Taxonomy alignment in accounting involves organizing financial data according to standardized classification systems to ensure consistency and comparability across entities and jurisdictions. Transfer pricing refers to the rules and methods for pricing transactions between related entities within multinational corporations, crucial for tax compliance and profit allocation. Explore more to understand how taxonomy alignment supports effective transfer pricing strategies and regulatory adherence.
Why it is important
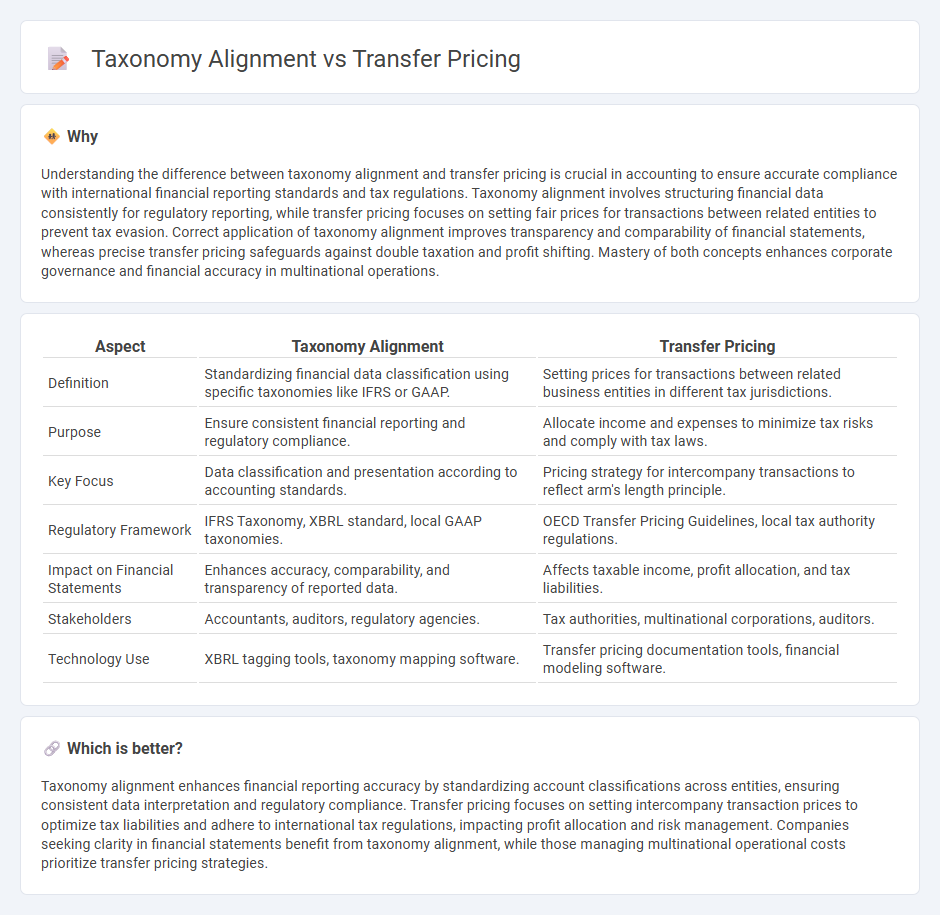
Understanding the difference between taxonomy alignment and transfer pricing is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate compliance with international financial reporting standards and tax regulations. Taxonomy alignment involves structuring financial data consistently for regulatory reporting, while transfer pricing focuses on setting fair prices for transactions between related entities to prevent tax evasion. Correct application of taxonomy alignment improves transparency and comparability of financial statements, whereas precise transfer pricing safeguards against double taxation and profit shifting. Mastery of both concepts enhances corporate governance and financial accuracy in multinational operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Taxonomy Alignment | Transfer Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Standardizing financial data classification using specific taxonomies like IFRS or GAAP. | Setting prices for transactions between related business entities in different tax jurisdictions. |
| Purpose | Ensure consistent financial reporting and regulatory compliance. | Allocate income and expenses to minimize tax risks and comply with tax laws. |
| Key Focus | Data classification and presentation according to accounting standards. | Pricing strategy for intercompany transactions to reflect arm's length principle. |
| Regulatory Framework | IFRS Taxonomy, XBRL standard, local GAAP taxonomies. | OECD Transfer Pricing Guidelines, local tax authority regulations. |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Enhances accuracy, comparability, and transparency of reported data. | Affects taxable income, profit allocation, and tax liabilities. |
| Stakeholders | Accountants, auditors, regulatory agencies. | Tax authorities, multinational corporations, auditors. |
| Technology Use | XBRL tagging tools, taxonomy mapping software. | Transfer pricing documentation tools, financial modeling software. |
Which is better?
