Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional accounting by adding a cryptographic verification layer, improving transaction transparency and fraud prevention. Continuous auditing leverages real-time data analysis to provide ongoing financial oversight, ensuring compliance and accuracy throughout reporting periods. Explore how these innovative approaches reshape financial accountability and audit processes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between triple entry bookkeeping and continuous auditing is crucial for enhancing financial transparency and security. Triple entry bookkeeping integrates blockchain technology to create an immutable record of transactions, reducing fraud risks and improving trust. Continuous auditing enables real-time evaluation of financial data, allowing for rapid detection and correction of discrepancies. Businesses leveraging both methods can achieve comprehensive, accurate, and timely financial oversight.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Triple Entry Bookkeeping | Continuous Auditing |
|---|---|---|
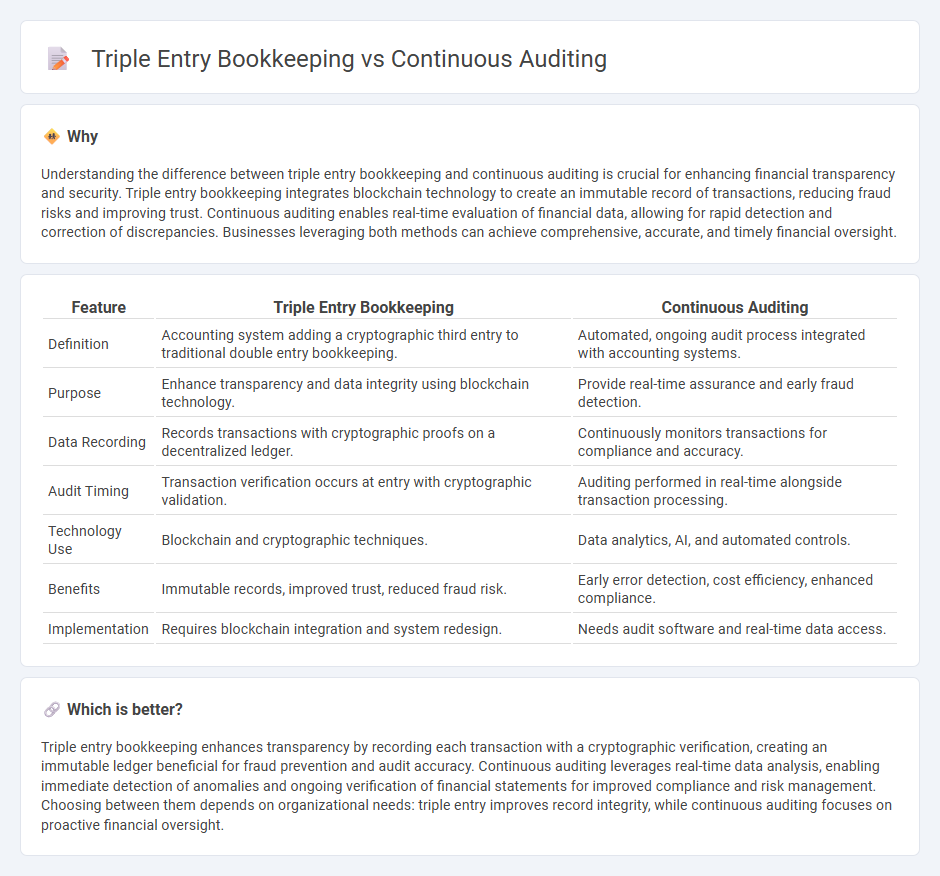
| Definition | Accounting system adding a cryptographic third entry to traditional double entry bookkeeping. | Automated, ongoing audit process integrated with accounting systems. |
| Purpose | Enhance transparency and data integrity using blockchain technology. | Provide real-time assurance and early fraud detection. |
| Data Recording | Records transactions with cryptographic proofs on a decentralized ledger. | Continuously monitors transactions for compliance and accuracy. |
| Audit Timing | Transaction verification occurs at entry with cryptographic validation. | Auditing performed in real-time alongside transaction processing. |
| Technology Use | Blockchain and cryptographic techniques. | Data analytics, AI, and automated controls. |
| Benefits | Immutable records, improved trust, reduced fraud risk. | Early error detection, cost efficiency, enhanced compliance. |
| Implementation | Requires blockchain integration and system redesign. | Needs audit software and real-time data access. |
Which is better?
Triple entry bookkeeping enhances transparency by recording each transaction with a cryptographic verification, creating an immutable ledger beneficial for fraud prevention and audit accuracy. Continuous auditing leverages real-time data analysis, enabling immediate detection of anomalies and ongoing verification of financial statements for improved compliance and risk management. Choosing between them depends on organizational needs: triple entry improves record integrity, while continuous auditing focuses on proactive financial oversight.
Connection
Triple entry bookkeeping integrates blockchain technology to create an immutable ledger, enabling real-time verification of transactions. Continuous auditing leverages this transparent and tamper-proof data to perform ongoing, automated checks, enhancing accuracy and fraud detection. The connection lies in the synergistic use of blockchain's immutable records and continuous auditing's real-time monitoring for improved financial transparency.
Key Terms
**Continuous Auditing:**
Continuous auditing leverages real-time data analytics and automated processes to provide ongoing assurance and immediate detection of anomalies within financial transactions. This approach enhances transparency and reduces the risk of errors or fraud compared to traditional audit methods. Explore detailed insights and practical applications of continuous auditing to transform your audit strategy.
Real-time Data Monitoring
Continuous auditing leverages real-time data monitoring to provide ongoing assurance by automatically analyzing financial transactions as they occur, enhancing transparency and reducing the risk of errors or fraud. Triple entry bookkeeping integrates blockchain technology to create immutable records with cryptographic verification, enabling secure and tamper-proof transaction tracking. Explore the differences in depth to understand how these methods revolutionize financial integrity and oversight.
Automated Controls
Continuous auditing leverages automated controls to provide real-time assurance by continuously monitoring financial transactions and compliance, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in detecting anomalies. Triple entry bookkeeping incorporates cryptographic verification and blockchain technology to ensure transaction integrity and transparency through an immutable ledger, reducing fraud risks and manual reconciliations. Explore how integrating automated controls in these advanced accounting methods revolutionizes financial auditing and record-keeping.
Source and External Links
Best Practices for Implementing a Continuous Audit Approach - Continuous auditing is a technology-driven method that performs real-time and systematic assessments of financial and operational processes to detect issues as they occur, differing from traditional audits by its ongoing and automated nature, which enhances risk management and compliance.
Continuous audit and monitoring - PwC - Continuous auditing involves the continuous application of analytical rules on transactional data to detect anomalies soon after they occur, enabling organizations to reduce losses from fraud and control deficiencies through timely investigation and remediation.
Continuous Auditing: Advantages & Challenges - DataSnipper - Continuous auditing allows auditors to analyze every transaction in near real time using automation, greatly increasing accuracy and providing a more comprehensive, up-to-date view of an organization's financial activities compared to periodic sample-based audits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com