A sustainability ledger focuses on tracking financial and non-financial data related to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics to support transparent reporting and long-term value creation. A green ledger specifically records transactions and investments tied to environmentally friendly initiatives, such as renewable energy projects and carbon offsetting efforts. Explore how these ledgers enhance corporate accountability and drive sustainable business practices.
Why it is important
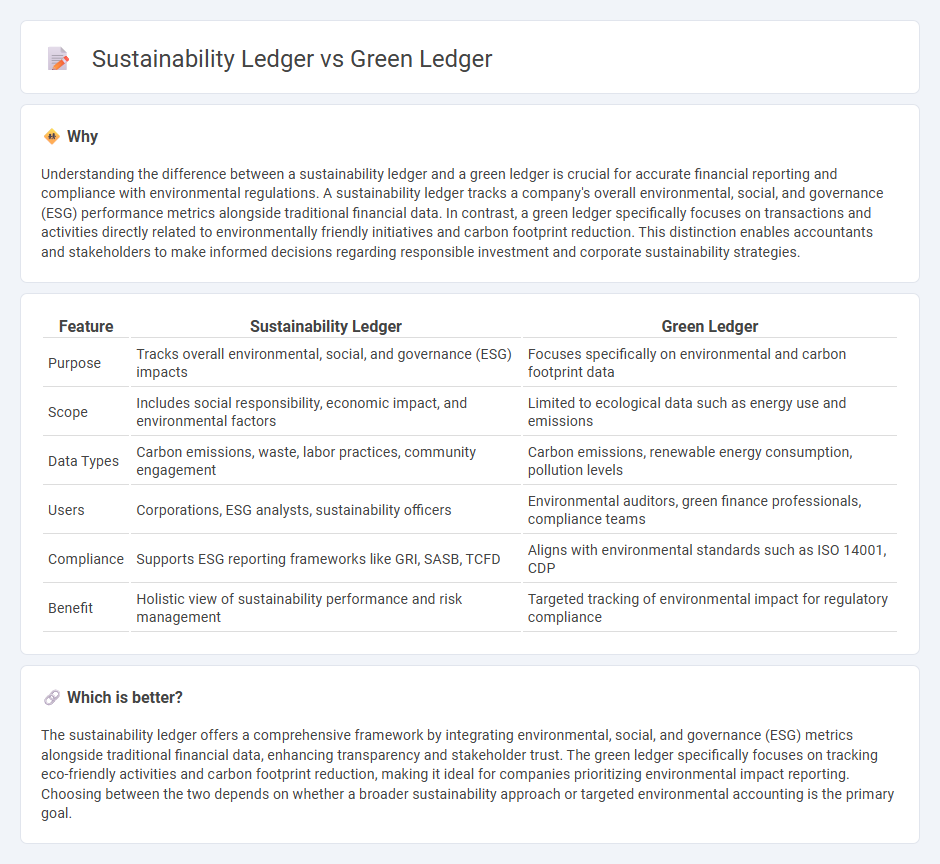
Understanding the difference between a sustainability ledger and a green ledger is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with environmental regulations. A sustainability ledger tracks a company's overall environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance metrics alongside traditional financial data. In contrast, a green ledger specifically focuses on transactions and activities directly related to environmentally friendly initiatives and carbon footprint reduction. This distinction enables accountants and stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding responsible investment and corporate sustainability strategies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Sustainability Ledger | Green Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Tracks overall environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts | Focuses specifically on environmental and carbon footprint data |
| Scope | Includes social responsibility, economic impact, and environmental factors | Limited to ecological data such as energy use and emissions |
| Data Types | Carbon emissions, waste, labor practices, community engagement | Carbon emissions, renewable energy consumption, pollution levels |
| Users | Corporations, ESG analysts, sustainability officers | Environmental auditors, green finance professionals, compliance teams |
| Compliance | Supports ESG reporting frameworks like GRI, SASB, TCFD | Aligns with environmental standards such as ISO 14001, CDP |
| Benefit | Holistic view of sustainability performance and risk management | Targeted tracking of environmental impact for regulatory compliance |
Which is better?
The sustainability ledger offers a comprehensive framework by integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics alongside traditional financial data, enhancing transparency and stakeholder trust. The green ledger specifically focuses on tracking eco-friendly activities and carbon footprint reduction, making it ideal for companies prioritizing environmental impact reporting. Choosing between the two depends on whether a broader sustainability approach or targeted environmental accounting is the primary goal.
Connection
Sustainability ledgers and green ledgers both track environmental and social impact data to support corporate responsibility and regulatory compliance. Sustainability ledgers encompass broader metrics including social, economic, and environmental factors, while green ledgers specifically focus on carbon footprints, energy usage, and resource consumption. Integration of these ledgers enhances transparency in ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting, enabling companies to align financial accounting with sustainability goals.
Key Terms
Carbon Accounting
Green ledger emphasizes recording environmentally related financial transactions, integrating carbon emissions data into traditional accounting systems for enhanced transparency. Sustainability ledger expands this scope by including broader environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics alongside carbon accounting to assess overall corporate impact. Explore how these ledgers transform carbon accounting practices for more effective climate action.
ESG Reporting
Green ledger emphasizes tracking environmental impacts such as carbon emissions and renewable energy usage within ESG reporting frameworks. Sustainability ledger integrates broader metrics including social responsibility, governance practices, and long-term organizational resilience in addition to environmental factors. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each ledger supports comprehensive ESG reporting strategies.
Double Materiality
Green ledger emphasizes environmental data recording, capturing carbon footprints, energy consumption, and waste management metrics. Sustainability ledger expands scope by integrating social, governance, and financial impacts with environmental data, adhering to double materiality principles that reflect both the company's impact on the environment and how environmental factors affect the company's financial performance. Explore deeper insights on leveraging double materiality for comprehensive sustainability accounting.
Source and External Links
SAP Launches SAP Green Ledger, a Carbon Accounting and Reporting System - SAP Green Ledger is a global carbon accounting solution that integrates emissions data directly into financial systems, enabling businesses to track, report, and optimize both environmental impact and financial performance in a single platform.
Maximize SAP Green Ledger: A Guide to Carbon Accounting Readiness - SAP Green Ledger combines ESG data, granular carbon footprint calculations, and supply chain carbon data sharing to streamline compliance, risk management, and audit-ready sustainability reporting for enterprises preparing for global regulations like CSRD and CBAM.
SAP Green Ledger - SAP Green Ledger addresses the growing need for credible emissions reporting by tightly integrating greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting with core business systems, helping organizations mitigate greenwashing risks, comply with regulations, and unlock new opportunities for growth and resilience.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com