Taxonomy alignment enhances financial reporting accuracy by standardizing account classifications across entities, ensuring consistent data interpretation and regulatory compliance. Transfer pricing focuses on setting intercompany transaction prices to optimize tax liabilities and adhere to international tax regulations, impacting profit allocation and risk management. Companies seeking clarity in financial statements benefit from taxonomy alignment, while those managing multinational operational costs prioritize transfer pricing strategies.
Connection
Taxonomy alignment ensures consistent classification of financial transactions and assets across jurisdictions, which supports accurate documentation required for transfer pricing compliance. Accurate taxonomy alignment enables multinational corporations to systematically categorize intercompany transactions, facilitating transparent transfer pricing analyses. This consistency minimizes risks of regulatory discrepancies and tax adjustments by aligning financial reporting with transfer pricing policies.
Key Terms
Arm's Length Principle
Transfer pricing regulations enforce the Arm's Length Principle, ensuring intercompany transactions reflect market conditions to prevent profit shifting and tax base erosion. Taxonomy alignment, though primarily environmental and sustainability-focused, indirectly influences transfer pricing by promoting transparent and standardized reporting frameworks. Discover how integrating transfer pricing compliance and taxonomy alignment can optimize multinational tax strategies.
OECD Guidelines
Transfer pricing under OECD Guidelines ensures transactions between related parties are conducted at arm's length to prevent tax base erosion and profit shifting. Taxonomy alignment involves integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria into corporate reporting, a concept not directly addressed by transfer pricing rules but increasingly important for multinational enterprises. Explore further how OECD frameworks harmonize fiscal compliance with sustainable business practices.
ESG Criteria
Transfer pricing and taxonomy alignment both address ESG criteria by promoting transparency and sustainability in financial practices; transfer pricing ensures fair intra-company transactions reflecting economic realities, while taxonomy alignment classifies economic activities based on their environmental impact. Effective integration of these frameworks supports corporate compliance with regulatory demands and drives investment toward sustainable projects. Explore how harmonizing transfer pricing and taxonomy alignment can enhance your ESG strategy and regulatory compliance.
Source and External Links
Intra-group transactions: the principles of transfer pricing - This article explores the principles of transfer pricing, which are used to determine the taxable profits of multinational enterprises by setting prices for goods and services between related parties.
What is transfer pricing? - Transfer pricing is a technique used by multinational corporations to shift profits out of the countries where they operate and into tax havens.
Transfer Pricing and Cross-Border Transactions - This resource discusses transfer pricing as a mechanism for determining arm's length pricing in related-party transactions across borders.
Transfer pricing in The United States - This article provides an overview of transfer pricing rules in the U.S., including acceptable methods for tangible and intangible property transactions.
Transfer pricing examination process - The IRS offers guidelines for conducting transfer pricing examinations to ensure compliance with tax laws.
Transfer Pricing and Cross-Border Transactions - This article discusses U.S. transfer pricing regulations under SS482 and international guidelines from the OECD to prevent profit shifting.
What is transfer pricing? - Transfer pricing strategies can be used to shift profits to tax havens, avoiding tax in countries where business is conducted.
Intra-group transactions: the principles of transfer pricing - Transfer pricing is essential for multinational enterprises to set prices for goods and services between related parties, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
Transfer Pricing and Cross-Border Transactions - International regulations aim to ensure that transfer prices reflect arm's length transactions, preventing profit shifting and double taxation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com