Smart contracts accounting automates transaction verification through blockchain technology, reducing errors and increasing transparency compared to traditional double-entry bookkeeping. Double-entry bookkeeping records financial transactions in two accounts, ensuring accuracy and consistency in financial statements. Explore the differences and benefits of each method to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
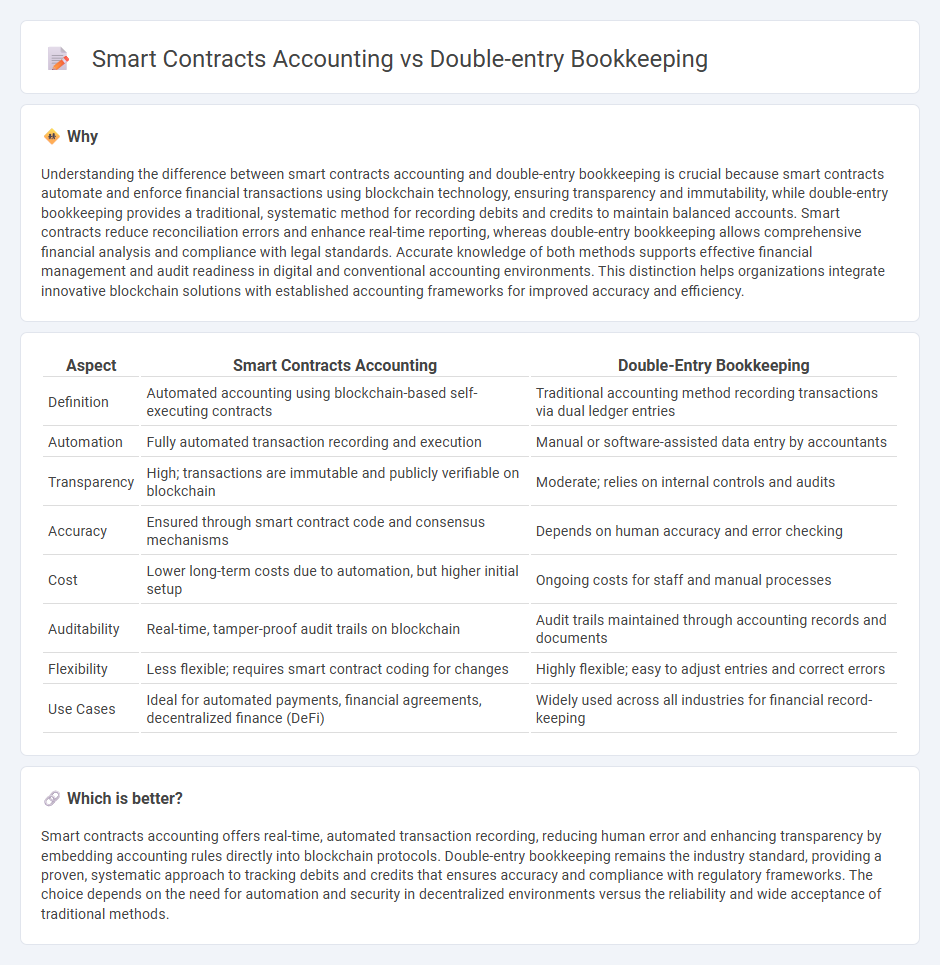
Understanding the difference between smart contracts accounting and double-entry bookkeeping is crucial because smart contracts automate and enforce financial transactions using blockchain technology, ensuring transparency and immutability, while double-entry bookkeeping provides a traditional, systematic method for recording debits and credits to maintain balanced accounts. Smart contracts reduce reconciliation errors and enhance real-time reporting, whereas double-entry bookkeeping allows comprehensive financial analysis and compliance with legal standards. Accurate knowledge of both methods supports effective financial management and audit readiness in digital and conventional accounting environments. This distinction helps organizations integrate innovative blockchain solutions with established accounting frameworks for improved accuracy and efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Contracts Accounting | Double-Entry Bookkeeping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated accounting using blockchain-based self-executing contracts | Traditional accounting method recording transactions via dual ledger entries |
| Automation | Fully automated transaction recording and execution | Manual or software-assisted data entry by accountants |
| Transparency | High; transactions are immutable and publicly verifiable on blockchain | Moderate; relies on internal controls and audits |
| Accuracy | Ensured through smart contract code and consensus mechanisms | Depends on human accuracy and error checking |
| Cost | Lower long-term costs due to automation, but higher initial setup | Ongoing costs for staff and manual processes |
| Auditability | Real-time, tamper-proof audit trails on blockchain | Audit trails maintained through accounting records and documents |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; requires smart contract coding for changes | Highly flexible; easy to adjust entries and correct errors |
| Use Cases | Ideal for automated payments, financial agreements, decentralized finance (DeFi) | Widely used across all industries for financial record-keeping |
Which is better?
Smart contracts accounting offers real-time, automated transaction recording, reducing human error and enhancing transparency by embedding accounting rules directly into blockchain protocols. Double-entry bookkeeping remains the industry standard, providing a proven, systematic approach to tracking debits and credits that ensures accuracy and compliance with regulatory frameworks. The choice depends on the need for automation and security in decentralized environments versus the reliability and wide acceptance of traditional methods.
Connection
Smart contracts automate and record financial transactions on blockchain platforms, enhancing transparency and accuracy in accounting processes. Double-entry bookkeeping ensures that every transaction recorded by a smart contract affects two accounts, maintaining the accounting equation's balance. Integrating smart contracts with double-entry bookkeeping streamlines audit trails and reduces errors in financial reporting.
Key Terms
**Double-entry bookkeeping:**
Double-entry bookkeeping is a foundational accounting method where every financial transaction is recorded in at least two accounts, with debits equaling credits to maintain balance and accuracy. This system enhances error detection, financial integrity, and detailed traceability of business activities, widely used in traditional finance and corporate accounting. Explore how double-entry bookkeeping remains indispensable despite digital innovations by learning more about its principles and applications.
Debit and Credit
Double-entry bookkeeping systematically records every financial transaction with equal debit and credit entries, ensuring accuracy and balance in accounting ledgers. Smart contracts accounting automates these principles on blockchain platforms, instantly verifying and executing transactions based on predefined rules without manual oversight. Explore deeper insights into how smart contracts optimize traditional debit and credit processes for transparent, immutable financial management.
Ledger
Double-entry bookkeeping systematically records each transaction with debits and credits, ensuring balanced ledgers and accurate financial statements crucial for traditional accounting systems. Smart contract accounting automates ledger entries on blockchain, providing immutable, transparent, and real-time transaction records without manual intervention. Explore how these technologies transform ledger management and financial auditing to optimize accuracy and efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Double-Entry Bookkeeping? - Double-entry bookkeeping is a method where every transaction is recorded twice, as a debit in one account and a credit in another, ensuring the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) stays balanced by reflecting equal increases and decreases across accounts.
Double-Entry Accounting: What It Is and Why It Matters - This bookkeeping method requires recording two entries per transaction (a debit and a credit) which tracks assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses to keep books balanced and provide a complete financial picture.
What Is Double-Entry Bookkeeping? A Simple Guide for ... - Double-entry bookkeeping records each transaction in at least two accounts with total debits equaling total credits, following the fundamental accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) and involving five types of accounts: assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com