Forensic analytics involves examining financial data to detect fraud, errors, and irregularities, utilizing advanced statistical techniques and investigative procedures. Valuation analysis focuses on determining the economic value of assets, companies, or investments through methods like discounted cash flow, market comparables, and asset-based valuation. Explore the differences between forensic analytics and valuation analysis to enhance your accounting expertise.
Why it is important
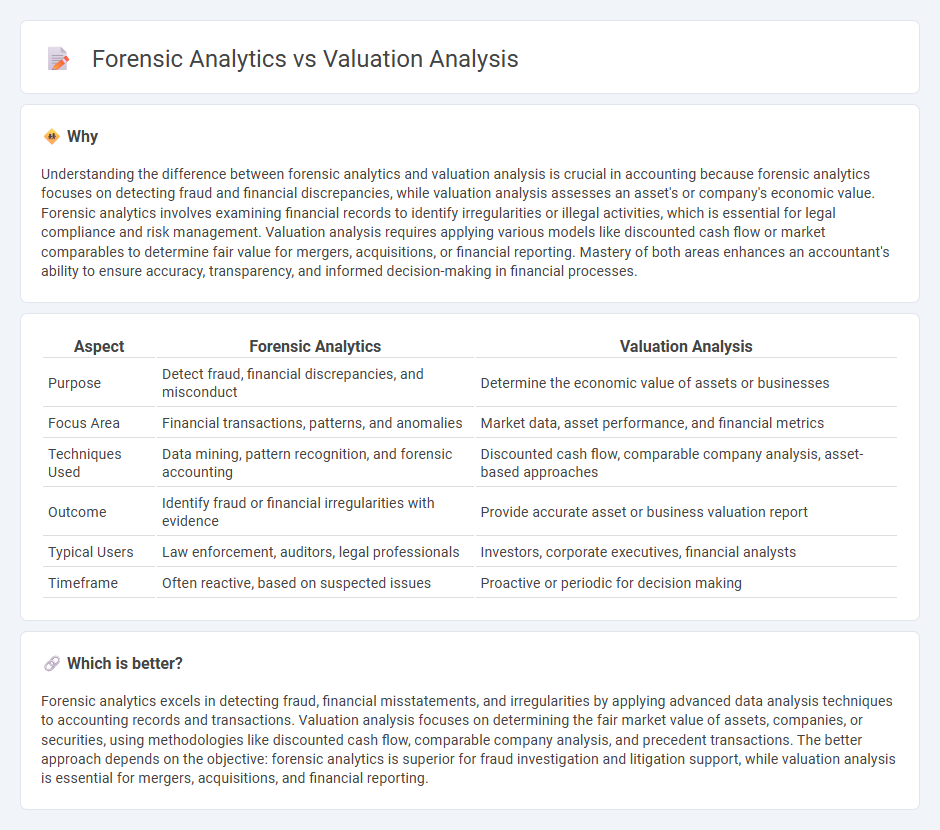
Understanding the difference between forensic analytics and valuation analysis is crucial in accounting because forensic analytics focuses on detecting fraud and financial discrepancies, while valuation analysis assesses an asset's or company's economic value. Forensic analytics involves examining financial records to identify irregularities or illegal activities, which is essential for legal compliance and risk management. Valuation analysis requires applying various models like discounted cash flow or market comparables to determine fair value for mergers, acquisitions, or financial reporting. Mastery of both areas enhances an accountant's ability to ensure accuracy, transparency, and informed decision-making in financial processes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Forensic Analytics | Valuation Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, financial discrepancies, and misconduct | Determine the economic value of assets or businesses |
| Focus Area | Financial transactions, patterns, and anomalies | Market data, asset performance, and financial metrics |
| Techniques Used | Data mining, pattern recognition, and forensic accounting | Discounted cash flow, comparable company analysis, asset-based approaches |
| Outcome | Identify fraud or financial irregularities with evidence | Provide accurate asset or business valuation report |
| Typical Users | Law enforcement, auditors, legal professionals | Investors, corporate executives, financial analysts |
| Timeframe | Often reactive, based on suspected issues | Proactive or periodic for decision making |
Which is better?
Forensic analytics excels in detecting fraud, financial misstatements, and irregularities by applying advanced data analysis techniques to accounting records and transactions. Valuation analysis focuses on determining the fair market value of assets, companies, or securities, using methodologies like discounted cash flow, comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions. The better approach depends on the objective: forensic analytics is superior for fraud investigation and litigation support, while valuation analysis is essential for mergers, acquisitions, and financial reporting.
Connection
Forensic analytics and valuation analysis intersect by utilizing financial data examination to detect discrepancies and assess asset worth accurately. Forensic analytics uncovers fraudulent activities and irregularities impacting valuation models, ensuring reliable financial reporting. Valuation analysis relies on these findings to adjust asset values, providing a transparent basis for legal and investment decisions.
Key Terms
Valuation analysis:
Valuation analysis involves determining the fair market value of assets, companies, or securities through methods like discounted cash flow, comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions to guide investment decisions and financial reporting. It requires a deep understanding of financial statements, market conditions, and industry trends to produce accurate and reliable valuations. Explore detailed methodologies and real-world applications to enhance your valuation analysis expertise.
Fair Value
Valuation analysis assesses the fair value of assets or companies by examining market conditions, financial performance, and comparable transactions to ensure an accurate financial representation. Forensic analytics investigates discrepancies in fair value assessments by analyzing data patterns and potential manipulations, often uncovering financial misstatements or fraud. Explore detailed methodologies and case studies to understand how each approach refines fair value accuracy.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
Valuation analysis using Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) focuses on estimating the intrinsic value of an asset by projecting future cash flows and discounting them to present value using a specific discount rate. Forensic analytics leverages DCF in investigating potential financial discrepancies, fraud, or manipulation by closely examining cash flow assumptions and discount rates for inconsistencies. Explore deeper insights into how DCF supports both valuation accuracy and forensic investigations.
Source and External Links
Valuation Analysis Definition, Methods & Ratios - Valuation analysis is the process of determining the fair value of a company or asset using various methods and ratios like the price-to-earnings ratio, EBIT multiple, and enterprise value to sales ratio, with emphasis on using multiple metrics for a comprehensive assessment.
What is Valuation in Finance? Methods to Value a Company - Valuation determines a company's intrinsic value via approaches including discounted cash flow (DCF), comparable company analysis, and precedent transactions, and applies asset, income, or market methods depending on context.
How to Value a Company: 6 Methods and Examples - Company valuation can be performed through multiple methods such as discounted cash flow analysis, which estimates present value of expected future cash flows, and market capitalization, which multiplies share price by total shares to estimate equity value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com