting as practices that follow accounting rules but manipulate financial reporting, often for misleading purposes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com