Data lake reconciliation involves consolidating and verifying vast amounts of unstructured financial data stored in data lakes to ensure accuracy and consistency. Payables reconciliation focuses on matching accounts payable records against vendor invoices and payments to detect discrepancies and prevent errors in liability reporting. Explore how these reconciliation methods enhance financial integrity and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
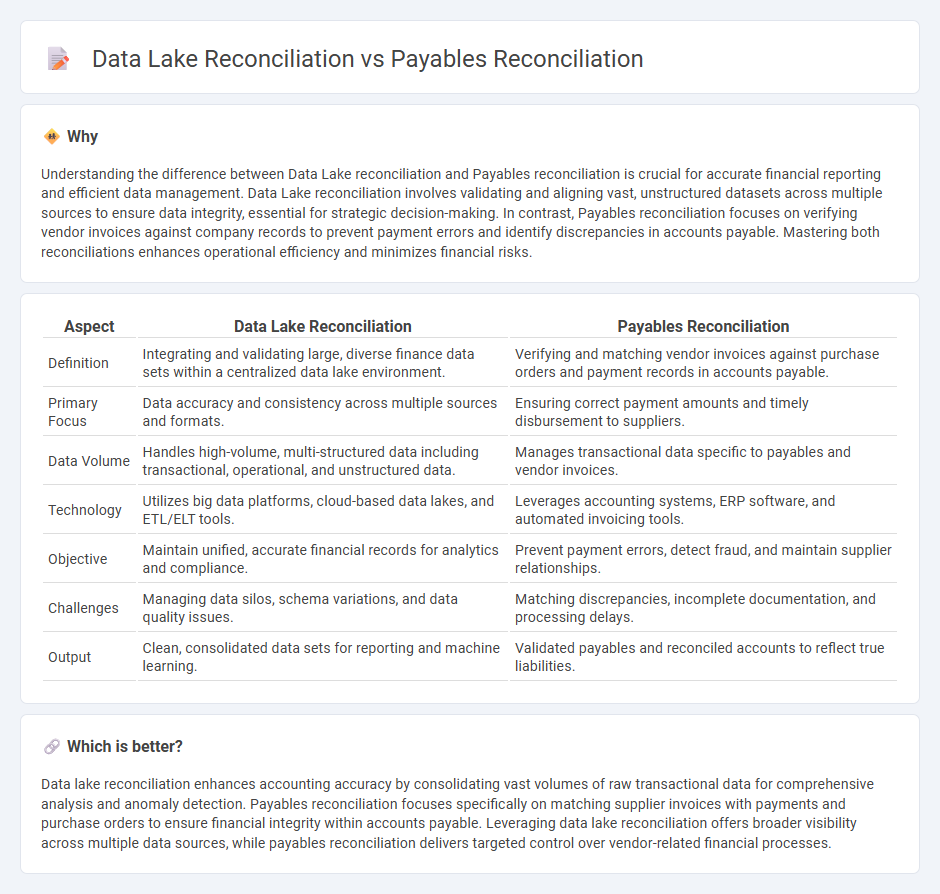
Understanding the difference between Data Lake reconciliation and Payables reconciliation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and efficient data management. Data Lake reconciliation involves validating and aligning vast, unstructured datasets across multiple sources to ensure data integrity, essential for strategic decision-making. In contrast, Payables reconciliation focuses on verifying vendor invoices against company records to prevent payment errors and identify discrepancies in accounts payable. Mastering both reconciliations enhances operational efficiency and minimizes financial risks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Data Lake Reconciliation | Payables Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrating and validating large, diverse finance data sets within a centralized data lake environment. | Verifying and matching vendor invoices against purchase orders and payment records in accounts payable. |
| Primary Focus | Data accuracy and consistency across multiple sources and formats. | Ensuring correct payment amounts and timely disbursement to suppliers. |
| Data Volume | Handles high-volume, multi-structured data including transactional, operational, and unstructured data. | Manages transactional data specific to payables and vendor invoices. |
| Technology | Utilizes big data platforms, cloud-based data lakes, and ETL/ELT tools. | Leverages accounting systems, ERP software, and automated invoicing tools. |
| Objective | Maintain unified, accurate financial records for analytics and compliance. | Prevent payment errors, detect fraud, and maintain supplier relationships. |
| Challenges | Managing data silos, schema variations, and data quality issues. | Matching discrepancies, incomplete documentation, and processing delays. |
| Output | Clean, consolidated data sets for reporting and machine learning. | Validated payables and reconciled accounts to reflect true liabilities. |
Which is better?
Data lake reconciliation enhances accounting accuracy by consolidating vast volumes of raw transactional data for comprehensive analysis and anomaly detection. Payables reconciliation focuses specifically on matching supplier invoices with payments and purchase orders to ensure financial integrity within accounts payable. Leveraging data lake reconciliation offers broader visibility across multiple data sources, while payables reconciliation delivers targeted control over vendor-related financial processes.
Connection
Data lake reconciliation enhances payables reconciliation by aggregating and harmonizing vast financial datasets from multiple sources, enabling more accurate and comprehensive matching of invoices and payments. The integration of real-time data lakes reduces errors and discrepancies in payables reconciliation processes by providing a unified, transparent view of transaction histories. Consequently, this connection streamlines financial reporting, improves compliance, and accelerates the resolution of outstanding payable balances.
Key Terms
Invoice Matching
Invoice matching in payables reconciliation involves verifying supplier invoices against purchase orders and payment records to ensure accuracy and prevent duplicate payments. In contrast, data lake reconciliation uses large-scale, unstructured data storage to aggregate and analyze invoice data from multiple sources, enabling advanced anomaly detection and comprehensive audit trails. Explore the detailed methodologies and benefits of each approach to optimize your invoice matching process.
Data Ingestion
Data ingestion in payables reconciliation involves extracting, validating, and matching vendor invoices and payment records to ensure accurate financial reporting, emphasizing source system integration and real-time updates. In contrast, data lake reconciliation focuses on consolidating diverse, large-scale datasets from multiple sources into a central repository, enabling advanced analytics and historical trend analysis for improved decision-making. Explore more about how efficient data ingestion strategies differentiate payables and data lake reconciliation processes.
Variance Analysis
Payables reconciliation involves matching supplier invoices against payment records to identify discrepancies in amounts due, while data lake reconciliation consolidates large volumes of heterogeneous data sources to ensure consistency across the enterprise. Variance analysis in payables typically centers on invoice matching errors, payment timing issues, and discrepancies in quantities or prices, whereas data lake variance analysis detects anomalies across integrated datasets, highlighting data quality issues or system integration gaps. Explore deeper insights into variance analysis techniques to enhance your reconciliation accuracy and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
How to Reconcile Accounts Payable in 8 Steps - BILL - Accounts payable reconciliation involves verifying beginning balances, collecting vendor invoices, payment receipts, and accounts payable aging reports, and ensuring all these match perfectly before closing the books each period.
How to reconcile accounts payable successfully in 10 steps - Brex - Effective accounts payable reconciliation requires gathering documentation like invoices, purchase orders, payment records, validating starting balances, and matching all transactions carefully to maintain accurate business finances.
How to reconcile accounts payable transactions for your business? - Accounts payable reconciliation compares supplier invoices against purchase orders and accounting records to confirm accuracy, revealing exact company dues and aiding in expense management and profit calculation at year's end.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com