Decentralized ledger accounting enhances transparency and security by distributing transaction records across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities. Blockchain accounting builds upon this concept by using cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms to create immutable, verifiable financial records that streamline audit processes and increase trust. Discover how these innovative technologies transform traditional accounting practices and improve financial integrity.
Why it is important
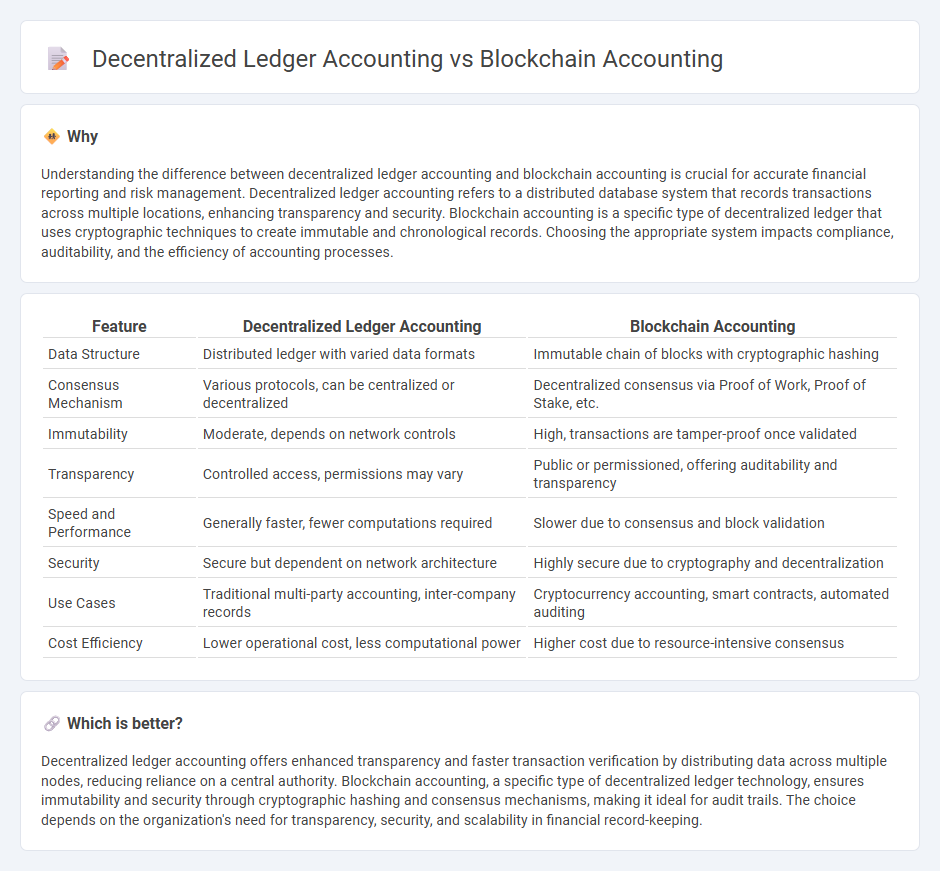
Understanding the difference between decentralized ledger accounting and blockchain accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and risk management. Decentralized ledger accounting refers to a distributed database system that records transactions across multiple locations, enhancing transparency and security. Blockchain accounting is a specific type of decentralized ledger that uses cryptographic techniques to create immutable and chronological records. Choosing the appropriate system impacts compliance, auditability, and the efficiency of accounting processes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Ledger Accounting | Blockchain Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Data Structure | Distributed ledger with varied data formats | Immutable chain of blocks with cryptographic hashing |
| Consensus Mechanism | Various protocols, can be centralized or decentralized | Decentralized consensus via Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, etc. |
| Immutability | Moderate, depends on network controls | High, transactions are tamper-proof once validated |
| Transparency | Controlled access, permissions may vary | Public or permissioned, offering auditability and transparency |
| Speed and Performance | Generally faster, fewer computations required | Slower due to consensus and block validation |
| Security | Secure but dependent on network architecture | Highly secure due to cryptography and decentralization |
| Use Cases | Traditional multi-party accounting, inter-company records | Cryptocurrency accounting, smart contracts, automated auditing |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational cost, less computational power | Higher cost due to resource-intensive consensus |
Which is better?
Decentralized ledger accounting offers enhanced transparency and faster transaction verification by distributing data across multiple nodes, reducing reliance on a central authority. Blockchain accounting, a specific type of decentralized ledger technology, ensures immutability and security through cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms, making it ideal for audit trails. The choice depends on the organization's need for transparency, security, and scalability in financial record-keeping.
Connection
Decentralized ledger accounting and blockchain accounting are interconnected through their use of distributed ledger technology, which enables transparent, immutable, and secure recording of financial transactions across multiple nodes. Blockchain accounting applies cryptographic hashing and consensus algorithms to ensure data integrity and facilitate real-time auditing, reducing fraud and errors. This connection enhances trust and efficiency in accounting processes by providing a verifiable and tamper-proof transaction history.
Key Terms
Immutability
Blockchain accounting ensures immutability by recording transactions in a cryptographically secured, append-only ledger that prevents unauthorized alterations, maintaining data integrity over time. Decentralized ledger accounting distributes transaction validation across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and resilience but may vary in immutability based on consensus mechanisms used. Explore the differences in immutability standards and their impact on accounting practices to understand which system best suits your needs.
Consensus Mechanism
Blockchain accounting employs consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions through network-wide agreement, ensuring data integrity and preventing double-spending. Decentralized ledger accounting similarly uses consensus protocols but often adopts more scalable models like Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) or Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)-based approaches to achieve faster transaction finality and reduced energy consumption. Explore the nuances of various consensus algorithms to understand how they impact transparency, security, and efficiency in distributed accounting systems.
Trustless Transactions
Blockchain accounting employs a distributed ledger ensuring transparent, immutable records without centralized control, enhancing data integrity and auditability. Decentralized ledger accounting expands on this by enabling trustless transactions through consensus mechanisms, eliminating reliance on intermediaries and reducing fraud risks. Explore how trustless transactions redefine financial accountability and operational efficiency in modern accounting systems.
Source and External Links
How Blockchain is Changing Accounting Practices - Paystand - Blockchain revolutionizes accounting by providing a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger that automates transaction recording, reconciliations, audit trails, fraud detection, and enhances financial reporting and taxation processes through smart contracts and decentralized data security.
What is Blockchain Accounting? - FreshBooks - Blockchain accounting stores transactional data in an immutable, chronological chain that auditors can verify easily, helping reduce manual audit efforts while complementing traditional accounting by confirming transaction legitimacy but not detailed context.
Blockchain Accounting - Guide & Use Cases - Blockchain accounting enables real-time, immutable recording of financial transactions on shared ledgers with automation via smart contracts and AI, supporting triple-entry accounting and reducing errors, fraud, and auditing costs through neutral and tamper-proof data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com