Supply chain finance accounting focuses on managing cash flow and optimizing payment processes between suppliers and buyers to improve working capital efficiency. Cost accounting, on the other hand, emphasizes tracking, recording, and analyzing production costs to aid in budgeting and financial decision-making. Explore the key differences between supply chain finance accounting and cost accounting to enhance your financial management strategies.
Why it is important
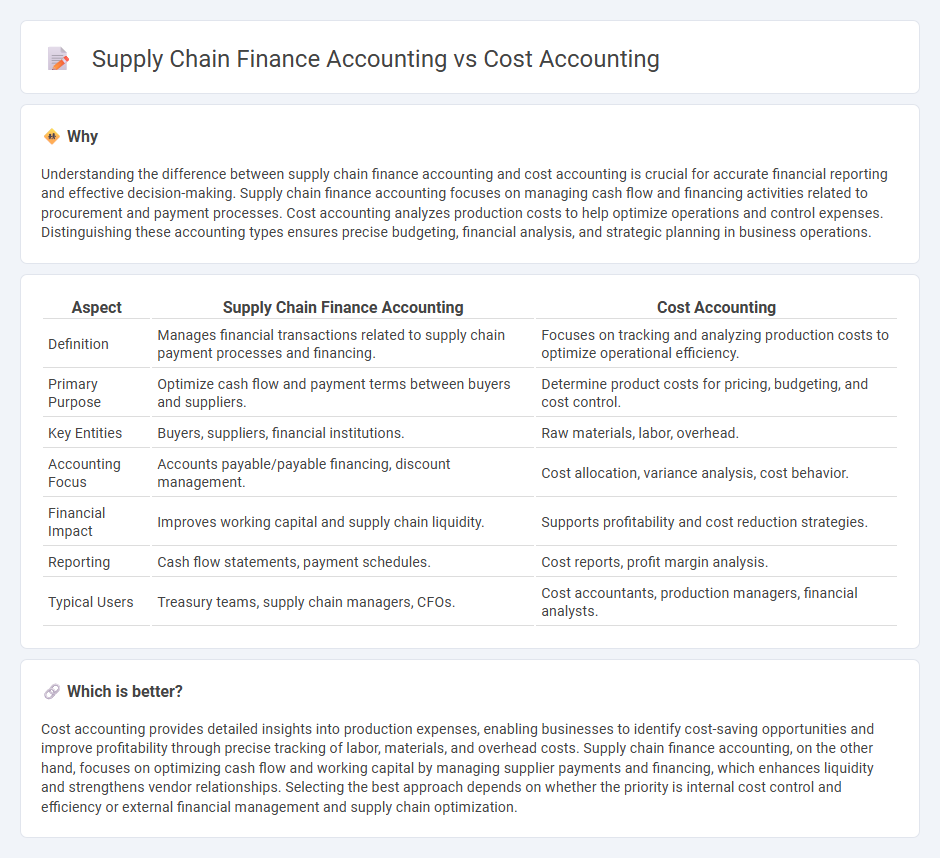
Understanding the difference between supply chain finance accounting and cost accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and effective decision-making. Supply chain finance accounting focuses on managing cash flow and financing activities related to procurement and payment processes. Cost accounting analyzes production costs to help optimize operations and control expenses. Distinguishing these accounting types ensures precise budgeting, financial analysis, and strategic planning in business operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Supply Chain Finance Accounting | Cost Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manages financial transactions related to supply chain payment processes and financing. | Focuses on tracking and analyzing production costs to optimize operational efficiency. |
| Primary Purpose | Optimize cash flow and payment terms between buyers and suppliers. | Determine product costs for pricing, budgeting, and cost control. |
| Key Entities | Buyers, suppliers, financial institutions. | Raw materials, labor, overhead. |
| Accounting Focus | Accounts payable/payable financing, discount management. | Cost allocation, variance analysis, cost behavior. |
| Financial Impact | Improves working capital and supply chain liquidity. | Supports profitability and cost reduction strategies. |
| Reporting | Cash flow statements, payment schedules. | Cost reports, profit margin analysis. |
| Typical Users | Treasury teams, supply chain managers, CFOs. | Cost accountants, production managers, financial analysts. |
Which is better?
Cost accounting provides detailed insights into production expenses, enabling businesses to identify cost-saving opportunities and improve profitability through precise tracking of labor, materials, and overhead costs. Supply chain finance accounting, on the other hand, focuses on optimizing cash flow and working capital by managing supplier payments and financing, which enhances liquidity and strengthens vendor relationships. Selecting the best approach depends on whether the priority is internal cost control and efficiency or external financial management and supply chain optimization.
Connection
Supply chain finance accounting and cost accounting are interconnected through the detailed tracking and analysis of expenses related to procurement, production, and logistics. Accurate cost accounting data facilitates effective supply chain financing decisions by identifying cost drivers and optimizing cash flow management across the supply chain. This integration enhances financial transparency, reduces working capital requirements, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Key Terms
**Cost Accounting:**
Cost accounting focuses on recording, analyzing, and controlling costs related to production processes, providing detailed insight into direct and indirect expenses of manufacturing goods or services. It plays a crucial role in budgeting, cost control, and performance evaluation by tracking material, labor, and overhead costs. Explore how cost accounting drives efficiency and profitability in your business operations.
Overhead Allocation
Overhead allocation in cost accounting involves assigning indirect costs like utilities, rent, and salaries to specific products or departments based on predetermined rates to accurately determine product cost and profitability. In supply chain finance accounting, overhead allocation emphasizes the distribution of financing costs and operational expenses across various supply chain activities, ensuring accurate cost control and cash flow management within procurement, production, and logistics. Explore comprehensive techniques and best practices in overhead allocation for both fields to optimize financial performance and decision-making.
Standard Costing
Standard costing in cost accounting involves assigning predetermined costs to products to measure performance and control expenses within manufacturing operations. In supply chain finance accounting, standard costing aids in evaluating financial efficiency across procurement, inventory management, and logistics by comparing actual costs against set benchmarks. Discover how integrating standard costing enhances financial transparency and operational efficiency in both fields.
Source and External Links
What Is Cost Accounting | A Guide for Businesses - BPM - Cost accounting is a specialized field focused on tracking, analyzing, and managing the expenses of producing goods or delivering services to help businesses improve profitability and operational efficiency.
Cost Accounting Defined: What It Is & Why It Matters - NetSuite - Cost accounting involves tracking, analyzing, and summarizing all fixed and variable input costs related to production or service delivery, providing internal management with data to control costs and inform pricing decisions.
Cost accounting - Wikipedia - Cost accounting uses systematic procedures to record and report the costs of manufacturing goods and delivering services, employing techniques like standard costing and variance analysis to aid managerial decision-making and inventory valuation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com